What is the difference between espalier and Pollarding? A Comprehensive Guide to Two Popular Tree Shaping Techniques

Espalier and pollarding are two distinct tree shaping techniques that have captivated gardeners and landscape designers for centuries. Both methods serve unique purposes, enhancing aesthetics and controlling tree growth, but they do so in fundamentally different ways. While espalier involves training trees to grow flat against a structure, creating stunning visual displays, pollarding focuses on maintaining a specific size and encouraging dense foliage. This comprehensive guide will delve into the differences between these two popular practices, exploring their history, techniques, and the best applications for each method. Understanding these unique approaches will empower you to make informed decisions for your garden.
What is the difference between espalier and pollarding?
Espalier and pollarding are two distinct horticultural techniques used for shaping and managing trees and shrubs. Espalier involves training plants against a wall or fence to create a flat, two-dimensional form, often used for aesthetic purposes as well as optimizing space for fruit production. In contrast, pollarding is a pruning method where the upper branches of a tree are cut back to encourage a dense mass of new growth, typically used to control the size of a tree or to produce wood for crafts. While both methods aim to control and shape plant growth, their applications, techniques, and visual outcomes differ significantly.
Definition of Espalier
Espalier is a technique of training plants to grow flat against a support structure, such as a wall or trellis. This method allows for efficient use of space and can enhance sunlight exposure and air circulation for the plant. The practice dates back centuries, originating in ancient China and Europe, and is often employed with fruit-bearing trees to facilitate easier harvesting. The technique involves carefully pruning and tying branches to achieve the desired shape, which can be both functional and ornamental.
Definition of Pollarding
Pollarding is a pruning technique that involves cutting back the upper branches of a tree to promote bushy growth at a certain height. This method creates a canopy of new shoots that can be harvested for various uses, including fuel and crafts. Pollarding is typically practiced on deciduous trees and can help maintain size and shape, preventing overgrowth. This technique not only serves aesthetic purposes but also encourages a healthier tree by preventing the weight of older branches from damaging the tree structure.
Purpose of Espalier
The primary purpose of espalier is to maximize space in gardens or urban areas while also providing an interesting visual element. By training trees to grow flat against walls or supports, gardeners can create living fences or artistic displays. Additionally, espaliered fruit trees often yield more concentrated harvests as they receive better sunlight and are easier to care for, making this technique highly beneficial for both residential and boutique orchards.
Purpose of Pollarding
Pollarding serves various practical purposes in landscape management, including controlling the height of trees, promoting the growth of new shoots, and producing wood material for crafts. This method is commonly applied in urban areas where tree overgrowth might obstruct views, cause structural damage, or interfere with overhead lines. Moreover, pollarding can create a unique aesthetic, presenting trees with a distinctive manicured appearance that complements both traditional and modern landscape designs.
Comparative Visual Outcomes
The visual outcomes of espalier and pollarding are notably different, reflecting their distinct methodologies. Espalier produces a flat, widely spaced arrangement that can take various decorative forms, such as geometric patterns or abstract shapes. In contrast, pollarded trees appear more rounded and compact, characterized by a dense canopy of new growth emerging from the cut branches. These contrasting appearances influence their aesthetic applications within landscape design, with espalier providing a sculptural element and pollarding offering a more uniform, orderly look.
| Aspect | Espalier | Pollarding |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Training against a support to achieve a flat structure | Pruning to cut back upper branches for bushy growth |
| Purpose | Maximize space and enhance aesthetics, especially for fruit | Control height and maintain tree size, produce material |
| Visual Appearance | Flat, geometric, or artistic shapes | Compact, dense canopy with round shapes |
| Historical Roots | Originated in ancient China and Europe | Developed as a practical urban management technique |
| Main Applications | Gardens, orchards, and decorative elements in landscapes | Urban settings and landscapes requiring size control |
What are the disadvantages of espalier trees?

Espalier trees have gained popularity for their aesthetic appeal and space-saving attributes, but they also come with several disadvantages that should be considered before choosing this method of tree cultivation. Understanding these drawbacks is essential for anyone thinking about adopting this fascinating technique.
Limited Fruit Production
The fruit production of espalier trees can be significantly affected by their training and pruning methods. While some trees may still produce fruit, others may yield less than expected due to restricted growth and increased stress from significant pruning.
- Training restricts the natural growth of branches, potentially leading to reduced fruit-bearing capacity.
- Less foliage can translate to less photosynthesis, impacting overall health and yield.
- Some varieties may not adapt well to espalier conditions, resulting in minimal or no fruit.
Increased Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining espalier trees requires a more intensive care regime compared to standard trees. Regular monitoring, pruning, and tying of branches necessitate a time commitment that might not be feasible for all gardeners.
- Espalier trees need frequent pruning to ensure proper shape and to encourage optimal growth.
- Support systems must be regularly inspected and adjusted to accommodate growth.
- Additional care may be needed to prevent diseases and pests, given the compact nature of the trees.
Initial Establishment Challenges
Establishing espalier trees can be a challenging process. The initial training stage requires careful management and an understanding of the tree’s growth habits, which may deter some novice gardeners.
- Training takes time, often requiring several years before the desired shape is achieved.
- Incorrect training may lead to poor structure and health, resulting in wasted efforts.
- It requires knowledge of specific pruning techniques to avoid damaging the tree.
Space Limitation Issues
While espalier trees are designed to save space, they can also lead to limitations on future garden design. Once trained, their fixed position may affect the arrangement of other plants in the garden.
See also:
- Placement is crucial; poor decisions can hinder access to light and create shadow issues for other plants.
- Scout for any potential conflicts with other garden elements, as their growth can be restrictive.
- If spaced out incorrectly, the structure can become overcrowded, limiting airflow and light.
Potential for Structural Damage
Espalier trees can be prone to structural damage due to their unique growth orientation and support requirements. This can result from environmental factors or improper training protocols.
- Strong winds or heavy snow can stress the branches, leading to breakage.
- Improper ties can restrict growth or cause injury to the bark.
- Forcing a tree into an unnatural shape may result in site vulnerabilities and long-term health issues.
What is the point of pollarding?
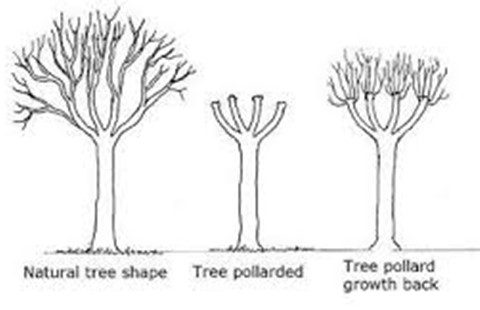
Pollarding is a horticultural practice primarily used for managing the growth of trees and shrubs. It involves the systematic removal of the upper branches of a tree, allowing new shoots to develop from the remaining stubs. This technique is often employed for various reasons, including aesthetics, safety, and promoting healthier growth.
Benefits of Pollarding
Pollarding provides several notable benefits to both the environment and the trees themselves. These include:
- Improved light penetration: By reducing the height of the tree, more sunlight can reach lower plants and vegetation, promoting ecosystem diversity.
- Enhanced safety: Pollarding reduces the risk of branch failure, particularly in urban settings, where large branches can cause significant damage to property or pose a safety hazard to pedestrians.
- Longevity of trees: Regular pollarding can extend the lifespan of certain tree species by preventing them from becoming top-heavy and reducing stress on the trunk.
Pollarding and Tree Management
Pollarding is an essential technique for effective tree management, particularly in urban areas where space and safety are concerns. It allows for:
- Controlled growth: By regularly cutting back branches, trees can be kept at a manageable height, preventing them from interfering with power lines or buildings.
- Regulation of root systems: The practice minimizes the size of the canopy, which in turn can reduce competition for nutrients and space among trees and nearby plants.
- Health monitoring: Regular maintenance through pollarding allows arborists to monitor tree health closely, identifying diseases or infestations early.
Cultural and Aesthetic Aspects
Pollarding is often practiced for its aesthetic appeal in landscape design. The effects of pollarding result in:
- Unique shapes: The distinct form created by pollarding can contribute to an eye-catching landscape, enhancing the beauty of parks and gardens.
- Seasonal interest: With new growth appearing each season, pollarded trees provide visual diversity and interest throughout the year.
- Historical significance: Many cities have a rich history of pollarding, and maintaining this practice can preserve cultural heritage related to urban forestry.
Environmental Impact of Pollarding
Pollarding also has significant environmental implications, contributing to a healthier ecosystem. Some important points include:
- Biodiversity support: By encouraging the growth of underbrush and smaller flora beneath the canopy, pollarding helps sustain habitats for wildlife.
- Carbon capture: Healthy and well-maintained trees can better capture and store carbon dioxide, contributing positively to combatting climate change.
- Soil health: The increased light and space due to pollarding can enhance soil quality and promote beneficial microbial activity.
Best Practices for Pollarding
To achieve the best results from pollarding, adhering to specific practices is crucial. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- Timing: Pollarding is usually performed in late winter or early spring when trees are still dormant, minimizing stress.
- Proper cuts: Make clean cuts at the correct locations to encourage healthy regrowth and prevent disease.
- Regular intervals: Establish a routine for pollarding, typically every 2 to 5 years, depending on the species and growth rate.
What is another name for an espalier tree?
The other name for an espalier tree is fan-trained tree. This term reflects the method of training the tree's branches in a fan shape against a wall or trellis, optimizing space and light exposure. The practice of espaliering has been utilized for centuries, particularly in small gardens where maximizing limited space is crucial. This technique allows for artistic designs while maintaining the health and productivity of the plant.
What is Espalier?
Espalier is a horticultural practice where trees or shrubs are trained to grow flat against a support, typically a wall, fence, or trellis. This method serves several purposes:
- Space-saving: By growing vertically or flat, it takes less ground space.
- Aesthetic appeal: Creates beautiful patterns and shapes in the garden.
- Improved fruit production: Allows better light exposure to the branches, enhancing fruit quality.
Benefits of Espalier Trees
Espalier trees are beneficial for both ornamental and practical purposes in gardening. Some key advantages include:
- Maximized sunlight: The flat surface allows for better light distribution.
- Enhanced accessibility: Easier to maintain and harvest due to reduced height.
- Wind protection: Can shield plants from strong winds when positioned against walls.
Common Varieties of Espalier Trees
Various tree species can be trained as espalier, and some common varieties include:
See also:
- Apple trees: Popular for fruit production and adaptable to many climates.
- Pear trees: Similar to apple trees, they are ideal for stunning floral displays.
- Citrus trees: These can also be trained to create vibrant wall formations.
Espalier Training Techniques
Training a tree to become an espalier involves specific techniques, which include:
- Initial pruning: Begin by selecting a main stem and pruning side shoots.
- Support installation: Use wires or trellis systems to guide the branches.
- Regular maintenance: Prune and tie branches down as they grow to maintain shape.
Espalier Tree Care
Caring for espalier trees requires particular attention to ensure their health and productivity:
- Watering: Regular watering is essential, especially in dry seasons.
- Fertilization: Use organic fertilizers to promote growth and fruiting.
- Pest control: Monitor for pests and diseases, applying treatments as necessary.
What is an espalier pruning?
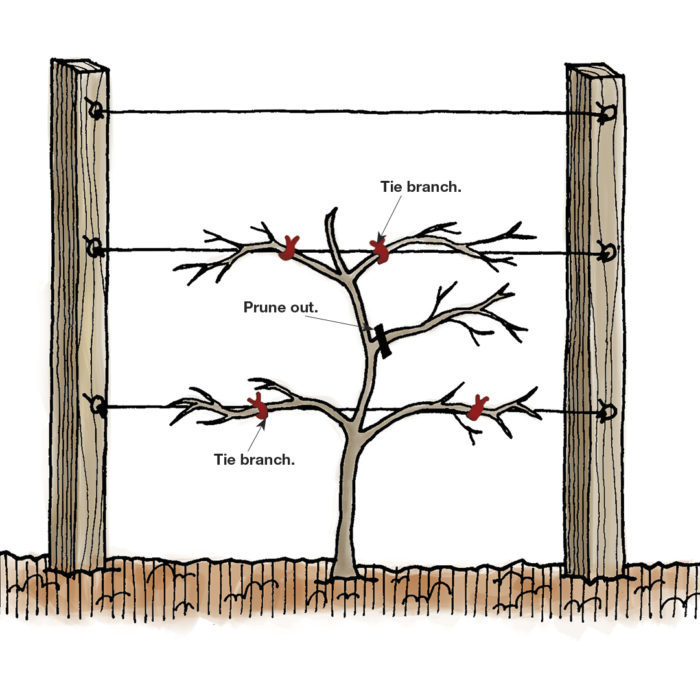
Espalier pruning is a specialized technique of training trees or shrubs in a flat plane against a wall, fence, or other vertical structures. This horticultural practice not only maximizes space in smaller gardens but also increases sunlight exposure and facilitates easier maintenance. By selectively cutting and bending the branches, gardeners can create an aesthetically pleasing shape while ensuring optimal growth and fruit production.
What is the Purpose of Espalier Pruning?
The primary purpose of espalier pruning is to cultivate a plant in a particular form that enhances its growth and fruiting potential. This method serves multiple functions, including:
- Space Efficiency: Suitable for small gardens or urban settings by maximizing vertical space.
- Light Exposure: Allows for better light penetration, which promotes healthier growth and fruiting.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Creates a visually appealing garden feature that can serve as a focal point.
How to Begin Espalier Pruning?
Starting with espalier pruning requires clear planning and understanding of the types of plants suited for this technique. Here are some steps involved:
- Select the Right Species: Choose fruit trees or ornamental shrubs that respond well to training, such as apple, pear, or fig.
- Establish a Framework: Install a trellis, wire, or other supports against which the plant will be trained.
- Initial Training: At planting, select strong stems and begin to train them along the support structure using ties.
Essential Tools for Espalier Pruning
Having the right tools is crucial to successful espalier pruning. Here is a list of essential tools:
- Pruning Shears: For precise cuts and maintaining plant structure.
- Wire Cutters: Necessary if using wire for training branches.
- Garden Ties: Soft ties help to secure branches without damaging them.
Common Mistakes in Espalier Pruning
While practicing espalier pruning, certain mistakes can hinder the effectiveness of the technique. Here are some common pitfalls:
- Over-pruning: Removing too many shoots can weaken the plant and reduce fruit production.
- Poor Tie Placement: Failing to secure branches correctly can lead to awkward growth.
- Neglecting Regular Maintenance: Without regular check-ups and adjustments, branches can become unruly.
The Benefits of Espalier Pruning
Espalier pruning provides numerous benefits to home gardeners and professional landscapers alike. Some of the key advantages include:
- Increased Yield: Controlled growth can lead to more fruit per area compared to traditional methods.
- Enhanced Airflow: Open structures promote better airflow, reducing the risk of disease.
- Year-Round Interest: Creates a dynamic landscape that can change with the seasons.
Questions from Our Readers
What is espalier?
Espalier is a pruning technique that involves training trees or shrubs to grow flat against a framework, creating a two-dimensional shape. This method allows for better sunlight exposure and air circulation, making it ideal for small spaces and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of gardens.
What is pollarding?
Pollarding is a form of pruning where the upper branches of a tree are cut back to a certain height, encouraging a dense head of foliage. This technique not only helps in controlling the size of the tree but also promotes healthy new growth, making it a popular practice for managing trees in urban areas.
How do espalier and pollarding differ in their application?
The main difference between espalier and pollarding lies in their intended outcomes; espalier focuses on creating a flat, decorative shape for aesthetic reasons, while pollarding is primarily used for size control and maintaining tree health. Each technique serves different purposes in landscape design and tree management.
Can any tree be trained using espalier or pollarding?
Not every tree is suitable for either espalier or pollarding. Espalier works best with certain fruit trees and shrubs that can tolerate regular shaping, while pollarding is typically applied to deciduous trees that can regenerate new growth from the cut areas. It's important to choose the right species for successful implementation of these techniques.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like What is the difference between espalier and Pollarding? A Comprehensive Guide to Two Popular Tree Shaping Techniques, we recommend you check out our Landscaping category.
Leave a Reply

Related Articles