What is the Most Profitable Thing to Grow in a Greenhouse? Top Crops for Maximum Profit

Growing crops in a greenhouse offers unique opportunities for maximizing profit due to controlled environments that enhance yields and extend growing seasons. As the demand for organic and locally-sourced produce continues to rise, savvy growers are turning their attention to the most lucrative crops to cultivate in these settings. This article explores the top crops that can deliver significant financial returns, examining factors such as market demand, growth cycles, and investment requirements. Whether you're an aspiring greenhouse entrepreneur or an experienced grower looking to diversify, discovering the most profitable options can elevate your agricultural success.
What are the Most Profitable Crops to Grow in a Greenhouse?
Growing crops in a greenhouse can significantly increase yields and profits due to controlled environments that protect against harsh weather and pests. Among various options, herbs such as basil, parsley, and cilantro tend to be the most profitable, as they require less time to grow and provide high market value. Additionally, high-demand vegetables like tomatoes and peppers can command premium prices while having a relatively quick turnaround in production. Microgreens are another lucrative choice, as they can be harvested within weeks and sold to restaurants and health-conscious consumers at a premium price. Ultimately, the most profitable crop depends on local market conditions, but focusing on niche products can yield the best financial results.
Benefits of Growing Herbs
Growing herbs in a greenhouse can be incredibly profitable due to their short growing cycle and high market demand. Herbs require minimal space and can be harvested multiple times throughout the season, maximizing yield. Additionally, their popularity among restaurants and home cooks continues to increase, making them a sought-after product in local markets. The relatively low input costs associated with herbs also contribute to their profitability, allowing growers to see a return on investment in a shorter timeframe.
Top Vegetables for Greenhouse Cultivation
Vegetables like tomatoes, cucumbers, and bell peppers are among the top choices for greenhouse cultivation. These crops thrive in controlled environments, reducing issues related to pests and diseases. Tomatoes, in particular, are a favorite due to their versatility and high consumer demand, allowing for various pricing strategies based on market fluctuations. Greenhouse cultivation also allows for extended growing seasons, enabling growers to capitalize on early and late market opportunities.
Microgreens: A Growing Trend
Microgreens have gained immense popularity in recent years, making them a profitable choice for greenhouse growers. These young plants, which are harvested just after the first leaves develop, can be sold at high prices due to their nutritional benefits and culinary uses. They require minimal space and can be produced in small batches, allowing for rapid turnover. The short growing period—often just 7 to 21 days—ensures that growers can produce multiple harvests throughout the year, creating consistent income streams.
Importance of Market Research
Conducting thorough market research is crucial for finding the most profitable crops to grow in a greenhouse. Understanding local demand, competition, and pricing trends can help growers identify niche markets and tailor their crop selections accordingly. Additionally, farmers should stay informed about consumer preferences and emerging food trends, as these factors can significantly impact the profitability of their greenhouse operations. By aligning their production with current market demands, growers can maximize their financial success.
Factors Influencing Crop Profitability
Several factors influence the profitability of greenhouse crops, including input costs, investment in technology, and resource management. Effective greenhouse management practices, such as optimization of water and nutrient delivery systems, can substantially enhance crop yields and reduce costs. Additionally, choosing the right variety for local climate conditions within the greenhouse can also have a significant impact on overall profitability. Understanding and mitigating labor expenses are another critical aspect that can determine the financial success of a greenhouse venture.
| Crop Type | Average Yield (lbs/sq ft) | Market Price ($/lb) | Profit Potential ($/sq ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Herbs | 1-2 | 20 | 20-40 |
| Tomatoes | 3-5 | 3 | 9-15 |
| Microgreens | 10-15 | 30 | 300-450 |
| Peppers | 2-4 | 2.5 | 5-10 |
What is the easiest cash crop to grow?

The easiest cash crop to grow highly depends on the local climate, soil conditions, and available resources. However, one of the most commonly regarded easy cash crops for beginners is corn (Zea mays). Corn is not only a widely consumed staple food but also serves various purposes, including animal feed and biofuel production. Here’s an in-depth look at this cash crop.
Growing Conditions for Corn
Corn thrives in warm weather and well-drained loamy soil with plenty of nutrients. Essential requirements for growing corn include:
- Soil pH: Ideal pH is between 6.0 and 6.8 for optimal nutrient absorption.
- Temperature: Corn requires a temperature of 60°F (15°C) or higher to germinate effectively.
- Sunlight: Corn needs full sun for at least 6-8 hours a day to grow successfully.
Financial Aspects of Growing Corn
Corn can provide a lucrative return on investment, making it an appealing cash crop. Key points to understand include:
- Market Demand: There is a consistent demand for corn both as food and an industrial product, ensuring strong market prices.
- Cost of Production: Compared to other cash crops, corn has relatively low costs associated with fertilizers and pesticides.
- Yield Potential: Corn has a high yield potential, often producing 150-200 bushels per acre under ideal conditions.
Pest and Disease Management
While corn is relatively easy to grow, it is also vulnerable to pests and diseases. Important management strategies include:
- Crop Rotation: Implementing crop rotation can help reduce pest populations and improve soil health.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Employing IPM strategies can minimize pest damage while reducing chemical use.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular field inspections are crucial for early detection and management of diseases and pests.
Harvesting and Processing
Harvesting corn involves specific techniques to maximize its quality and yield. Key considerations include:
See also:
- Timing: Harvest should occur when kernels reach their desired moisture content (around 15-20%) for optimal storage.
- Equipment: Using proper harvesting equipment, such as combines, can significantly reduce labor time.
- Post-Harvest Handling: Adequate post-harvest handling is essential to prevent spoilage and maintain quality for market sales.
Alternative Easy Cash Crops
While corn is a popular choice, other cash crops may also be considered easy to grow, such as:
- Tomatoes: Easy to grow with high market demand and multiple varieties.
- Soybeans: Require less water and can be planted with minimal inputs.
- Pumpkins: Grow well in many climates and have lucrative fall markets.
What crop has the highest profit potential?
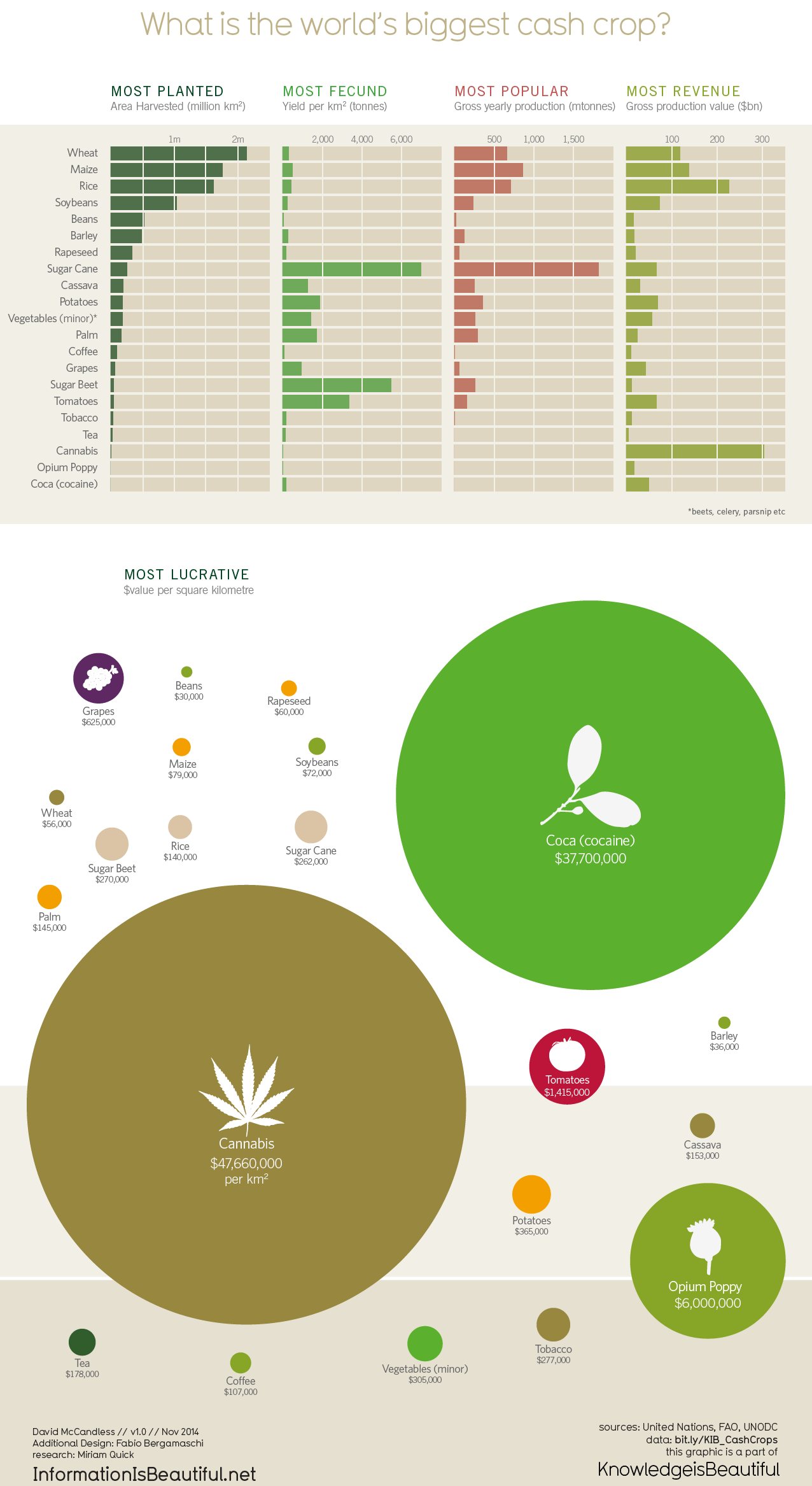
The crop with the highest profit potential can vary depending on several factors, including location, market demand, and production costs. However, two crops often highlighted for their strong profit potential are saffron and organic fruits and vegetables.
Saffron, known as the most expensive spice globally, can offer extraordinarily high returns on investment due to its labor-intensive harvesting process and the significant demand in culinary and medicinal markets. Meanwhile, organic fruits and vegetables can yield high prices because of the increasing consumer preference for healthy and sustainable food options.
Factors Influencing Crop Profitability
Profitability from crops can depend on various factors that farmers and producers need to consider:
- Market Demand: Understanding the consumer trends and preferences can significantly influence profit margins.
- Production Costs: Evaluating the costs associated with planting, maintaining, and harvesting crops is crucial for budgeting.
- Climate and Soil Conditions: The suitability of an area for specific crops affects both yield and quality, impacting overall profits.
Investment and Labor Requirements
Different crops typically require various levels of investment and labor:
- Initial Investment: Some high-profit crops, like saffron, necessitate a substantial initial financial outlay for planting and maintenance.
- Labor Intensity: Saffron, in particular, is highly labor-intensive, necessitating a workforce for its delicate harvesting process.
- Time to Yield: The duration from planting to harvest varies; crops with shorter cycles may offer quicker profits, while others may require patience.
Market Trends for High-Value Crops
Keeping abreast of market trends is essential for maximizing profitability:
- Consumer Preferences: There is a growing preference for organic produce, which typically commands higher prices in the market.
- Global Demand: Foods such as saffron and organic crops are in high demand worldwide, thus presenting lucrative opportunities.
- Health Trends: Increased focus on health and wellness has boosted organic produce sales, enhancing profit potential.
Geographic Considerations
Location plays a crucial role in determining which crop might yield the highest profits:
- Climate Suitability: Certain crops thrive better in specific climates; understanding local conditions can help select the right crop.
- Proximity to Markets: Being near markets can reduce transportation costs and enhance the freshness of products, leading to better prices.
- Regional Regulations: Different areas may have varying regulations regarding organic certification, which can impact profitability.
Growth Potential of Emerging Crops
Emerging crops might present new opportunities for profit:
- Specialty Crops: Uncommon or specialty crops like exotic fruits or medicinal herbs can attract niche markets willing to pay premium prices.
- Innovative Techniques: Utilizing advanced agricultural techniques, such as vertical farming or hydroponics, can increase yields and profitability.
- Climate-Resilient Varieties: Developing or adopting crops that can withstand climate extremes may offer better long-term profit potential.
What is the best thing to grow in a greenhouse?

The best things to grow in a greenhouse depend on several factors including climate, space, and personal preferences. However, some of the most popular choices that thrive in greenhouse environments are vegetables, herbs, and flowering plants. Among these, tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers often rank highly due to their adaptability and yield.
Benefits of Growing Tomatoes in a Greenhouse
Growing tomatoes in a greenhouse allows for extended growing seasons and better control over the growing environment. They require warmth and sunlight, which a greenhouse provides effectively. This leads to larger and juicier fruits.
- Consistent Temperature: Greenhouses help maintain an optimal temperature for tomatoes.
- Protection from Pests: The enclosed environment reduces the risk of pest infestations.
- Improved Air Circulation: Proper ventilation can enhance growth and reduce disease.
Ideal Cucumber Varieties for Greenhouse Cultivation
Cucumbers are well-suited for greenhouse growth due to their rapid growth rate and high yield. They benefit from the warmth and humidity that a greenhouse can provide, leading to more prolific production.
See also:
- High Yielding: Greenhouse cucumbers often produce more fruit than outdoor varieties.
- Pest Management: Growing them in a greenhouse allows for easier pest control strategies.
- Extended Season: They can be grown year-round in the right conditions.
Choosing the Right Peppers for Your Greenhouse
Peppers, both sweet and hot, thrive in greenhouses where temperatures can be easily controlled. They prefer warm conditions and benefit from extended light exposure, resulting in a rich flavor profile.
- Variety Selection: Consider growing bell peppers, jalapeños, or habaneros based on preference.
- Humidity Control: Greenhouses allow for humidity management which is crucial for pepper health.
- Cross-Pollination: A controlled environment can enhance cross-pollination for better yields.
Herbs That Flourish in Greenhouses
Herbs are another excellent choice for greenhouse cultivation as they generally require less space and can be grown throughout the year. Their aromatic qualities and culinary uses make them highly sought after.
- Easy to Grow: Common herbs like basil, parsley, and mint thrive easily in a greenhouse.
- Year-Round Production: A controlled environment promotes continuous herb growth.
- Space Efficiency: Herbs can be grown in small pots or vertical systems, maximizing space.
Flowers for Greenhouse Gardening
Floral plants can also thrive in greenhouses, offering beauty and potential profit for gardeners. Certain flowers prefer the conditions that a greenhouse can provide, especially in cooler climates.
- Diverse Selection: Flowers such as orchids, geraniums, and petunias grow well in a greenhouse.
- Environmental Control: Greenhouses offer protection from fluctuations in weather, yielding healthier blooms.
- Commercial Opportunities: Growing flowers can lead to profitable sales during peak seasons.
What is the most profitable indoor crop?

Understanding Indoor Crops
Indoor crops refer to plants grown in a controlled environment, such as greenhouses or indoor farms. The primary aim is to produce high yields year-round, regardless of external weather conditions. Due to advances in technology, indoor farming has gained popularity for its efficiency and sustainability. Some key factors to consider include:
- Environment control: Temperature, humidity, and light can be optimized to ensure healthy plant growth.
- Space utilization: Indoor farming maximizes space use, often employing vertical farming techniques.
- Resource efficiency: Indoor crops require less water and pesticide compared to traditional farming.
Top Profitable Indoor Crops
While many crops can be cultivated indoors, some stand out due to their profitability. Among these, herbs, leafy greens, and high-demand fruits are often highlighted, making them great choices for indoor cultivation. Key considerations include:
- Microgreens: Fast-growing and highly nutritious, microgreens require minimal space and can fetch high prices in markets.
- Herbs: Varieties like basil, mint, and cilantro are popular in culinary applications, providing good returns on investment.
- Lettuce: With consistent demand for fresh greens, indoor-grown lettuce can be harvested continuously.
Financial Aspects of Indoor Farming
Understanding the financial aspects is crucial when determining the most profitable indoor crop. Costs of setup and maintenance, along with expected returns, play a vital role in crop selection. Important factors include:
- Initial investment: Equipment for lighting, irrigation, and climate control can be significant.
- Operating costs: Ongoing expenses such as utilities and labor must be factored into profit calculations.
- Market prices: Staying informed about market demand helps in selecting the most lucrative crops.
Sustainability and Indoor Farming
Indoor farming is often seen as more sustainable than traditional agriculture. By minimizing water usage and avoiding pesticides, it addresses some environmental issues. Key components of sustainability include:
- Water conservation: Hydroponic and aeroponic systems use significantly less water.
- Reduced carbon footprint: Growing closer to consumers decreases transportation emissions.
- Minimized land use: Vertical farming techniques allow for higher yields per square foot.
Challenges in Indoor Crop Production
Despite the advantages of indoor farming, various challenges can affect profitability. Managing these issues is vital for successful operations. Some common challenges include:
- Technical issues: Equipment failure can disrupt the growing process, leading to potential losses.
- Pest management: Even in controlled environments, pests can still pose a threat, requiring vigilance.
- Market competition: As indoor farming grows, competition increases, making it crucial to differentiate products.
Questions from Our Readers
What crops are considered the most profitable to grow in a greenhouse?
The most profitable crops to grow in a greenhouse typically include tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers, as these plants have high market demand and can yield significant profits. Additionally, herbs like basil and chives are also lucrative options due to their popularity in culinary use.
How does climate affect the profitability of greenhouse crops?
The climate plays a crucial role in the profitability of greenhouse crops because optimal temperature and humidity conditions can enhance growth rates and yield quality. By using controlled environments, growers can maximize crop production throughout the year, leading to increased revenue.
What are the start-up costs associated with a greenhouse farming operation?
Start-up costs for a greenhouse farming operation can vary significantly depending on the size, location, and type of greenhouse. Expenses may include construction materials, heating systems, and irrigation setups, which can add up quickly but can lead to a profitable venture if well-planned.
Are there specific techniques to maximize profits in greenhouse agriculture?
To maximize profits in greenhouse agriculture, employing techniques such as crop rotation, vertical farming, and integrated pest management can enhance productivity. Additionally, using hydroponics or aeroponics systems can allow for more efficient use of space and resources, resulting in higher crop yields.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like What is the Most Profitable Thing to Grow in a Greenhouse? Top Crops for Maximum Profit, we recommend you check out our Greenhouse category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles