What is the device called that collects rainwater? A Comprehensive Guide to Rainwater Harvesting Solutions

Rainwater harvesting is an ancient practice that has gained renewed attention in recent years due to its sustainability and environmental benefits. Central to this process is a device known as a rainwater collection system, which captures and stores rainwater for various uses. This comprehensive guide will explore the different types of devices designed for rainwater collection, their features, benefits, and how they contribute to water conservation efforts. By understanding these solutions, homeowners and communities can make informed decisions about integrating rainwater harvesting into their water management strategies, thus promoting a more sustainable future.
What is the Device Called That Collects Rainwater?
Rainwater is often collected using devices known as rainwater harvesting systems. These systems are designed to capture, store, and utilize rainwater for various purposes, such as irrigation, toilet flushing, or even potable water supply, depending on the system's filtration and treatment methods. The most common component of these systems is the rainwater tank, which collects water from roofs via gutters and downspouts. The effectiveness of a rainwater harvesting system can significantly reduce reliance on other water sources and help in sustainable water management, especially in areas prone to drought or water scarcity.
Components of a Rainwater Harvesting System
A typical rainwater harvesting system consists of several components including a catchment area (usually the roof), a gutter system to channel the water, a storage tank to hold the collected water, and a series of pipes and filters to ensure clean and efficient water flow. Each of these components plays a critical role in the overall efficiency and maintenance of the system, ensuring that rainwater is collected effectively and safely stored for future use.
Benefits of Collecting Rainwater
Collecting rainwater provides numerous environmental and economic benefits. It reduces the demand on municipal water systems, helps in lowering water bills, and supports sustainable water usage, particularly in agricultural settings. Moreover, it can mitigate stormwater runoff, which can lead to urban flooding and water pollution, ultimately contributing to a more resilient and sustainable urban infrastructure.
Types of Rainwater Storage Tanks
Rainwater can be stored in various types of tanks, each suited for different applications. Above-ground tanks are commonly used for residential applications as they are easier to install and maintain, while underground tanks are often used for larger systems where space is limited or aesthetics are a concern. Furthermore, tanks can vary in materials, such as plastic, concrete, or metal, each offering different advantages in terms of insulation, durability, and cost.
Rainwater Filtration and Treatment
To ensure the potability of collected rainwater, filtration and treatment processes are essential. Common methods include first-flush diverters, which prevent the initial contaminated runoff from entering the storage tank, and various filtration systems that remove debris and pathogens. Chemical treatments, UV purification, and reverse osmosis can also be employed to further enhance water quality, making rainwater safe for drinking and cooking.
Regulations and Guidelines
Regulations regarding rainwater harvesting vary across different regions and jurisdictions. Some areas encourage the practice by offering incentives, while others may impose restrictions on the use of harvested rainwater. It is essential for homeowners and businesses to consult local guidelines and regulations to ensure compliance, which often includes obtaining permits for installation, adhering to safety standards, and using certified materials throughout the system.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Catchment Area | Catches rainwater from the roof |
| Gutter System | Channels water to storage |
| Storage Tank | Stores collected rainwater |
| Filtration System | Removes debris and contaminants |
What are rain water collectors called?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rainwater-harvesting-system-isometric-diagram-1201105579-34cb7b27492f42c387b89fd903a16ba4.jpg)
Rainwater collectors are commonly known as rainwater harvesting systems or simply rainwater collectors. These systems are designed to capture, store, and utilize rainwater for various purposes, helping to conserve water and reduce reliance on traditional water sources.
What are Rainwater Harvesting Systems?
Rainwater harvesting systems consist of various components that work together to collect and manage rainwater. They can be simple or complex, depending on the needs of the user.
- Collection Surface: Usually a roof or another structure that captures rainwater.
- Conveyance System: Gutters and downspouts that transport rainwater from the collection surface to the storage system.
- Storage Container: A tank or cistern where the collected rainwater is stored for future use.
Types of Rainwater Collectors
There are several types of rainwater collectors, each with specific applications and benefits. Some popular designs include:
- Above-ground Systems: Containers placed above ground for easy access and visibility.
- Underground Tanks: Cisterns that are buried, which can conserve space and maintain water temperature.
- Modular Systems: Flexible systems that can be expanded or configured to fit different spaces and requirements.
Benefits of Using Rainwater Collectors
Utilizing rainwater collectors offers numerous advantages, especially in areas where water scarcity is a concern. Key benefits include:
- Water Conservation: Reduces dependence on municipal water systems and preserves freshwater resources.
- Cost Savings: Lowers water bills by utilizing collected rainwater for irrigation, flushing toilets, and other uses.
- Environmental Impact: Decreases stormwater runoff and the associated risk of flooding and pollution in local waterways.
Applications of Collected Rainwater
Collected rainwater can be used in various applications, making it a versatile resource. Common uses include:
See also:
- Irrigation: Watering gardens, lawns, and agricultural fields, enhancing plant growth while conserving treated water.
- Household Uses: Flushing toilets, doing laundry, and other non-potable applications to reduce fresh water consumption.
- Groundwater Recharge: Augmenting local groundwater supplies, contributing to ecosystem health and sustainability.
Maintenance of Rainwater Collectors
To ensure efficiency and effectiveness, regular maintenance of rainwater collectors is essential. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning Gutters and Filters: Preventing clogging and ensuring proper flow of rainwater into the storage system.
- Inspecting Tanks: Checking for leaks, sediment buildup, and the general condition of the storage containers.
- Monitoring Water Quality: Testing collected rainwater periodically to ensure it is safe for its intended use.
Why is collecting rainwater illegal in the US?

Collecting rainwater is a practice that can raise eyebrows in the United States, as it is subject to various legal regulations that can vary significantly from one state to another. The legality of rainwater harvesting often stems from historical, environmental, and water rights considerations.
Many states impose restrictions on collecting rainwater due to concerns about water rights. Water in the U.S. is traditionally governed by riparian law or prior appropriation, which means that water usage is often tied to land ownership or specific permits. Thus, collecting rain can be viewed as a potential infringement on the rights of others who have legal claims to that water.
Historical Water Rights and Ownership Laws
The history of water rights in the U.S. is complex and deeply rooted in the notion that water is a public resource. Specific legal frameworks have been established over decades to manage its distribution:
- Riparian Law: This law grants owners of land adjacent to water sources the rights to access that water.
- Prior Appropriation: Based mainly in Western states, this principle allows water to be allocated based on the principle of first in time, first in right.
- State Regulations: Some states have specific laws regulating the collection of rainwater to protect water rights and manage resources more efficiently.
Environmental Concerns
Another important factor in the legality of rainwater collection is the potential impact on the environment. Regulatory bodies may argue that unauthorized rainwater harvesting can disrupt local ecosystems:
- Water Supply Management: Collecting rainwater without proper permits can complicate the management of local water supplies.
- Stormwater Runoff: Improper collection can affect stormwater runoff patterns, potentially leading to flooding or erosion.
- Impact on Native Species: Altering water distribution could have detrimental effects on local flora and fauna that depend on specific water availability.
Health and Safety Regulations
In many places, the legal restrictions surrounding rainwater collection are also tied to health and safety issues. Ensuring that collected water is safe for use is a top priority:
- Water Quality: Collected rainwater can contain pollutants that affect its potability.
- Proper Storage: There are often regulations regarding how rainwater must be stored to prevent contamination or mosquito breeding.
- Usage Restrictions: Even where collection is allowed, there may be restrictions on how that water can be used (e.g., irrigation, flushing toilets, etc.).
State-specific Regulations
The legality of collecting rainwater varies significantly depending on the state, leading to a patchwork of rules:
- Prohibition vs. Permits: Some states completely prohibit rainwater harvesting while others require permits or specific systems.
- Incentives: Certain states encourage rainwater collection through incentives or subsidies for proper systems.
- Model Laws: Some states have adopted model laws that improve legality while aligning with environmental stewardship.
Public Perception and Advocacy
Public perception plays a critical role in how rainwater harvesting laws are shaped. Advocacy groups often work to change existing regulations:
- Public Awareness: Education campaigns can increase understanding of the benefits of rainwater collection, influencing public opinion.
- Environmental Movements: These groups often lobby for more permissive laws to promote sustainable practices.
- Legal Challenges: Advocacy efforts can lead to legal challenges against restrictive regulations, leading to changes in the law.
What equipment is used to collect rainwater?
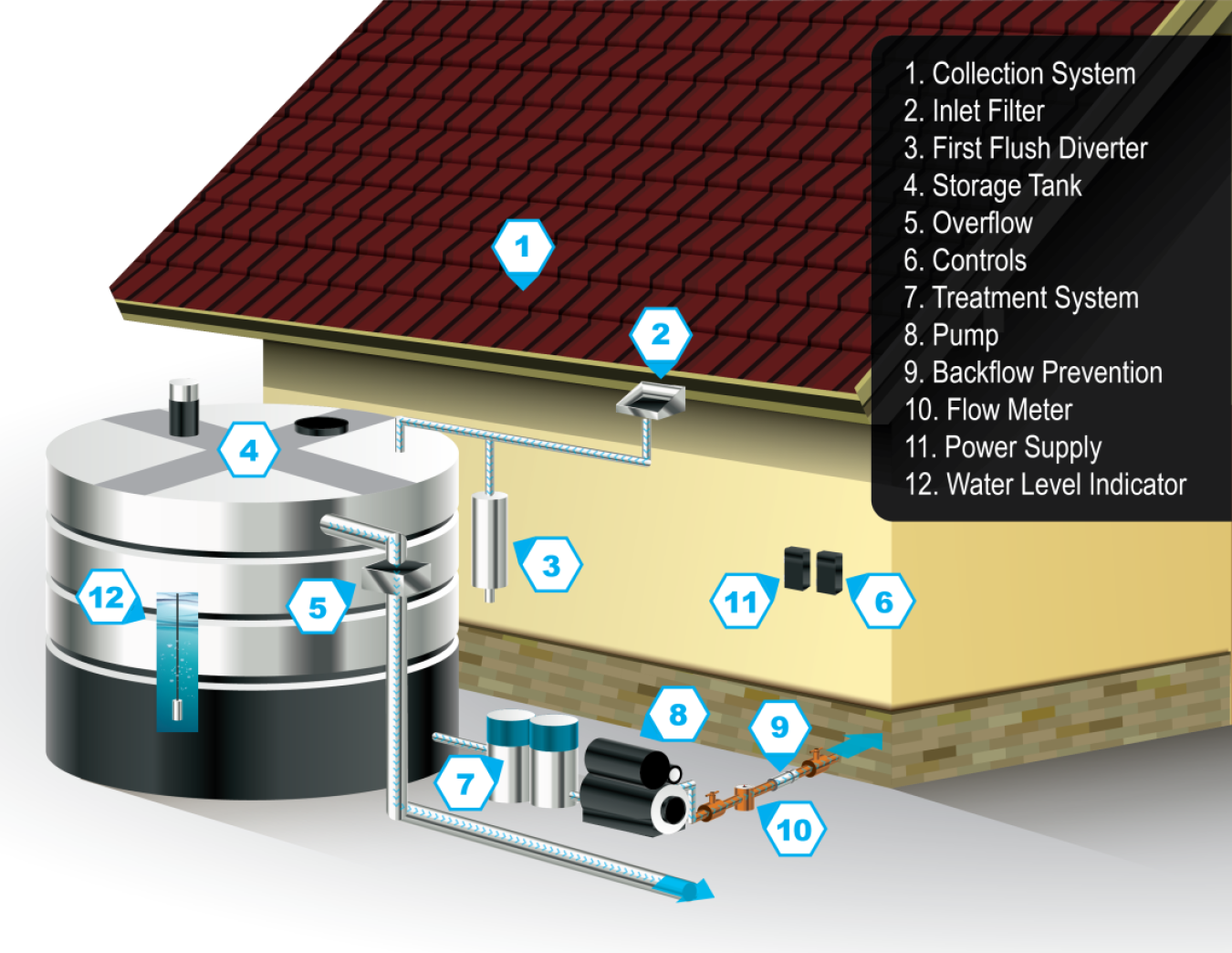
To collect rainwater effectively, a variety of equipment is used to ensure that the water is captured, stored, and utilized properly. Here’s a detailed exploration of the primary tools and equipment involved in rainwater harvesting.
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rainwater harvesting systems consist of a series of components that work together to collect and manage rainwater. These systems can be as simple as a barrel placed under a downspout or as complex as an integrated system that includes multiple components. The main components are:
- Catchment Area: This is usually the roof of a building where rainwater is initially collected.
- Conveyance System: The pipes or gutters that transport rainwater from the catchment area to the storage tank.
- Storage Tank: A container designed to store collected rainwater for later use.
Gutters and Downspouts
Gutters and downspouts play a crucial role in directing rainwater from the roof to the storage systems. Effective sizing and installation of gutters and downspouts can significantly enhance the efficiency of rainwater collection. Understanding their significance includes:
See also:
- Gutter Size: Appropriate sizing prevents overflow and ensures maximum water capture.
- Material: Materials such as vinyl, aluminum, or steel can affect durability and maintenance needs.
- Slope: Proper slope must be maintained to ensure water flows towards the downspouts effectively.
Storage Tanks
Storage tanks are essential for efficiently collecting and storing rainwater. These tanks come in various shapes and materials, impacting their usability and longevity. Considerations include:
- Tank Material: Options include plastic, fiberglass, concrete, and metal, each with different benefits.
- Tank Size: The capacity should be based on expected rainfall and water usage needs.
- Location: Tanks should be placed strategically to maximize accessibility and aeration.
Filtration Systems
To ensure that collected rainwater is clean and safe for use, filtration systems are implemented. These systems help remove debris, leaves, and contaminants before the water is stored. Key aspects include:
- First Flush Diverters: These devices discard the initial flow of water which often contains roof contaminants.
- Pre-filtration: Mesh screens or filters are used to trap larger particles before the water enters the storage tank.
- Post-treatment Filters: Additional purification methods, such as UV treatment and carbon filters, may be employed for further cleaning.
Distribution Systems
Once rainwater is collected and stored, distribution systems are needed to transport the water to where it is used. These systems can include pumps, pipes, and valves, which are important for functionality. The considerations are:
- Pumps: If water needs to be moved to higher elevations, a pump system is essential.
- Piping: PVC, polyethylene, or other materials are commonly used for transporting water.
- Valves and Fittings: These components help in controlling water flow and enabling connections to irrigation systems or taps.
What is the container that collects rainwater?

The container that collects rainwater is commonly known as a rainwater harvesting tank or cistern. This container is designed to capture, store, and manage rainwater runoff from roofs or other surfaces, enabling its use for various non-potable applications such as irrigation, flushing toilets, or washing vehicles. By utilizing this system, individuals can reduce their dependency on municipal water supply, lower their water bills, and contribute to sustainable water management practices.
The Importance of Rainwater Harvesting Tanks
Rainwater harvesting tanks serve multiple purposes that benefit both the individual and the environment. Their significance includes the following aspects:
- Water conservation: Collecting rainwater helps to conserve an essential resource and lessens the demand on local water supplies.
- Stormwater management: These tanks can mitigate flooding by capturing runoff, reducing soil erosion and the risk of water pollution.
- Cost savings: By using harvested rainwater for non-potable uses, households can significantly lower their water bills.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Tanks
There are various types of rainwater harvesting tanks, each suited for different applications and settings. They include:
- Above-ground tanks: These are installed on surfaces and are typically easier to install, but may have limited capacity.
- Below-ground tanks: These are buried underground, providing a larger storage capacity and protection from extreme weather.
- Modular systems: These consist of multiple smaller tanks that can be connected for larger storage, allowing for flexibility in installation.
Materials Used in Rainwater Harvesting Tanks
Rainwater harvesting tanks can be made from a variety of materials, each having distinct advantages. Common materials include:
- Plastic: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, plastic tanks are easy to install and maintain, but may have a shorter lifespan.
- Concrete: Highly durable and long-lasting, concrete tanks are excellent for underground storage but can be costly and heavy.
- Steel: Galvanized steel tanks can withstand extreme weather but may require protective coatings to prevent rust.
Installation Considerations for Rainwater Harvesting Tanks
Installing a rainwater harvesting tank involves several considerations to ensure optimal performance:
- Location: Choose a location that maximizes water collection and minimizes the distance to plumbing connections.
- Size: Determine the appropriate tank size based on the average rainfall in the area and water usage needs.
- Filtration: Incorporate a filtration system to remove debris and contaminants from the collected rainwater.
Maintenance of Rainwater Harvesting Tanks
To ensure effective operation, regular maintenance of rainwater harvesting tanks is essential. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the tank, roof gutters, and downspouts to prevent blockages and contamination.
- Inspection: Periodically check for leaks and structural integrity to ensure the tank remains in good condition.
- Water testing: Test the water quality periodically to ensure it remains suitable for its intended use.
Questions from Our Readers
What is the device called that collects rainwater?
The device that collects rainwater is commonly known as a rainwater harvesting system. This system can include various components such as storage tanks, gutters, and downspouts which work together to capture and store rainwater for various uses.
How does a rainwater harvesting system work?
A rainwater harvesting system works by from rooftops or surfaces, directing it through a series of gutters and pipes into a storage tank. The collected water can then be filtered and used for irrigation, flushing toilets, or other non-potable applications.
What are the benefits of using rainwater harvesting?
The benefits of using rainwater harvesting include reducing water bills, conserving water during dry periods, and providing a sustainable source of water for gardening and other uses. It also helps to mitigate stormwater runoff, which can reduce flooding and erosion.
See also:
Is rainwater safe to drink?
Rainwater can be safe to drink if it has been properly filtered and treated. However, it is important to ensure that the collection system is clean and that the water undergoes necessary purification processes, as it can be contaminated by environmental pollutants or bacteria.

If you want to read more articles like What is the device called that collects rainwater? A Comprehensive Guide to Rainwater Harvesting Solutions, we recommend you check out our Irrigation category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles