Discover Which Way Should a Greenhouse Face in Australia for Optimal Growth

When planning a greenhouse in Australia, understanding its optimal orientation can significantly enhance plant growth and productivity. The direction a greenhouse faces affects light intake, temperature regulation, and wind exposure, all of which are crucial for creating a conducive environment for your plants. Given Australia’s diverse climate zones, the ideal orientation may vary. In this article, we will explore the factors influencing greenhouse placement, including the sun’s path, prevailing winds, and unique regional characteristics. By determining the best orientation for your greenhouse, you can maximize sunlight exposure and create an ideal growing environment for a flourishing garden.
Choosing the Optimal Orientation for Greenhouses in Australia
The ideal orientation for a greenhouse in Australia is to face it north. This positioning allows for maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day, which is crucial for plant growth. Since Australia is located in the southern hemisphere, facing north ensures that the greenhouse captures the most sunlight during the winter months when the sun is lower in the sky. It also helps mitigate heating costs and improves temperature regulation inside the greenhouse, fostering an environment conducive to year-round gardening.
Importance of Sunlight Exposure
Maximizing sunlight exposure is essential for a greenhouse, particularly in regions with varying seasonal light levels. Greenhouses faced towards the north can absorb the sun's rays more effectively, promoting photosynthesis and overall plant health. This orientation reduces the need for artificial lighting and heating, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and productive growing environment.
Temperature Regulation
Proper temperature regulation inside a greenhouse is vital for plant health. A north-facing greenhouse benefits from stable temperatures due to consistent sunlight exposure, which helps maintain warmth during cooler months. This configuration allows for the efficient use of natural heat, reducing reliance on artificial heating systems and minimizing energy costs.
Wind Protection
In Australia, strong winds can adversely affect greenhouse conditions. By orienting a greenhouse towards the north, you can position sidewalls against prevailing winds, providing a natural barrier that protects plants from strong gusts. This strategic orientation reduces wind chill and protects delicate plants, promoting a more stable growing environment.
Consideration of Local Climate
Understanding the local climate is crucial when deciding the orientation of a greenhouse. Regions with hotter climates may benefit from slightly varying orientation to avoid overheating. For example, in areas with extremely high temperatures, it may be beneficial to angle the greenhouse or use shading techniques to minimize direct sunlight exposure while still maintaining a predominantly north-facing orientation.
Energy Efficiency
A well-oriented greenhouse enhances energy efficiency by utilizing natural light and heat effectively. North-facing greenhouses are naturally warmer and require less energy for heating during the winter months, leading to reduced overall energy consumption. This not only lowers operational costs but also supports sustainable practices in greenhouse management.
| Aspect | North-Facing Benefits | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Sunlight Exposure | Maximized throughout the year | Excessive heat in summer |
| Temperature Regulation | Consistent warmth | Possible overheating without management |
| Wind Protection | Reduced wind chill effects | Less protection from southern winds |
| Local Climate Adaptation | Enhances growth in diverse climates | Requires adjustments for heat management |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower heating costs | Need for cooling strategies in summer |
Should a greenhouse face east or west?
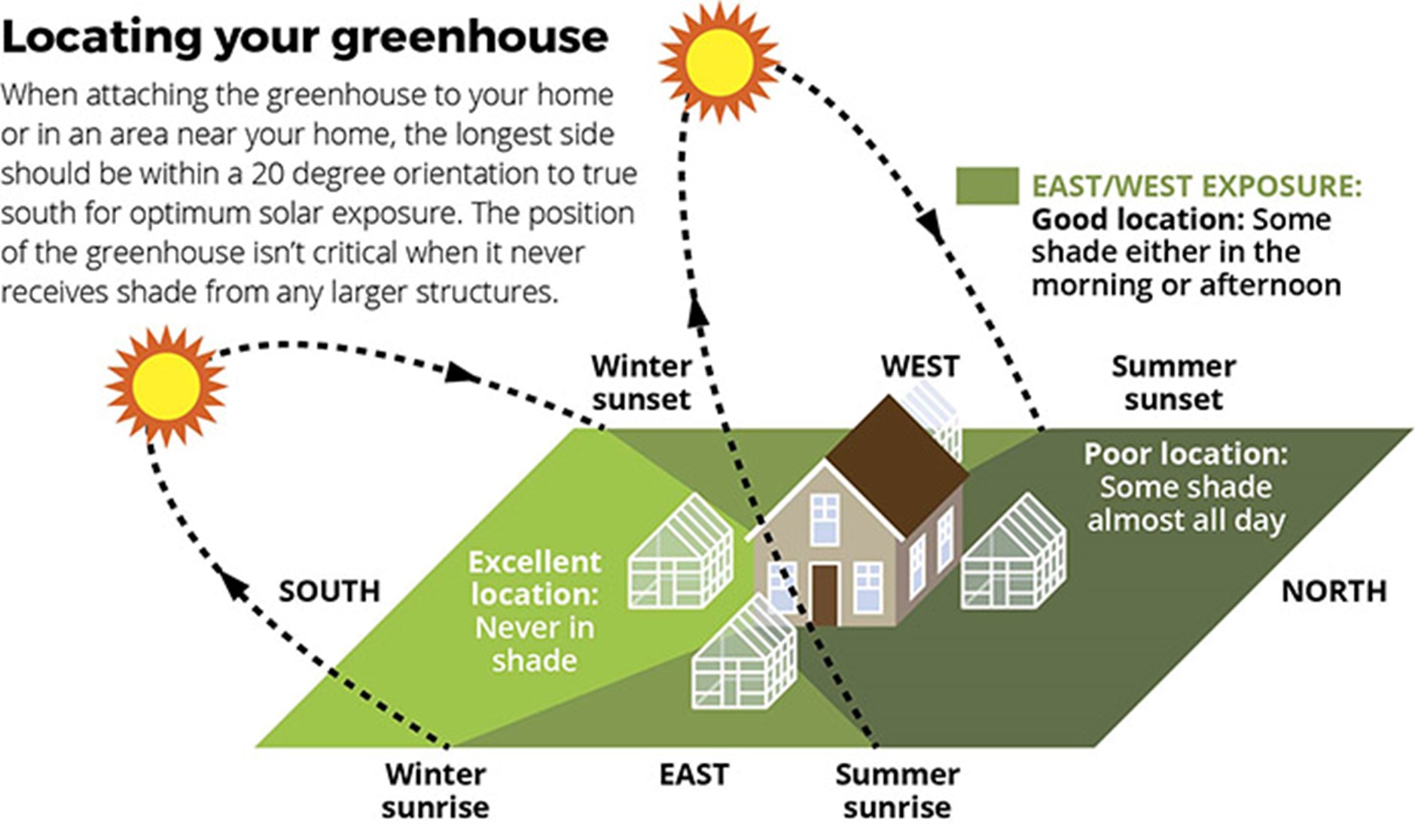
When deciding whether a greenhouse should face east or west, multiple factors can influence plant growth, temperature control, and overall efficiency. Here are the main considerations:
Sunlight Exposure
A greenhouse's orientation significantly impacts its sunlight exposure throughout the day.
See also:
- East-facing greenhouses receive direct sunlight in the morning, which can promote early growth and help warm the greenhouse during the cooler hours.
- West-facing greenhouses collect sunlight during the afternoon, which can be beneficial for plants that thrive in warmer conditions, especially in the later parts of the day.
- Either orientation can be beneficial, but choosing depends on the types of plants you are growing and their specific light requirements.
Temperature Management
Temperature management is critical for a successful greenhouse environment.
- Morning sun in an east-facing greenhouse can help warm the air and soil early, preventing frost on cooler mornings.
- A west-facing greenhouse may experience higher temperatures during the afternoon, which is useful for heat-loving plants but requires efficient ventilation strategies.
- Both orientations necessitate careful planning of shade structures and ventilation to avoid overheating on particularly sunny days.
Wind Protection
Incorporating wind protection into the positioning of a greenhouse can also affect its effectiveness.
- An east-facing greenhouse can benefit from morning calm, allowing for stable growth conditions early in the day.
- A west-facing greenhouse might need additional windbreaks to safeguard against potential afternoon gusts, especially in exposed areas.
- Positioning your greenhouse relative to nearby structures or natural land features can enhance wind protection for either orientation.
Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes can influence how much light and heat the greenhouse receives throughout the year.
- During winter, an east-facing greenhouse can capture the sun's lower angle, maximizing light exposure in shorter days.
- In summer, a west-facing greenhouse might be prone to excess heat in the late afternoon, requiring smart cooling solutions.
- Seasonal modifications, like adjusting shading or utilizing thermal mass, are critical for both types to optimize plant growth year-round.
Plant Types and Goals
The specific plant types and goals for a greenhouse will ultimately guide its optimal orientation.
- Consider the types of plants: if you are growing cool-weather crops, an east-facing greenhouse might be preferable.
- If your focus is on tropical plants that require more heat, a west-facing greenhouse could provide the necessary warmth.
- Your overall gardening goals — such as maximizing production or optimizing for seasonal foods — should influence the orientation decision as well.
Where to put a greenhouse in Australia?

When considering where to put a greenhouse in Australia, it is essential to take into account various factors that affect the growth and maintenance of plants. The climate can vary greatly from one region to another, affecting sunlight exposure, temperature regulation, and moisture levels.
Factors to Consider for Greenhouse Placement
Several factors play a crucial role in selecting the perfect location for your greenhouse. Understanding these can help optimize plant growth and greenhouse efficiency.
- Sunlight: Aim for a location that receives maximum sunlight throughout the day, ideally at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight.
- Wind Protection: Position your greenhouse in a spot that is sheltered from harsh winds, as strong gusts can damage plants and affect temperature control.
- Accessibility: Ensure your greenhouse is easily accessible for frequent visits, maintenance, and harvesting.
Climate Zones in Australia
Australia has numerous climate zones, which influence the decision on greenhouse placement. Each zone presents unique challenges and opportunities for gardeners.
- Tropical Regions: If you're in Northern Queensland, opt for a ventilated greenhouse to handle high humidity and temperatures.
- Desert Areas: In regions like Western Australia, consider shaded locations to protect plants from extreme heat and sunlight.
- Temperate Zones: In Sydney or Melbourne, a location with good sunlight exposure yet protection from frost is ideal.
Soil and Drainage Considerations
The type of soil and the drainage capabilities of the chosen location can significantly affect greenhouse health. Proper drainage prevents root rot and encourages robust plant growth.
- Well-Drained Soil: Look for areas where water does not pool, as excessive moisture can be detrimental to most plants.
- pH Levels: Test soil pH to ensure it is within an optimal range (usually between 6.0 and 7.5) for plant growth.
- Soil Amendments: In areas with poor soil quality, consider adding compost or other organic matter to improve the soil structure.
Proximity to Water Sources
Having easy access to water is critical for maintaining a greenhouse. The location must facilitate efficient irrigation practices.
See also:
- Natural Water Sources: If possible, choose a location near a pond or stream to make irrigation easier.
- Water Supply System: Ensure your greenhouse location is connected to a reliable water supply for consistent irrigation needs.
- Irrigation Method: Consider the type of irrigation system (drip, sprinkler, or manual) that will require adequate access to water.
Local Regulations and Zoning Laws
Before placing a greenhouse, it is essential to review local regulations and zoning laws that may affect the installation.
- Building Permits: Check if a permit is necessary for greenhouse installation in your area.
- Setback Requirements: Some communities have specific regulations on how far a greenhouse should be from property lines.
- Environmental Restrictions: Be aware of any protected land or restrictions on building in certain natural areas.
Which direction should lean-to the greenhouse face?

To determine which direction a lean-to greenhouse should face, several factors come into play, primarily related to sunlight exposure, wind protection, and climate conditions. Generally, a lean-to greenhouse should face south or southeast in the Northern Hemisphere and north or northeast in the Southern Hemisphere. This orientation maximizes sunlight exposure throughout the day, helping plants thrive.
Sunlight Exposure
The direction your lean-to greenhouse faces significantly impacts the amount of sunlight the plants receive.
- South-Facing: In the Northern Hemisphere, a south-facing greenhouse captures the most sunlight, keeping the interior warm and encouraging plant growth.
- East-Facing: An east-facing greenhouse receives morning sunlight, which is excellent for early warmth, although it may not be as effective in the afternoon.
- West-Facing: A west-facing greenhouse can get hot during the afternoons but may miss out on the consistent morning light needed for optimal growth.
Climate Considerations
The climate of your region can influence the ideal direction for your lean-to greenhouse.
- Cold Climates: In colder areas, maximizing sunlight during winter is essential; hence, a south-facing orientation is usually best.
- Hot Climates: In hotter regions, it may be beneficial to orient the greenhouse to minimize direct sun exposure during peak heat hours, possibly favoring a southeast or east direction.
- Mild Climates: For regions with mild temperatures, a south-facing orientation generally works well while providing adequate sunlight without excessive heat.
Wind Protection
Wind can affect the temperature and conditions within your greenhouse, so choosing a direction that considers prevailing winds is crucial.
- Natural Barriers: Positioning the lean-to greenhouse near walls or trees can reduce wind exposure. Ensure that the greenhouse faces away from the most troublesome winds.
- Orientation Against Winds: If prevailing winds come from the north or west, facing the greenhouse south or east can help in reducing wind chill and maintain higher temperatures inside.
- Windbreaks: If available, planting a windbreak (e.g., hedges or fences) can further protect the greenhouse while enhancing sunlight exposure depending on the placement.
Accessibility and Space Efficiency
The direction of your lean-to greenhouse should also consider accessibility and the efficient use of space.
- Proximity to Water Source: Position the greenhouse in a way that makes it easy to access water supplies for irrigation.
- Easy Access: Ensure that the greenhouse is positioned so that entry points provide convenient access for maintenance and harvesting.
- Minimizing Shadows: Consider the placement of nearby structures to minimize shadows that could impede sunlight on the greenhouse and its surrounding plants.
Plant Needs
Different plants may have varying light and heat requirements, which can influence how you orient your lean-to greenhouse.
- Sun-loving Plants: If you plan to grow vegetables or flowers that thrive in full sun, a south-facing greenhouse is ideal.
- Shade-loving Plants: For plants that prefer cooler conditions, consider areas that receive filtered sunlight throughout the day.
- Seasonal Cropping: Think about rotating different crops; the positioning can help maximize the greenhouse’s utility throughout different seasons.
Questions from Our Readers
Which way should a greenhouse face in Australia?
The optimal direction for a greenhouse in Australia is generally north-facing, as it allows for maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day. This orientation takes advantage of the sun's path, particularly in the southern hemisphere, ensuring that plants receive adequate light and warmth, which are crucial for healthy growth.
Why is it important for a greenhouse to receive ample sunlight?
A greenhouse that receives ample sunlight is essential for promoting photosynthesis in plants. Adequate light not only supports growth but also helps maintain an appropriate temperature inside the greenhouse, creating an ideal environment for various crops and improving overall yield.
See also:
Are there exceptions to the north-facing greenhouse rule?
Yes, there can be exceptions depending on local geography and specific crop requirements. In some regions, a slight east or west orientation might be beneficial to manage heat during the summer months or to protect delicate plants from harsh afternoon sunlight.
How can I optimize my greenhouse's orientation?
To optimize your greenhouse's orientation, consider the local climate, the specific needs of the plants, and any surrounding structures that might block sunlight. It's also helpful to track the sun's path during different seasons to make an informed decision about the best positioning for maximum light exposure.

If you want to read more articles like Discover Which Way Should a Greenhouse Face in Australia for Optimal Growth, we recommend you check out our Greenhouse category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles