What is the energy possessed by a running water called? Understanding Hydropower and Kinetic Energy

Water is an essential resource that not only sustains life but also serves as a powerful source of energy. The energy possessed by running water is primarily known as kinetic energy. This article delves into the fascinating world of hydropower, exploring how the movement of water can be harnessed to generate electricity. By understanding the principles of kinetic energy in flowing water, we can better appreciate the potential of hydropower as a renewable energy resource. Join us as we uncover the mechanisms behind this sustainable energy solution, its applications, and its pivotal role in addressing global energy needs.
What is the energy possessed by running water called?
The energy possessed by running water is known as hydropower or water energy, which is a form of renewable energy derived from the movement of water. This energy can be harnessed through various methods, such as dams and turbines, converting the kinetic energy from the flowing water into electrical energy. Hydropower is significant because it provides a clean and sustainable source of energy that can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions and promoting environmental sustainability.
The Basics of Hydropower
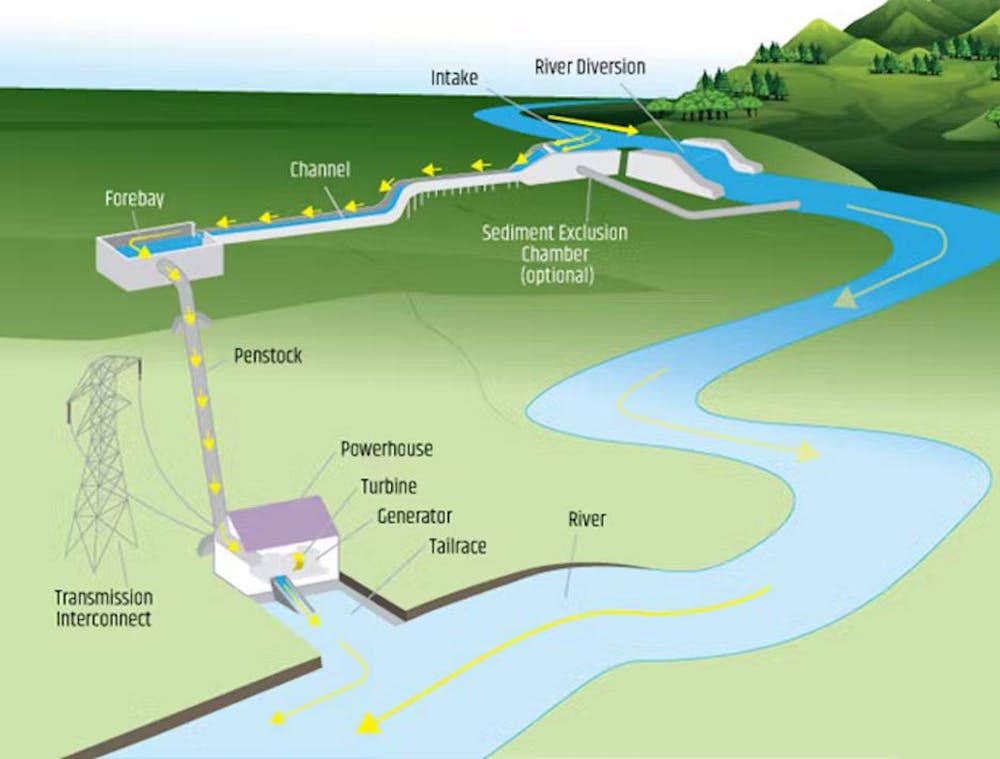
Hydropower refers to the generation of electricity using the kinetic and potential energy of flowing water. Typically, it involves the construction of hydroelectric power stations where water is stored in dams. As water is released, gravity causes it to flow down, turning turbines that generate electricity. The efficiency of this process makes hydropower one of the most effective forms of renewable energy available today.
Forms of Hydropower
There are several forms of hydropower, including run-of-the-river, pumped-storage, and reservoir systems. Run-of-the-river systems utilize the natural flow of rivers without large storage, while pumped-storage systems involve pumping water to an elevated reservoir during low-demand periods and releasing it during peak demand times. Reservoir systems create large bodies of water that can be released as needed to generate electricity, thus providing a more consistent energy source.
Advantages of Hydropower
Hydropower offers numerous advantages, including its ability to generate large amounts of electricity with minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuels. It is reliable and can be used for baseload power generation as well as peak load management. Additionally, hydropower facilities often provide recreational opportunities and can help in water management and irrigation.
Challenges Facing Hydropower
Despite its benefits, hydropower faces challenges such as environmental concerns related to ecosystem disruption, fish migration, and habitat loss. Moreover, climate change can impact water availability and flow patterns, affecting the reliability of hydropower production. There are also significant costs associated with building and maintaining dam infrastructures, which may deter investment in some regions.
The Future of Hydropower
The future of hydropower seems promising as technology advances, leading to more efficient and environmentally-friendly systems. Innovations such as small-scale and modular hydropower plants are being explored to minimize ecological disruption while providing sustainable energy solutions. Additionally, integrating hydropower within a broader renewable energy strategy could significantly reduce carbon emissions and help meet the global energy demands more responsibly.
| Key Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Hydropower | The energy generated by the movement of water. |
| Kinetic Energy | The energy possessed by a body due to its motion. |
| Potential Energy | The stored energy based on an object's position, such as water in a reservoir. |
| Renewable Energy | Energy derived from sources that are replenished naturally, such as the sun and wind. |
| Reservoir | A large water body created to store water for hydropower generation. |
What type of energy is running water?

Running water is a form of kinetic energy, which is derived from the motion of water as it flows. Kinetic energy is the energy that an object possesses due to its motion, and in the case of running water, this energy can be harnessed to perform work, such as generating electricity through hydroelectric power plants. The movement of water can also be classified as a type of renewable energy, as it is derived from natural processes that are replenished over time.
How Kinetic Energy is Generated in Running Water
The kinetic energy in running water is generated from the natural gravitational pull on water as it flows downhill. The steeper the gradient and the faster the water flows, the more kinetic energy it possesses. This energy is a result of several factors:
- Gravity: The force that pulls water downwards, contributing to its flow.
- Water Volume: A larger volume of water generally results in higher energy potential.
- Flow Speed: Faster-moving water has more kinetic energy than slower-moving water.
The Role of Hydropower in Energy Production
Hydropower is one of the most common uses of kinetic energy from running water. It involves converting the energy from flowing or falling water into electricity. The process typically involves:
- Dam Construction: Dams create reservoirs that store potential energy in water.
- Turbine Activation: As water flows through turbines, it converts kinetic energy into mechanical energy.
- Electricity Generation: The mechanical energy from turbines is transformed into electrical energy using generators.
Environmental Impacts of Using Running Water for Energy
While harnessing energy from running water is a clean and renewable method, it can have environmental impacts that must be considered:
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Changes in water flow can disrupt habitats for fish and other wildlife.
- Water Quality: Alterations in water levels and flow can affect water temperature and quality.
- Land Use: The construction of hydropower facilities can lead to habitat destruction and changes in land use.
Advantages of Using Kinetic Energy from Running Water
Utilizing running water for energy presents several advantages, making it a preferred choice in renewable energy sources:
See also:
- Renewability: Water is a sustainable resource that is cycled through the environment.
- Low Emissions: Hydropower plants produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
- Energy Efficiency: Hydroelectric power plants typically have high efficiency rates compared to fossil fuels.
Future Trends in Hydropower Technology
As the demand for renewable energy increases, there are advancements being made in hydropower technology that aim to make it more efficient and less impactful on the environment:
- Run-of-River Systems: These systems harness energy without the need for large dams, preserving more of the ecosystem.
- Small-Scale Hydropower: Utilizing smaller sites for energy production can minimize environmental disruption and provide localized energy solutions.
- Turbine Innovations: New turbine designs are being developed to increase efficiency and reduce impacts on aquatic life.
What type of energy does running water possess?
Running water possesses kinetic energy due to its movement. This energy is associated with the velocity of the water flowing in rivers, streams, or any water body. As the water flows, it has the potential to do work due to its mass and the speed at which it travels. The kinetic energy of running water can be harnessed through various technologies, especially in hydroelectric power generation, where it is converted into electrical energy.
Types of Energy in Water
Running water doesn't only possess kinetic energy. It also has potential energy, especially when it's at a height.
- Kinetic Energy: The energy possessed by water due to its motion. The faster the water flows, the more kinetic energy it has.
- Potential Energy: The stored energy in water when it is at height. This energy can be converted into kinetic energy when the water flows down.
- Hydraulic Energy: A form of potential energy that is available in water bodies caused by water pressure and elevation.
Hydroelectric Power Generation
The energy from running water can be transformed into electricity in hydroelectric dams. This process involves releasing stored water from a reservoir, allowing it to flow over turbines.
- Water Flow: The flow of water spins the turbines, which are connected to generators.
- Energy Conversion: The kinetic energy of flowing water is converted into mechanical energy as the turbines turn.
- Electricity Production: The mechanical energy is then transformed into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
Importance of Kinetic Energy
Understanding the kinetic energy of running water is crucial in renewable energy discussions. The potential for harnessing this energy is significant for sustainable solutions.
- Renewable Resource: Kinetic energy from running water is a renewable energy source, providing a consistent power supply.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Utilizing kinetic energy minimizes reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Hydro energy is among the most efficient forms of energy conversion compared to other renewable sources.
Factors Affecting Energy Production
Several factors influence the amount of energy that can be generated from running water, including flow rate and height difference.
- Flow Rate: The volume of water flowing influences the total kinetic energy. Higher flow rates yield more energy.
- Height Difference: The potential energy from gravity plays a role; greater elevation increases energy potential during descent.
- Turbine Efficiency: The technology used to convert the energy impacts the overall efficiency of energy production.
Environmental Considerations
While harnessing energy from running water has benefits, it also has to consider the environmental impact.
- Habitat Disruption: Construction of dams and hydro plants can alter local ecosystems and affect wildlife.
- Water Quality: Large scale hydroelectric projects may impact water quality and temperature, affecting aquatic life.
- Sustainable Practices: Implementing environmentally friendly practices is essential to minimize ecological effects.
What is energy produced by running water called?

The energy produced by running water is called hydropower or hydroelectric energy. This form of energy harnesses the kinetic and potential energy of water as it moves, typically through rivers or waterfalls, to generate electricity. Hydropower is one of the oldest and most widely used renewable energy sources in the world. It can be produced in various ways, but the most common method involves the use of turbines.
How Hydropower Works
Hydropower generation primarily relies on the conversion of gravitational potential energy into kinetic energy. When water flows from a higher elevation to a lower elevation, it turns turbines connected to generators. This process can be broken down into several steps:
- Water Source: Water is collected from rivers, dams, or reservoirs.
- Turbine Activation: The flowing water turns the turbine blades, creating mechanical energy.
- Electricity Generation: The mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy through the generator.
Types of Hydropower Plants
There are several types of hydropower plants, each designed to meet specific environmental and energy needs. The main types include:
- Conventional Dams: These large infrastructures store significant amounts of water and release it to generate electricity.
- Run-of-the-River Systems: These systems do not store water but generate power from the river's natural flow.
- Pumped Storage: This method involves moving water between two reservoirs at different elevations to manage energy supply and demand.
Benefits of Hydropower
Hydropower holds numerous advantages that contribute to its continued use and popularity as an energy source, including:
See also:
- Renewable Resource: Hydropower relies on the natural water cycle, making it a sustainable energy option.
- Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Unlike fossil fuels, hydropower production generates minimal emissions.
- Reliable and Flexible: It can provide a consistent power supply and can be adjusted quickly to meet energy demands.
Environmental Impact of Hydropower
While hydropower has many benefits, it also poses environmental challenges that must be considered, such as:
- Habitat Disruption: Dam construction can alter local ecosystems and affect wildlife.
- Water Quality Changes: Stagnant water in reservoirs may lead to changes in temperature and oxygen levels.
- Silt Accumulation: Dams can trap silt and nutrients, affecting downstream river health and sediment transport.
The Future of Hydropower
As global energy needs evolve, the future of hydropower will likely involve innovations and sustainability measures, such as:
- Small-Scale Projects: Increasing interest in mini and micro hydropower systems that can serve local communities.
- Environmental Mitigation Efforts: Strategies to minimize ecological impacts, including fish ladders and improved dam designs.
- Integration with Other Renewable Sources: Combining hydropower with solar or wind energy for more reliable and efficient energy systems.
What type of energy is possessed by flowing water?

Flowing water possesses kinetic energy due to its movement. This energy is a result of the mass of the water and its velocity. As water flows, its molecules are in constant motion, and this movement can be harnessed for various applications, especially in generating electricity through hydroelectric power plants. The kinetic energy of flowing water is defined by the formula:
[ KE = frac{1}{2} mv^2 ]
Where ( KE ) is the kinetic energy, ( m ) is the mass of the water, and ( v ) is the velocity of the water flow.
Types of Energy in Flowing Water
Flowing water primarily possesses two types of energy: kinetic energy and potential energy.
- Kinetic Energy: The energy associated with the motion of water as it flows.
- Potential Energy: The energy stored in water when it is elevated or contained in a dam or reservoir.
- Mechanical Energy: The combined energy from kinetic and potential forms that can be utilized in turbines.
Hydroelectric Power Generation
Hydroelectric power generation is one of the most effective uses of the kinetic energy in flowing water.
- Water Flow: As water flows through a dam, its kinetic energy turns the turbines connected to generators.
- Energy Conversion: The kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy, providing a renewable energy source.
- Efficiency: Hydroelectric plants are capable of high efficiency rates, effectively utilizing the energy of flowing water.
Factors Affecting Kinetic Energy
Several factors can influence the kinetic energy of flowing water, impacting its efficiency for power generation.
- Velocity: The speed of the water flow directly affects the amount of kinetic energy produced.
- Mass Flow Rate: Larger volumes of water flowing will yield more kinetic energy.
- Gradient: Steeper gradients can increase the speed and therefore the kinetic energy of the flow.
Advantages of Utilizing Kinetic Energy
Utilizing the kinetic energy of flowing water presents numerous advantages.
- Renewable Resource: As long as the water cycle continues, this source of energy is sustainable.
- Low Emissions: Hydroelectric power generation produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Regulatory Control: Water flow can be regulated to ensure consistent energy production.
Environmental Impact of Hydroelectric Energy
While hydroelectric energy is often viewed positively, there are ecological considerations to address.
- Habitat Disruption: Construction of dams can disrupt local ecosystems and habitats.
- Fish Migration: Flow alterations can affect the migratory patterns of fish and other aquatic organisms.
- Water Quality: Reservoirs may lead to changes in water temperature and sediment composition, impacting the quality.
Questions from Our Readers
What is the energy possessed by running water called?
The energy possessed by running water is called kinetic energy. This energy is generated due to the motion of water molecules as they flow, which can be harnessed for various applications, such as hydroelectric power.
How is the energy of running water utilized?
The energy of running water is utilized primarily through hydroelectric dams that convert kinetic energy into electrical energy. As water flows over turbines, it spins them, generating electricity that can be distributed for residential and industrial use.
See also:
What are the benefits of using running water as an energy source?
Using running water as an energy source offers multiple benefits, including renewability, low emissions, and the ability to generate electricity in a consistent manner. Additionally, it helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels and can support local economies through energy production.
Other forms of energy related to water include potential energy, which is stored in water when it is held at elevation in a reservoir, and thermal energy, harnessed from heated water sources like hot springs or steam from geothermal activity.

If you want to read more articles like What is the energy possessed by a running water called? Understanding Hydropower and Kinetic Energy, we recommend you check out our Irrigation category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles