What Direction Does a Greenhouse Need to Face? A Complete Guide to Optimal Sunlight and Growth

When it comes to maximizing the growth potential of plants in a greenhouse, the direction in which it faces plays a crucial role. Proper orientation not only ensures optimal sunlight exposure but also influences temperature regulation, ventilation, and even pest management. This complete guide will explore the best practices for positioning your greenhouse, taking into consideration geographical location, seasonal changes, and the specific needs of the plants you wish to cultivate. Whether you’re a novice gardener or a seasoned horticulturist, understanding the ideal direction for your greenhouse will enhance your gardening success and yield healthier, more productive plants.
What Direction Should a Greenhouse Face?
The optimal direction for a greenhouse to face generally depends on its geographical location, but typically, a south-facing orientation is preferred in the Northern Hemisphere. This positioning allows the structure to capture the maximum amount of sunlight throughout the day, promoting effective photosynthesis and creating a warm environment for plants. In contrast, a north-facing greenhouse can experience reduced light levels, which may affect plant growth negatively. Additionally, integrating elements such as structures, trees, or natural barriers can help moderate temperature fluctuations and provide desired shade or wind protection, further enhancing the greenhouse's microclimate.
Benefits of a South-Facing Greenhouse
A south-facing greenhouse harnesses the full spectrum of sunlight exposure, leading to increased warmth and better light conditions for plants year-round. The angle of the sun allows light to penetrate deeply into the greenhouse, promoting vigorous plant growth and extending the growing season. In specific climates, this orientation can also minimize heating costs, as the greenhouse can harness natural sunlight rather than relying solely on artificial heating systems.
Considerations in the Southern Hemisphere
For gardeners situated in the Southern Hemisphere, a north-facing orientation often proves optimal, as it similarly maximizes sunlight capture. This approach is crucial for the effective management of temperature and light within the greenhouse, facilitating better crop yields. Gardeners should also consider seasonal tracking of the sun’s path to ensure that any potential obstructions, such as nearby buildings or trees, do not hinder sunlight access.
The Impact of Local Climate
Local climate conditions play a vital role in determining the best direction for a greenhouse. In areas with extreme winds, the orientation may need adjustment to mitigate wind exposure, which can lead to increased heat loss. Conversely, regions that experience high summer temperatures may require strategic shading placements or ventilation solutions to prevent overheating. Assessing local weather patterns can greatly influence successful greenhouse management.
Utilizing Natural Barriers
Incorporating natural barriers such as trees or hills when positioning a greenhouse can enhance its effectiveness. These elements can provide beneficial shade during the hottest parts of the day, preventing overheating and conserving moisture levels inside the greenhouse. They can also act as windbreaks, reducing the effects of harsh winds that could disrupt temperature stability or damage plants.
Sunlight Exposure During Different Seasons
A greenhouse’s orientation also affects how it interacts with light throughout the changing seasons. In winter, for instance, a south-facing design allows sunlight to access the greenhouse even when the sun is lower in the sky. In contrast, during the summer months, careful planning of ventilation systems becomes essential to manage the increased heat, with appropriate shading measures protecting plants from direct sunlight during intense heat spikes.
| Orientation | Key Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| South (Northern Hemisphere) | Optimal light exposure, longer growing season | Manage summer heat with shading |
| North (Southern Hemisphere) | Maximized sunlight and warmth | Avoid potential obstructions |
| Wind consideration | Increased stability and reduced heat loss | Monitored orientation relative to dominant winds |
| Seasonal adjustments | Effective management of temperature | Need for ventilation in summer |
What direction should my greenhouse face?
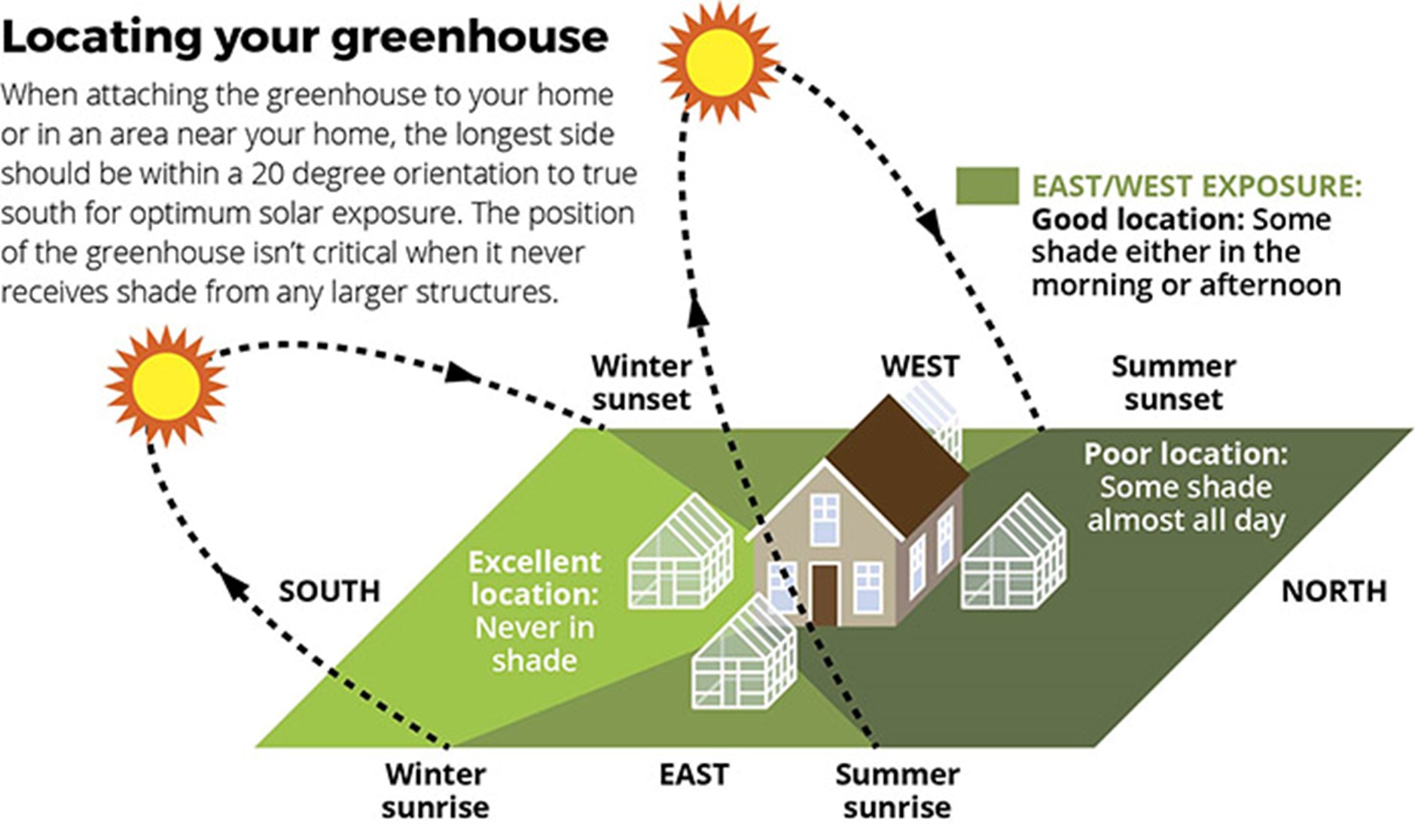
To determine the optimal direction for your greenhouse, it's essential to consider several factors that influence sunlight exposure, temperature control, and overall plant growth. The best orientation for a greenhouse generally depends on the local climate, but facing it towards the south is often recommended in the Northern Hemisphere. This orientation allows maximum sunlight penetration throughout the day, which is crucial for plant photosynthesis. In contrast, for those living in the Southern Hemisphere, a north-facing greenhouse will offer similar advantages.
Factors Influencing Greenhouse Orientation
The orientation of your greenhouse can significantly affect your growing conditions. Here are the primary factors to consider:
- Sunlight: A greenhouse should receive as much direct sunlight as possible. Optimal orientations allow for sunlight exposure for extended periods.
- Wind Exposure: Consider the prevailing winds in your region. Positioning your greenhouse to block harsh winds can help maintain a stable temperature inside.
- Temperature Control: Orientation impacts how heat is retained. For instance, south-facing greenhouses in winter can catch more sunlight, while summer may require shading.
Greenhouse Locations and Microclimates
The specific location of your greenhouse can create unique microclimates that affect plant growth:
- Nearby Structures: Buildings and trees can cast shadows, reducing sunlight exposure. Ensure that your greenhouse is placed in an area free of obstacles that block sunlight.
- Ground Type: The surrounding soil can influence drainage and heat retention. Choose a spot with well-draining soil that can absorb sunlight effectively.
- Water Sources: Proximity to water can help regulate humidity levels, but it's essential to protect your greenhouse from excessive moisture buildup.
Design Considerations for Greenhouse Orientation
When designing your greenhouse, consider how the orientation influences its structure and materials:
- Material Choice: Different materials (glass, polycarbonate, etc.) will react differently to sunlight and can influence heat retention.
- Ventilation Design: The orientation affects airflow. A south-facing greenhouse may benefit from ventilation strategies that optimize airflow during hot months.
- Layout Planning: Plan the internal layout considering light distribution; tall plants should be placed where they won't shade smaller ones.
Impact of Climate on Greenhouse Direction
Local climate conditions greatly influence the best orientation for your greenhouse:
- Temperature Variations: In colder climates, a south-facing orientation maximizes heat absorption, while tropical areas may require east-west orientation to reduce heat retention.
- Sunlight Intensity: Regions with intense sunlight might necessitate shading solutions or strategic placement to prevent overheating.
- Seasonal Changes: Consider how the sun's path changes with the seasons to maximize light availability throughout the year.
Recommendations for Different Regions
Different geographical locations may have unique recommendations for greenhouse orientation:
See also:
- Northern Hemisphere: Generally, a south-facing orientation is preferred for maximal light exposure.
- Southern Hemisphere: North-facing greenhouses are suitable to capture more sunlight.
- Equatorial Regions: Consider east-west orientation to balance sunlight exposure and temperature management throughout the day.
Should a greenhouse face east or west?

Determining whether a greenhouse should face east or west involves considering various factors that affect plant growth and energy efficiency. The orientation of a greenhouse can significantly impact its internal conditions, including light exposure, temperature, and humidity levels.
East-facing greenhouses receive sunlight in the morning, which can be beneficial for early plant growth. The morning sun helps to warm the greenhouse slowly, preventing plants from experiencing temperature shocks. Additionally, east-facing setups can help reduce overheating in the afternoon when sunlight is often most intense.
On the other hand, west-facing greenhouses capture the sunlight later in the day, which can increase the temperature during the afternoon and evening hours. This can be particularly advantageous for plants that thrive in warmer conditions. However, without proper ventilation or shading, these greenhouses might suffer from excessive heat during the hottest part of the day.
Ultimately, the choice between an east or west orientation may depend on local climate conditions, the type of plants being grown, and the specific goals of the grower.
Benefits of East-facing Greenhouses
East-facing greenhouses offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for many gardeners.
- Morning Sun: They absorb sunlight early in the day, ensuring a gentle warming effect.
- Reduced Heat Stress: By avoiding the harsh afternoon sun, plants experience less heat stress.
- Extended Growing Season: The early light can promote growth even in cooler temperatures.
Benefits of West-facing Greenhouses
There are numerous advantages to positioning a greenhouse to face west as well.
- Warm Afternoon Light: They receive strong sunlight in the afternoon, which is useful for heat-loving plants.
- Natural Warmth: The heat build-up in the evening can help maintain a stable temperature at night.
- Seasonal Adaptability: These greenhouses may perform better in cooler climates or seasons when additional warmth is desired.
Impact of Geographic Location
The location and latitude play crucial roles in deciding the optimal greenhouse orientation.
- Higher Latitudes: In areas further from the equator, maximizing sunlight exposure during shorter days is essential.
- Temperature Considerations: Warm regions may benefit from east-facing designs to prevent overheating.
- Local Microclimates: Environmental factors unique to the area can also influence the decision.
Type of Plants and Their Light Requirements
Different plants have varied light requirements, impacting the choice of greenhouse orientation.
- Cool-season Crops: These generally thrive in the morning sun, making an east-facing setup beneficial.
- Heat-loving Plants: These may prefer the stronger afternoon light available in west-facing greenhouses.
- Diverse Cultivation: Some growers might opt for a mixed approach with movable plants or adjustable shading.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Considerations
The placement of a greenhouse can directly affect its energy consumption and overall operating costs.
- Heating Costs: East-facing greenhouses may require less heating in the morning.
- Cooling Needs: West-facing designs may demand more cooling solutions during peak heat.
- Long-term Planning: Considering future energy costs can influence initial design decisions.
What should be the direction of Green House?

The direction of a greenhouse is crucial for maximizing plant growth and optimizing energy efficiency. Ideally, the greenhouse should be oriented along an east-west axis. This orientation allows for optimal sunlight exposure throughout the day, which is essential for photosynthesis and the overall health of plants. Here are the key factors to consider regarding the direction of your greenhouse:
Sunlight Exposure
The direction of the greenhouse affects the amount of sunlight the plants receive. Proper orientation can help ensure that the interior of the greenhouse is well-lit, promoting better growth and yield.
- Maximizes sunlight during the day.
- Reduces the risk of shading from nearby structures.
- Enhances the overall light distribution inside the greenhouse.
Temperature Regulation
The direction also impacts the internal temperature of the greenhouse. An east-west orientation can help maintain a more consistent temperature throughout the day.
See also:
- Promotes cooler temperatures during hot days.
- Minimizes heat loss during cold nights.
- Encourages better ventilation due to sunlight patterns.
Wind Protection
Location and orientation can aid in protecting the greenhouse from strong winds, which could damage plants or the structure itself. Proper direction helps in reducing wind load.
- Identifies natural barriers like trees or buildings.
- Reduces the effect of cold drafts.
- Enhances the durability of the greenhouse structure.
Seasonal Considerations
The angle of the sun changes with the seasons, affecting how much light a greenhouse receives throughout the year. Orientation is essential for seasonal adaptations.
- Improves winter sun exposure for warmth.
- Reduces excessive summer heat during peak sunlight.
- Allows for better adjustments of shading devices.
Crop Type and Growth Requirements
Different crops have varying sunlight and temperature requirements. The orientation can facilitate meeting these needs more effectively.
- Aligns with the growth patterns of specific plants.
- Facilitates crop rotation based on light needs.
- Enhances yield potential for diverse crops.
Do greenhouses need to be south-facing?

Greenhouses do not necessarily need to be south-facing, but positioning them to maximize sunlight exposure is crucial for their effectiveness. The orientation of a greenhouse influences how much natural light it receives, which is essential for plant growth. However, other factors, such as location and local climate, also play a significant role in determining the best orientation for a greenhouse.
Importance of Sunlight Exposure
The primary purpose of a greenhouse is to provide a controlled environment that promotes plant growth by optimizing sunlight exposure.
- Photosynthesis: Plants convert sunlight into energy, which is essential for growth.
- Temperature Regulation: Adequate sunlight helps maintain optimal temperatures inside the greenhouse.
- Plant Health: Sufficient light reduces the risk of diseases and promotes healthier plants.
South-Facing Benefits
A south-facing greenhouse often receives the most direct sunlight throughout the day, which can be beneficial in various climates.
- Consistent Sunlight: Maximizes the amount of light received during peak hours.
- Heat Retention: Helps maintain a warmer environment during colder months.
- Extended Growing Season: Enables year-round cultivation by optimizing light and temperature.
Influence of Local Climate
The ideal orientation for a greenhouse can depend on the local climate conditions, including sunlight intensity and prevailing winds.
- Latitude: In northern regions, south-facing may be preferable, while east or west-facing could be suitable in southern areas.
- Prevailing Winds: Proper orientation can help reduce heating costs by blocking cold winds.
- Seasonal Variations: Different orientations may work better during specific seasons, depending on sunlight angles.
Compensating for Less Than Ideal Orientation
If a greenhouse cannot be positioned south-facing, there are methods to enhance light absorption.
- Reflective Surfaces: Using reflective materials nearby can redirect sunlight into the greenhouse.
- Supplemental Lighting: Adding grow lights can help compensate for inadequate natural light.
- Insulation: Improved insulation can help retain heat, even with less optimal sunlight exposure.
Design and Structure Considerations
The design of the greenhouse itself can also impact how effectively it utilizes sunlight, regardless of orientation.
- Glazing Material: Choosing the right glazing can enhance light transmission while maintaining heat.
- Roof Angles: Adjustable roof angles can maximize sunlight entry during different seasons.
- Size and Shape: Larger and more open structures may capture more light effectively.
Questions from Our Readers
What direction should a greenhouse face for optimal sunlight?
To maximize sunlight exposure, a greenhouse should ideally face south or southeast. This positioning allows the structure to capture the morning sun and benefit from afternoon light, promoting better growth conditions for plants throughout the day.
Does the direction of a greenhouse vary by location?
Yes, the optimal direction can vary depending on your geographical location. In the northern hemisphere, a south-facing orientation is generally best, while in the southern hemisphere, a north-facing direction will provide the most effective light exposure for plant growth.
How does wind direction affect greenhouse orientation?
Wind direction can significantly impact greenhouse orientation, as you may want to position the structure to minimize wind exposure and enhance ventilation. In areas prone to strong winds, it's advisable to take the prevailing wind direction into account when deciding the best orientation.
Can a greenhouse's direction be adjusted seasonally?
While the fixed orientation of a greenhouse is generally best for consistent sunlight, in some cases, you can use temporary adjustments, such as shade cloths or reflectors, to modify light exposure. However, these adjustments do not replace the benefits of a well-oriented greenhouse based on its initial location.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like What Direction Does a Greenhouse Need to Face? A Complete Guide to Optimal Sunlight and Growth, we recommend you check out our Greenhouse category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles