Exploring When Dinosaurs Roamed Australia: A Journey Through Prehistoric Times

Australia’s prehistoric landscape was once a thriving realm dominated by dinosaurs. This article embarks on an exhilarating journey through time, exploring the diverse species that roamed this vast continent millions of years ago. From the towering sauropods grazing on lush vegetation to the swift theropods hunting in the woodlands, these magnificent creatures shaped the environment in unique ways. By delving into fossil discoveries and geological evidence, we will uncover the rich history of dinosaurs in Australia, their adaptations, and the impact of climatic changes on their existence. Join us as we explore the fascinating world of dinosaurs that once called Australia home.
Exploring Dinosaur Habitats in Ancient Australia
During the Mesozoic Era, particularly in the Late Cretaceous period, Australia was teeming with a variety of dinosaurs that roamed its vast landscapes. The continent, which was part of the supercontinent Gondwana, provided a diverse range of environments from lush forests to arid plains, creating ideal conditions for many dinosaur species. Some of the most notable dinosaurs that inhabited this region included large herbivores such as Austrosaurus and Matheronodon, as well as formidable predators like Rapator. The fossil evidence collected from various sites, particularly in Queensland and Victoria, allows paleontologists to piece together the ecosystem dynamics and the evolutionary history of dinosaurs specific to Australia, showcasing a unique assemblage that was distinct from other continents.
Diversity of Australian Dinosaurs
In Australia, dinosaur diversity flourished, with fossils revealing a range of species adapted to the unique environments. This included both herbivorous and carnivorous dinosaurs, with notable examples such as the Theropods, which were agile hunters, and the Sauropods, large long-necked dinosaurs that grazed on vegetation. The discoveries of new fossils continue to indicate unexpected diversity, suggesting that Australia had its own unique evolutionary paths that set it apart from dinosaur faunas found on other continents.
Fossil Sites in Australia
Key fossil sites across Australia, such as the Eromanga Basin and the Gippsland region, have yielded remarkable dinosaur discoveries. These areas boast well-preserved remains that provide insight into the physical characteristics and behaviors of the dinosaurs that lived there. Researchers excavate clay-rich deposits and sedimentary layers that were laid down during the Cretaceous, which enhances our understanding of the geological and environmental conditions those dinosaurs faced.
Australia's Unique Dinosaur Species
Several unique species have been identified in Australia that showcase the continent's distinct evolutionary journey. One prime example is Minmi, a small, armored dinosaur known for its bipedal stance and protective features. Additionally, the Australovenator, a swift theropod, adapted to the continental landscape, indicating that Australia hosted its own evolution of predatory and defensive adaptations, contributing to a unique ecological niche for its dinosaur inhabitants.
Climate and Environment During the Dinosaur Era
During the periods when dinosaurs roamed Australia, the climate varied significantly, influencing the types of species that could thrive. The environment was characterized by climatic shifts from tropical rainforests to dry savannas, particularly during the Late Cretaceous. This variability facilitated the evolution of specific adaptations amongst dinosaurs, with those in wetter regions developing features to exploit abundant plant life, while those in drier climates evolved strategies for survival in harsher conditions.
The End of the Dinosaurs in Australia
The extinction of dinosaurs around 65 million years ago, commonly attributed to the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, significantly affected Australia’s ecosystems. As global temperatures dropped and plant life diminished due to catastrophic events, the available food resources for the dinosaurs drastically declined. The fossil record indicates that Australia’s dinosaur population faced sudden extinction, marking the end of an era that had once been dominated by these magnificent creatures.
| Dinosaur Species | Type | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Austrosaurus | Herbivore | Long neck, large size |
| Rapator | Carnivore | Agile and fast |
| Minmi | Herbivore | Armored with bipedal posture |
| Australovenator | Carnivore | Swift and adaptable |
| Matheronodon | Herbivore | Unique dental structure |
When did dinosaurs live in Australia?
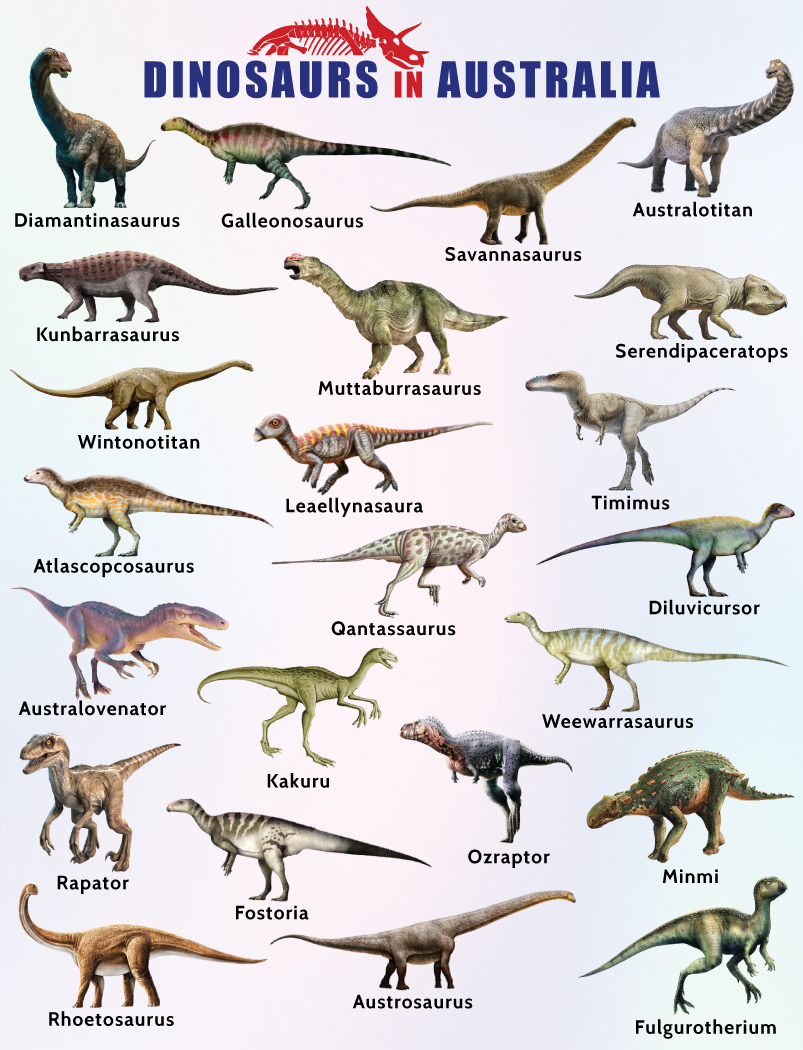
Dinosaurs lived in Australia during the Mesozoic Era, which lasted from about 252 to 66 million years ago. More specifically, they thrived during the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods. Fossil evidence indicates that dinosaurs were present in Australia from approximately 230 million years ago to the end of the Cretaceous period, coinciding with the mass extinction event that wiped out the majority of dinosaur species. Some of the most significant fossil discoveries have been made in several regions, illustrating the diverse range of dinosaur species that existed in prehistoric Australia.
The Mesozoic Era in Australia
The Mesozoic Era is crucial for understanding the evolution of dinosaurs in Australia. During this time, the continent was part of the Gondwana supercontinent, leading to diverse habitats.
- Triassic Period: Approximately 252 to 201 million years ago, when the first dinosaurs appeared in the region.
- Jurassic Period: About 201 to 145 million years ago, noted for the flourishing of large dinosaurs.
- Cretaceous Period: Spanning from 145 to 66 million years ago, when many well-known Australian dinosaurs lived.
Fossil Discoveries in Australia
Numerous fossil discoveries in Australia have significantly contributed to our understanding of dinosaurs in this region. Key sites around the continent have yielded vital specimens.
- Eromanga Basin: Home to several well-preserved dinosaur fossils, including Sauropods.
- Flinders Ranges: An area where various dinosaur footprints have been found.
- Victoria: Notable for fossils of Therapods, which include the famous Megalania.
Types of Dinosaurs Found in Australia
Australia has been home to a variety of dinosaur types over millions of years, ranging from herbivores to carnivores. The fossil record documents these varying species.
- Large Herbivores: Such as the Austroposeidon, which was one of the largest dinosaurs, found in the Cretaceous period.
- Predatory Dinosaurs: Including Allosaurus and other carnivorous species, highlighting a rich diversity.
- Flying Dinosaurs: Some regions yielded evidence of pterosaurs, which were present alongside terrestrial dinosaurs.
Impacts of Climate on Dinosaurs
The climate of Australia during the Mesozoic Era varied significantly, affecting the kinds of dinosaurs that could thrive in different areas.
See also:
- Warm and Wet: The climate during the Jurassic was predominantly warm and wet, supporting lush vegetation and large herbivores.
- Dry and Arid Conditions: By the Cretaceous, the climate became more varied, leading to both dry and arid conditions.
- Extinction Event: The climate changes towards the end of the Cretaceous contributed to the mass extinction of dinosaurs.
Significance of Australian Dinosaurs
The study of dinosaurs in Australia is essential for understanding global dinosaur evolution and paleobiogeography.
- Unique Specimens: Australia has unique dinosaurs that provide insights into the adaptive traits of dinosaurs in isolated environments.
- Biodiversity Insights: Examining the diverse species aids in comprehending ecosystem dynamics during the Mesozoic.
- Evolutionary Studies: These findings contribute to the broader understanding of dinosaur evolution across continents.
What killed the dinosaurs in Australia?
The extinction of the dinosaurs in Australia, like the rest of the world, is widely attributed to a combination of catastrophic events. The most prominent theory suggests that a massive asteroid impact played a critical role, alongside significant volcanic activity that could have contributed to dramatic climate changes.
The Asteroid Impact Theory
The primary catalyst for the dinosaurs' extinction is believed to be the impact of a large asteroid around 66 million years ago. This event created the Chicxulub crater in the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, but its effects were felt globally, including in Australia. The key points related to this theory include:
- A massive explosion that would have released enormous amounts of energy, equivalent to billions of atomic bombs.
- Subsequent wildfires across the globe, leading to a loss of vegetation crucial for the survival of many species.
- Dust and debris that blocked sunlight for months, causing a significant drop in temperatures and disrupting ecosystems.
Volcanic Activity and Its Role
Another critical factor in the extinction of dinosaurs in Australia is the intense volcanic activity during the late Cretaceous period. The Deccan Traps, located in present-day India, are a well-known example of this volcanic flow, but Australia experienced similar phenomena. Key points include:
- The release of large volumes of gas, including sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide, which could lead to acid rain and further temperature fluctuations.
- Long-term climate change as a result of volcanic eruptions that led to global cooling followed by warming, creating inhospitable environments.
- Alteration of habitats critical for the survival of various dinosaur species, contributing to their decline.
Impact on the Australian Ecozone
The extinction events affected different regions in various ways, particularly in the Australian ecozone. As Australia was largely isolated, the consequences of these global events manifested in unique ways. Key points about these effects include:
- A decline in herbivorous dinosaurs, due to the loss of plant life as a result of both asteroid impact and volcanic activity.
- Disruption of food chains, affecting predators and leading to a cascade of extinctions beyond just dinosaurs.
- The unique flora and fauna of Australia that evolved in isolation were particularly vulnerable to these rapid environmental changes.
Survival and Extinction Dynamics
While many species went extinct, it's essential to understand that not all organisms were affected equally. Some species displayed differing survivability traits that allowed them to endure the harsh conditions. Important aspects include:
- Smaller species, such as certain mammals and reptiles, may have adapted better to the changing environment, allowing them to survive.
- Climate resilience, with some species having evolutionary adaptations that permitted survival in fluctuating temperatures.
- The ecosystem dynamics that allowed for diverse pathways of survival despite the overall decline of larger species like dinosaurs.
Lasting Effects on Biodiversity
The extinction of the dinosaurs in Australia contributed significantly to the overall biodiversity shifts observed in subsequent epochs. The aftermath of these events has had lasting implications, such as:
- The opening up of niches that allowed for the evolution of mammals and birds in the absence of dinosaurs.
- The recuperation of ecosystems which led to the emergence of new species and adaptations.
- Long-term biodiversity impacts, influencing the types of flora and fauna that would develop in Australia over millions of years post-extinction.
Were humans alive when dinosaurs roamed the earth?

No, humans were not alive when dinosaurs roamed the Earth. Dinosaurs existed during the Mesozoic Era, which is divided into three periods: the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods. This era spanned from approximately 252 million years ago to about 66 million years ago. Dinosaurs first appeared about 230 million years ago and went extinct around 65 million years ago due to a mass extinction event.
Humans, on the other hand, belong to the species Homo sapiens, which evolved much later. The earliest ancestors of modern humans appeared around 6 to 7 million years ago, and anatomically modern humans emerged approximately 300,000 years ago. This timeline clearly indicates that there was a significant gap of millions of years between the extinction of dinosaurs and the appearance of humans.
Evolution of Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs began to evolve in the Triassic period, diversifying into various forms and sizes during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. They thrived across the Earth in numerous habitats.
- Origin: The earliest dinosaurs evolved from small reptiles.
- Diversity: Dinosaurs ranged from tiny bird-like creatures to enormous sauropods.
- Adaptation: Different species adapted to diverse environments, leading to varied evolutionary paths.
The Extinction of Dinosaurs
The extinction of dinosaurs is believed to have been caused by a combination of catastrophic events, including an asteroid impact and volcanic activity. This led to a dramatic change in the Earth's climate.
See also:
- Asteroid Impact: A massive asteroid struck the Yucatán Peninsula, creating the Chicxulub crater.
- Volcanic Activity: Extensive volcanic eruptions contributed to climate change and habitat destruction.
- Aftermath: The resulting environmental changes led to the extinction of nearly 75% of all species, including dinosaurs.
Timeline of Human Evolution
Human evolution is a complex process that spans millions of years, starting long after the disappearance of dinosaurs.
- Hominins: The first hominins appeared around 6 to 7 million years ago.
- Development: Australopithecus species displayed bipedalism and tool use.
- Modern Humans: Homo sapiens emerged approximately 300,000 years ago in Africa.
Comparative Timeline of Dinosaurs and Humans
When comparing the timelines of dinosaurs and humans, it's evident that they do not overlap.
- Dinosaurs' Reign: Lasted from about 230 million to 66 million years ago.
- Mass Extinction: Occurred around 66 million years ago, leading to the end of the dinosaur era.
- Human Emergence: Beginning around 300,000 years ago, many millions of years after dinosaurs were extinct.
Fossil Evidence and Research
Fossil evidence plays a crucial role in understanding the timelines of dinosaurs and early human ancestors.
- Fossils: Provide insight into the types of dinosaurs that existed and their environments.
- Human Fossils: Help trace the evolution of early hominins and modern humans.
- Dating Techniques: Methods like radiometric dating help establish the ages of fossils accurately.
What kind of dinosaurs once roamed Australia?

Dinosaurs that once roamed Australia represent a fascinating aspect of the continent's paleontological record. Australia was home to a diverse range of dinosaur species during the Mesozoic Era, particularly in the Late Cretaceous period. Fossils discovered across various states, especially in Queensland, provide significant insights into these prehistoric creatures.
Theropods: The Fearsome Hunters
Theropods were predominantly bipedal carnivores known for their sharp claws and teeth. In Australia, notable examples include the Tyrannosaurus rex's smaller relatives, which were agile hunters that preyed on smaller animals.
- Australovenator: A fast, agile theropod believed to have lived in what is now Queensland.
- Ornithomimus: A bird-like theropod that could run quickly, it adapted well to the Australian landscape.
- Megalosaurus: A larger predatory dinosaur that illustrates the diverse hunting strategies of theropods.
Herbivorous Dinosaurs: The Gentle Giants
Australia also hosted a variety of herbivorous dinosaurs, many of which were large and had unique adaptations for feeding on vegetation. These dinosaurs played a vital role in the ecosystems of their time.
- Diamantinasaurus: A large sauropod that could have measured over 20 meters in length, known for its long neck and tail.
- Matheronodon: A unique hadrosaurid known for its duck-bill shaped snout.
- Minmi: A smaller ankylosaur that had armor plating and spikes for protection against predators.
Unique Australian Dinosaurs
Some dinosaurs found in Australia exhibit unique features that set them apart from their global counterparts. These species are indicative of the isolated evolutionary paths that occurred on the continent.
- Flickia: A lesser-known, possibly feathered dinosaur that highlights the diversity among theropod species.
- Serenjisaurus: A possible sauropod that showcases Australia’s unique evolutionary history.
- Qantassaurus: A small iguanodontian that underscores the evolutionary adaptations of herbivores in Australia.
Evidence of Dinosaurs: Fossil Discoveries
The fossil record in Australia has provided crucial information about the types of dinosaurs that inhabited the region. Key fossil sites have yielded valuable remains and footprints.
- Winton Formation: A rich fossil site in Queensland known for its abundance of dinosaur remains and footprints.
- The Eromanga Basin: Known for both marine and terrestrial fossils, providing insight into the diverse ecosystems.
- Gould's Platypus Fossil Site: A location that highlights both dinosaur and non-dinosaur fossils, illustrating the rich biodiversity.
Impact of Climate on Dinosaur Habitats
In Australia, the climate and geography during the Mesozoic Era significantly influenced the habitats where dinosaurs lived. These factors contributed to the diversity and adaptations observed in Australian dinosaurs.
- Fluctuating Environments: Changes in climate may have caused shifts in habitats, leading to diverse adaptations in dinosaur species.
- Seasonal Wetlands: Seasonal changes created varied ecosystems that supported different dinosaur species.
- Isolation Effects: The geographical isolation of Australia fostered unique evolutionary paths among dinosaurs.
Questions from Our Readers
When did dinosaurs roam Australia?
During the Mesozoic Era, specifically from the Triassic to the Cretaceous periods, dinosaurs were present in what is now known as Australia. This era, spanning approximately 180 million years, saw a variety of species inhabit the continent, as it was positioned very differently than it is today.
What types of dinosaurs lived in Australia?
Australia was home to a range of dinosaur species, including Theropods, Sauropods, and Ornithopods. Notable examples include the Australovenator, a carnivorous theropod, and Matheronodon, a herbivorous dinosaur, highlighting the diverse range of dinosaurian life that existed during this time.
What evidence do we have of dinosaurs in Australia?
Fossils, including bones, tracks, and eggs, provide significant evidence of dinosaurs in Australia. Notable fossil sites, such as the Lightning Ridge and the Eromanga Basin, contain valuable records that help paleontologists understand the dinosaur species that once inhabited the region.
See also:
How did dinosaurs survive in the Australian environment?
Dinosaurs adapted to diverse climates and ecosystems in Australia, from lush forests to arid deserts. Their survival depended on their ability to find food, shelter, and suitable surroundings, with many species evolving specific traits that allowed them to thrive in a variety of habitats across the continent.

If you want to read more articles like Exploring When Dinosaurs Roamed Australia: A Journey Through Prehistoric Times, we recommend you check out our Landscaping category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles