What are the Top 3 Fertilizers? A Comprehensive Guide for Optimal Plant Growth

In the world of gardening and agriculture, the importance of fertilizers cannot be overstated. They provide essential nutrients that plants need to thrive, ultimately leading to lush greenery and bountiful yields. However, with so many products available on the market, it can be overwhelming to determine which fertilizers are truly the most effective. This comprehensive guide will explore the top three fertilizers, delving into their compositions, advantages, and best applications. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or a beginner, understanding these fertilizers will help you make informed decisions that promote optimal plant growth and health.
What Are the Top 3 Fertilizers?
When it comes to promoting healthy plant growth, understanding the top fertilizers is crucial for both novice and experienced gardeners. The top three fertilizers are typically Nitrogen-rich fertilizers, Phosphorus-rich fertilizers, and Potassium-rich fertilizers. Each type of fertilizer plays a vital role in nurturing plants by supplying essential nutrients that may be deficient in the soil. For example, nitrogen is key for leaf growth, phosphorus supports root and flower development, while potassium enhances overall plant health and resistance to diseases. By using these fertilizers judiciously, gardeners can cultivate vibrant and thriving gardens.
Nitrogen-Rich Fertilizers
Nitrogen-rich fertilizers are essential for fostering leaf and stem growth in plants. These fertilizers typically contain a high percentage of nitrogen, which is one of the three primary nutrients required for plant health. Available in various forms such as ammonium nitrate and urea, they are particularly beneficial for vegetables, grasses, and leafy plants. However, it is important to apply these fertilizers at the right time and in appropriate amounts to avoid nitrogen burn, which can damage plants.
Phosphorus-Rich Fertilizers
Phosphorus-rich fertilizers contain a high level of phosphorus, which is crucial for root development and flowering. This nutrient supports the formation of strong root systems, enhances flowering, and increases seed production in plants. Common sources of phosphorus include bone meal, superphosphate, and rock phosphate. When applied properly, phosphorus-rich fertilizers can significantly improve plant vigor, promote blooming, and ensure successful fruiting in a wide range of crops.
Potassium-Rich Fertilizers
Potassium-rich fertilizers are vital for overall plant health, as potassium plays a significant role in regulating various physiological processes. This nutrient helps plants withstand stress, enhances nutrient uptake, and improves disease resistance. Common forms of potassium include potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and organic options like kelp meal. Utilizing potassium-rich fertilizers can lead to better fruit quality, increased yield, and greater resilience against extreme weather conditions and pests.
Organic Fertilizer Options
Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources and provide a balanced arrangement of essential nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These fertilizers improve soil health by promoting beneficial microbial activity and enhancing soil structure. Examples include compost, manure, and bone meal. Using organic fertilizers fosters long-term soil fertility and sustainability, making them an excellent choice for environmentally conscious gardeners looking to enhance plant growth naturally.
Best Practices for Fertilizer Application
Effective fertilizer application is key to maximizing the benefits of nutrient-rich products. Best practices include understanding soil nutrient levels through testing, applying fertilizers when plants are actively growing, and following recommended dosages for specific plants. Additionally, incorporating fertilizers into the soil or using slow-release options can reduce the risk of nutrient leaching and enhance plant uptake. Regular monitoring of plant health will help gardeners adjust their fertilization methods for optimal results.
| Fertilizer Type | Main Nutrient | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen-rich | Nitrogen | Encourages leaf and stem growth |
| Phosphorus-rich | Phosphorus | Enhances root and flower development |
| Potassium-rich | Potassium | Improves overall plant health and stress resistance |
What are the top 3 fertilizers for plants?

The top three fertilizers for plants include organic, synthetic, and slow-release fertilizers. Each type has its own unique benefits and is suitable for different plant needs.
1. Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources, providing a more sustainable way to nourish plants. These fertilizers improve soil health by enhancing its microbial activity and creating a rich environment for plant growth.
- Types: Common organic fertilizers include compost, manure, and bone meal.
- Benefits: They not only provide nutrients but also improve soil structure and water retention.
- Usage: They are generally less concentrated than synthetic fertilizers, requiring more frequent applications.
2. Synthetic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers are manufactured chemically and are usually high in nutrients. They are designed for quick absorption by plants, making them ideal for situations where immediate nutrient availability is needed.
- Types: Common examples include urea, ammonium nitrate, and superphosphate.
- Benefits: They provide a concentrated source of nutrients, often leading to faster plant growth.
- Usage: Require careful application to avoid burning plants, and may lead to soil depletion over time.
3. Slow-Release Fertilizers
Slow-release fertilizers are designed to release nutrients over an extended period, reducing the need for frequent applications while ensuring that plants receive a steady supply of nutrients.
- Types: These include coated fertilizers and organic fertilizers with natural slow-release properties.
- Benefits: They minimize nutrient runoff and are less likely to burn plants.
- Usage: Ideal for potted plants and landscapes where consistent feeding is important.
4. Liquid Fertilizers
Liquid fertilizers are nutrient solutions that can be applied directly to the soil or foliage. They are popular among gardeners for their ease of use and quick nutrient uptake.
See also:
- Types: They come in formulated mixtures for specific plant needs, such as flower boosters or vegetable fertilizers.
- Benefits: Fast-acting and easily customizable, providing quick nutrient support during the growing season.
- Usage: Best used alongside other fertilizers to meet diverse nutritional needs.
5. Specialty Fertilizers
Specialty fertilizers are formulated for specific types of plants or conditions, ensuring optimal growth and health by addressing unique nutritional requirements.
- Types: Examples include fertilizer blends for orchids, roses, or acid-loving plants like blueberries.
- Benefits: These fertilizers target specific deficiencies or promote blooming and fruiting.
- Usage: Following the manufacturer's instructions is critical to prevent over-fertilization.
What are the big three fertilizers?
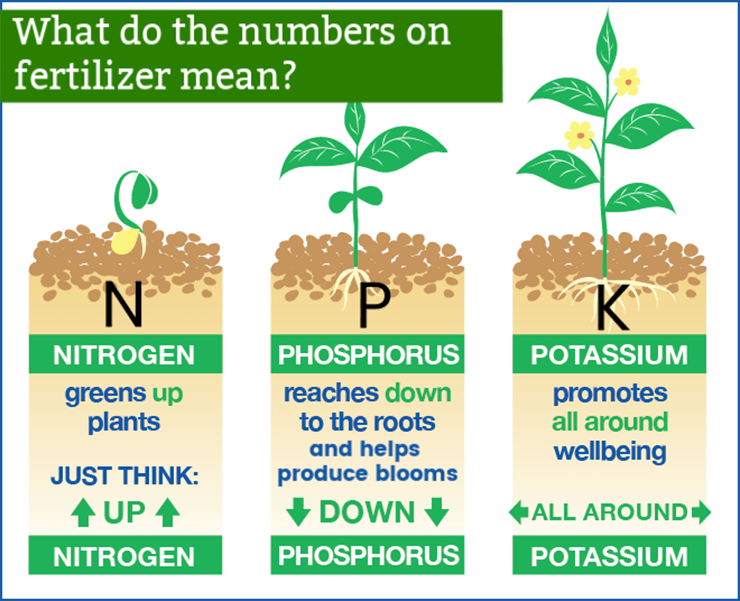
The big three fertilizers, commonly referred to as NPK fertilizers, are essential for providing plants with the necessary nutrients they require for growth. These three components represent the primary macronutrients that are vital for plant health and development.
Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is one of the key components in NPK fertilizers, playing a critical role in plant growth and development. It is primarily responsible for promoting vigorous leaf and stem growth, as it is a crucial component of amino acids and proteins. Additionally, nitrogen is involved in chlorophyll production, which is essential for photosynthesis.
- Nitrogen enhances leaf growth and overall vitality of the plant.
- It improves photosynthetic efficiency, leading to better yield.
- Deficiency in nitrogen causes yellowing of leaves known as chlorosis.
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is another essential nutrient found in NPK fertilizers, contributing significantly to root development and flowering. This nutrient is vital for the formation of DNA, RNA, and energy-carrying molecules like ATP, which are necessary for cellular functions and energy transfer in plants.
- Phosphorus promotes strong root systems and enhances nutrient uptake.
- It is crucial for the production of flowers and fruits, contributing to improved yields.
- Deficiency can lead to poor growth and delayed flowering, often characterized by dark or purplish leaf edges.
Potassium (K)
Potassium plays a significant role in regulating plant metabolism and overall health. It is essential for water regulation within plants, improving drought resistance and nutrient transport. Potassium aids in activating enzymes that promote several physiological processes, enhancing the plant's ability to manage stress conditions.
- Potassium improves disease resistance and overall plant longevity.
- It enhances fruit quality and improves the plant's ability to withstand adverse conditions.
- Deficiency manifests as browning of leaf edges and poor fruit development.
Importance of NPK Ratio
The ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in fertilizers is crucial for meeting the specific nutritional needs of various plants. Different crops require different balances of these nutrients, and understanding their NPK ratio helps in formulating appropriate fertilization strategies.
- The NPK ratio is often labeled in a series of three numbers (e.g., 10-10-10), indicating the percentage of each nutrient.
- Adjusting the ratio can optimize growth for specific crops, leading to improved yield and quality.
- Each crop stage (germination, vegetative, flowering) may require different NPK ratios for optimal performance.
Application Methods
Proper application methods for NPK fertilizers are essential to maximize their benefits and minimize environmental impact. Understanding how to apply these fertilizers efficiently is key to achieving the desired growth outcomes while avoiding over-fertilization.
- Fertilizers can be applied as granules, in liquid form, or through foliar sprays.
- Timing of application (pre-planting, during growth stages) is critical for nutrient uptake.
- Utilizing soil testing can guide the appropriate amounts and timing of fertilizer applications.
What is the king of fertilizer?

What is the King of Fertilizer?
The title of the king of fertilizer is often attributed to urea, a synthetic nitrogen fertilizer that has become the most widely used in agriculture. Urea contains 46% nitrogen by weight, making it one of the most concentrated nitrogen fertilizers available. This high nitrogen content promotes rapid plant growth and increased yields, key factors sought after by farmers.
Urea is favored not just for its efficacy but also for its cost-effectiveness, transportability, and ease of application. Farmers appreciate its ability to be used in various soil types and crop systems. However, the management of urea applications is crucial since improper usage can lead to nitrogen loss through volatilization and leaching, diminishing its effectiveness and contributing to environmental concerns.
The Composition of Urea
Urea is a molecule that consists of one nitrogen atom and two amidogen groups, which makes it a simple and efficient source of nitrogen.
- High Nitrogen Content: With 46% nitrogen, urea is highly efficient.
- Solubility: Urea is easily soluble in water, making it readily available to plants.
- Environmental Impact: While it boosts growth, mismanaged urea can lead to runoff and nitrogen pollution.
Benefits of Using Urea in Agriculture
The usage of urea provides several advantages that farmers and agronomists recognize in their crop production strategies.
See also:
- Enhanced Growth: Urea significantly improves plant growth due to its rich nitrogen content.
- Improved Crop Yield: Proper application can lead to higher yields of crops compared to other fertilizers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Urea is generally cheaper than other nitrogen fertilizers, making it more accessible to farmers.
Application Methods for Urea
Urea can be applied through various methods, depending on the crop and soil conditions.
- Broadcasting: Spreading urea evenly over the soil surface.
- Incorporation: Mixing urea into the soil to reduce volatilization losses.
- Foliar Feeding: Applying dissolved urea directly onto the leaves for quick nitrogen uptake.
Challenges Associated with Urea Use
Despite its benefits, using urea also poses some challenges that need to be managed effectively.
- Nitrogen Loss: Urea can lose nitrogen through volatilization if not incorporated properly.
- Environmental Concerns: Excessive use can lead to soil and water contamination.
- pH Changes: High usage can alter the soil pH, affecting nutrient availability.
Alternatives to Urea Fertilizer
While urea is a popular choice, several alternatives exist that provide similar benefits with potential environmental advantages.
- Ammonium Nitrate: A quick-release nitrogen fertilizer that is less prone to volatilization losses.
- Slow-Release Fertilizers: Formulations that release nitrogen slowly over time to minimize loss.
- Organic Options: Composts and manure that improve soil health and provide nutrients over longer periods.
What are the three important fertilizers?
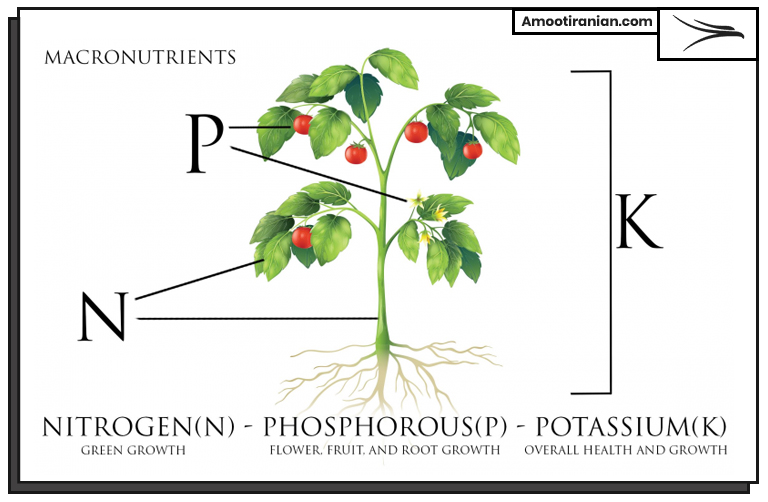
The three important fertilizers are nitrogenous fertilizers, phosphorus fertilizers, and potassium fertilizers. Each of these fertilizers plays a crucial role in plant growth and development, contributing essential nutrients that enhance agricultural productivity.
Nitrogenous Fertilizers
Nitrogenous fertilizers are vital for promoting leaf and stem growth in plants. They primarily contain nitrogen, which is a key component of chlorophyll and proteins. Increased nitrogen levels can lead to lush, green foliage and improved overall plant health. Common forms of nitrogenous fertilizers include ammonium nitrate, urea, and anhydrous ammonia.
- Ammonium Nitrate: A quick-release fertilizer that can be easily absorbed by plants.
- Urea: A widely used, cost-effective nitrogen source that breaks down into ammonia in the soil.
- Anhydrous Ammonia: A concentrated nitrogen form that requires careful application due to its potential volatility.
Phosphorus Fertilizers
Phosphorus fertilizers are essential for the development of strong root systems, flower, and fruit production. Phosphorus is crucial for energy transfer within the plant, acting as a fundamental component of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which fuels various physiological processes. Common phosphorus fertilizers include superphosphate, triple superphosphate, and bone meal.
- Superphosphate: A water-soluble fertilizer that enhances crop yield and quality.
- Triple Superphosphate: A highly concentrated form of phosphorus with greater efficiency compared to regular superphosphate.
- Bone Meal: A natural organic fertilizer rich in phosphorus, often used in organic farming.
Potassium Fertilizers
Potassium fertilizers are crucial for overall plant health, aiding in crucial functions such as water regulation and enzyme activation. Potassium enhances a plant's resistance to diseases and environmental stress, leading to improved quality and yield of crops. Common potassium fertilizers include potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and potassium nitrate.
- Potassium Chloride: The most commonly used potassium fertilizer, known for its high potassium content.
- Potassium Sulfate: A source of potassium and sulfur, beneficial for crops sensitive to chloride.
- Potassium Nitrate: A soluble fertilizer that provides both potassium and nitrogen, promoting rapid plant growth.
Importance of Balanced Fertilization
Balanced fertilization involves using the right proportions of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to meet the specific needs of crops. Each nutrient plays a distinctive role in plant growth, and an imbalance can lead to deficiencies or toxicities that hinder productivity. Understanding nutrient requirements based on soil health and crop type is essential for sustainable agriculture.
- Soil Testing: Conduct regular tests to determine nutrient levels and deficiencies.
- Crop Rotation: Use different crops to maintain soil nutrient balance and health.
- Custom Fertilization Plans: Develop plans tailored to specific crop needs and local soil conditions.
Environmental Considerations
The use of fertilizers has significant implications for the environment, particularly in terms of water quality and soil health. Over-fertilization can lead to nutrient runoff, causing algae blooms and other ecological problems. Implementing best management practices is critical for minimizing environmental impact while maximizing agricultural productivity.
- Buffer Strips: Establish vegetative strips to absorb excess nutrients before they enter waterways.
- Precision Agriculture: Use technology to apply fertilizers efficiently, reducing waste.
- Organic Alternatives: Consider organic fertilizers that enhance soil health and reduce chemical runoff.
Questions from Our Readers
What are the top 3 fertilizers?
The top three fertilizers widely recommended are Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. These essential nutrients play a crucial role in plant growth, with nitrogen promoting leaf growth, phosphorus supporting root and flower development, and potassium enhancing overall plant health and disease resistance.
Why is nitrogen important in fertilizers?
Nitrogen is vital in fertilizers because it is a primary component of amino acids and proteins, which are essential for plant growth and development. Adequate nitrogen levels lead to vibrant foliage and increased crop yields, making it an important nutrient in agricultural practices.
How does phosphorus benefit plants?
Phosphorus is essential for the formation of DNA and ATP, which are critical for plant energy transfer and cellular functions. It promotes strong root systems and improves flowering and fruiting, ultimately leading to healthier plants and better agricultural outputs.
See also:
What role does potassium play in fertilizers?
Potassium plays a crucial role in regulating plant metabolism and maintaining water balance. It enhances the plant's ability to resist stress, boosts disease resistance, and improves overall vigor, making it an essential nutrient in promoting healthy plant growth.

If you want to read more articles like What are the Top 3 Fertilizers? A Comprehensive Guide for Optimal Plant Growth, we recommend you check out our Fertiliser category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles