What Are the Stages of Pruning? A Comprehensive Guide to Perfecting Your Hedges and Trees

Pruning is an essential gardening technique that helps maintain the health and aesthetics of hedges and trees. Understanding the various stages of pruning is crucial for achieving optimal results and ensuring the longevity of your plants. From the initial assessment of growth patterns to the final cleanup process, each stage plays a vital role in shaping and rejuvenating your greenery. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key stages of pruning, providing tips and best practices to perfect your technique. Whether you are a novice gardener or a seasoned green thumb, mastering these stages will help you cultivate vibrant and thriving outdoor spaces.
The Stages of Pruning
Pruning involves several key stages aimed at promoting healthy growth and maintaining the structure of plants. The process typically begins with planning, where the specific goals of pruning are established, such as improving air circulation, enhancing light penetration, or encouraging fruit production. Following this is the assessment stage, where a thorough evaluation of the plant's current condition is conducted, identifying which branches or stems require removal. Next comes the cutting stage, where precise and strategic cuts are made using appropriate tools to ensure minimal damage to the plant. The clean-up phase is essential, involving the disposal of cuttings to prevent disease spread. Finally, the last stage, post-pruning care, ensures that the plant receives adequate water and nutrients to recover and thrive after the process.
Planning the Pruning Process
Planning is crucial in the pruning process as it defines the overall objectives and desired outcomes for the plant. During this stage, one must determine the type of pruning technique to be utilized based on the species and age of the plant. It often involves deciding whether to perform thinning cuts or heading cuts, considering factors such as the plant's health, its growth habits, and environmental conditions. Effective planning contributes significantly to the success of the pruning, driving healthy growth and maximizing the plant's aesthetic appeal.
Assessing the Plant's Condition
Before any cuts are made, a comprehensive assessment of the plant's condition is essential. This includes checking for signs of disease, damage, or excessive growth. Identifying any dead or diseased branches is particularly important, as these can pose a risk to the health of the entire plant. A close examination of the plant will also reveal the best locations for cuts to promote new growth and maintain a balanced shape. This assessment sets the stage for the actual cutting process.
Executing the Cutting Techniques
During the cutting stage, the focus is on making precise cuts that will aid in the plant's growth and health. Employing the right tools, such as pruning shears or saws, is fundamental to achieving clean cuts that minimize trauma to the plant. Various techniques like thinning, which reduces density for better air circulation, or topping, which removes the tops of branches to encourage bushier growth, can be utilized depending on the objectives identified in earlier stages. Careful execution during this phase is crucial in preventing harm to the plant.
Cleaning Up After Pruning
After the cutting stage, the focus shifts to clean-up which is vital for maintaining plant health. This involves the proper disposal of cut branches and leaves to avoid the potential spread of pests and diseases. It is also a good practice to sanitize pruning tools after use to eliminate any harmful pathogens that may have been present. Effective clean-up promotes a healthier environment for the plant and contributes to the overall landscape's beauty.
Post-Pruning Care and Maintenance
Post-pruning care is crucial for ensuring that the plant recovers effectively and thrives after the pruning process. This stage often includes providing adequate water, particularly during dry spells, and ensuring that the plant receives necessary nutrients through fertilization or mulching. Monitoring the plant's growth following pruning is also essential to determine if further adjustments are needed in the care regimen. Proper post-pruning maintenance enhances the longevity and vibrancy of the plant.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Planning | Establishing objectives and techniques for pruning. |
| Assessing | Evaluating the plant’s condition for optimal cutting locations. |
| Cutting | Executing precise cuts with appropriate techniques. |
| Cleaning Up | Disposing of cuttings to maintain plant health. |
| Post-Pruning Care | Providing water and nutrients to support recovery. |
What are the 5 D's of pruning?
The 5 D's of pruning are essential guidelines that help ensure effective and healthy pruning practices for plants and trees. They are focused on removing specific types of branches and growth to enhance the plant's overall health and appearance. The 5 D's stand for:
1. Dead: This refers to removing branches that are no longer alive. Dead branches can harbor pests or diseases that may affect the rest of the plant. Removing them promotes healthy growth.
2. Damaged: Branches that have been damaged by storms, pests, or disease should be pruned. This prevents further decay and reduces the risk of disease spreading to healthy parts of the plant.
3. Diseased: Any parts of the plant that show signs of disease must be removed. This includes branches with visible disease symptoms to stop the spread and maintain the vigor of the rest of the plant.
4. Dubious: Dubious branches are those that appear weak, weakly attached, or growing in a manner that could affect the plant’s integrity. Removing these branches helps the plant distribute its energy more effectively.
5. Descending: Branches that grow downwards can crowd the interior of the plant and impede airflow and light penetration. Pruning these back helps ensure that the plant remains open, healthy, and thriving.
Understanding the Importance of Dead Branches
Removing dead branches is one of the most critical components of pruning. Dead branches often contribute nothing to the plant and can actually harbor pest infestations. Here are the reasons why focusing on dead branches is essential:
See also:
- Prevention of disease spread.
- Improvement of plant appearance.
- Promotion of healthy growth.
Identifying Damaged Branches
When assessing a plant for pruning, it's essential to identify damaged branches. These branches can become a significant entry point for pathogens and pests. By removing them, one can:
- Help the plant recover from accidental harm.
- Ensure a healthier overall structure.
- Reduce the risk of future damage.
Effectively Removing Diseased Parts
It's crucial to address diseased branches promptly. Those affected by diseases can potentially spread their issues to surrounding healthy areas, leading to extensive damage. Removal serves several benefits:
- Stops disease spread.
- Encourages a healthier regeneration of growth.
- Increases the overall longevity of the plant.
Assessing Dubious Growth
Dubious branches often represent a critical decision point in pruning. These branches might not be explicitly dead or diseased, but their formation can lead to future problems. The reasons for their removal include:
- Improving the structure and stability of the plant.
- Directing growth towards stronger branches.
- Enhancing aesthetic appeal.
The Significance of Descending Branches
When pruning, it's essential to look for descending branches as they can obstruct light and airflow within the plant. Their removal is beneficial because:
- Facilitates light penetration to the middle of the plant.
- Encourages better air circulation.
- Promotes even growth throughout the entire plant.
How do you prune step by step?
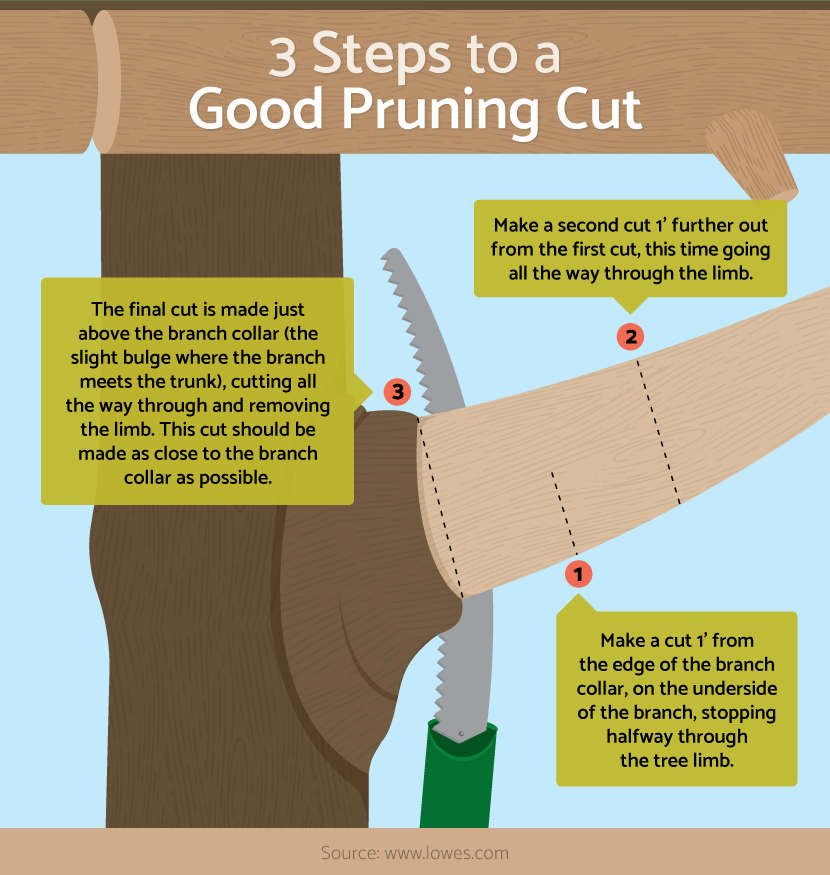
Pruning is a vital aspect of maintaining the health and aesthetics of plants, trees, and shrubs. It involves the selective removal of specific parts of a plant, such as branches, buds, or roots, to improve its growth, enhance fruit production, or maintain its shape. Below are detailed steps to effectively prune your plants.
Understand the Best Time to Prune
Knowing when to prune is essential for the health of your plants. The timing can vary based on the type of plant:
- Deciduous trees: Generally pruned during the late winter or early spring while dormant.
- Flowering bushes: Prune in late spring or early summer, after blooming.
- Fruit trees: Prune in late winter to early spring to promote healthier fruit production.
Gather the Right Tools
Having the appropriate tools makes the pruning process smoother and more effective. Key tools include:
- Pruning shears: For small branches and precise cuts.
- Loppers: For thicker branches that can't be cut with shears.
- Saw: For larger branches and limbs.
- Gloves: To protect your hands from thorns and sharp edges.
- Safety glasses: To protect your eyes from debris.
Identify What to Prune
Evaluate the plant and decide which parts to remove. Focus on:
- Dead or diseased branches: Remove any branches that are lifeless or show signs of disease.
- Crowded sections: Thin out branches that are too close to each other to improve airflow.
- Crossing branches: Eliminate overlapping branches that rub against each other, which can cause damage.
- Long stems: Shorten overly long stems to maintain the desired shape and size.
Make Clean Cuts
To prevent damage to the plant, making clean cuts is essential. Here’s how:
- Angle your cuts: Make cuts at a 45-degree angle about 1/4 inch above a bud or lateral branch.
- Avoid tearing: Ensure your tools are sharp to minimize tearing the bark.
- Don’t leave stubs: Cut just above the desired bud or branch without leaving a stub, which can invite disease.
Monitor and Maintain Your Plants
After pruning, ongoing care is vital for plant recovery and health:
- Watering: Ensure your plants receive adequate water but avoid overwatering.
- Fertilizing: Apply a balanced fertilizer to support new growth.
- Pest control: Monitor for pests and disease that can invade through pruning cuts.
- Regular inspection: Keep an eye on the plant for signs of stress or disease following pruning.
What is the pruning process in the Bible?

The pruning process in the Bible is a significant metaphor that reflects God's plan for the spiritual growth and development of believers. This process emphasizes the necessity of removing distractions and obstacles, allowing for greater spiritual fruitfulness. Pruning is commonly referenced in the context of the vine and branches analogy found in John 15:1-8, where Jesus describes Himself as the true vine and His followers as the branches.
In this metaphor, God, the vinedresser, carefully tends to each branch, providing care and discipline to ensure they yield maximum fruit. The process of pruning involves cutting away dead or unproductive parts of the plant for the overall health and growth of the vine. In the same way, God may permit trials and challenges in the lives of believers to cultivate deeper faith and perseverance.
The Purpose of Pruning in the Biblical Context
The purpose of pruning in the Bible serves to enhance believers' spiritual lives. It is a divine action meant to foster growth and increase one's capacity to bear fruit.
See also:
- Spiritual Growth: Pruning helps believers grow in faith, producing more patience, love, and devotion.
- Removing Obstacles: Just as a gardener removes dead branches, God eliminates distractions or sins that hinder a believer’s walk.
- Preparation for New Growth: Pruning prepares the soul to receive new strength, insights, and greater revelations from God.
The Nature of God's Pruning
God's pruning is often characterized by His loving and wise approach. It may involve challenging times, but these are crafted for specific purposes.
- Disciplinary Actions: When God prunes, it may be through discipline, guiding believers back to His path when they stray.
- Transformative Experiences: Trials and tribulations can serve to reshape character, leading to spiritual maturity.
- Encouragement to Rely on God: Pruning often reminds believers to depend on God's strength rather than their own.
Examples of Pruning in Biblical Narratives
Several Biblical narratives illustrate the concept of pruning, demonstrating its importance across different scenarios.
- The Israelites in the Wilderness: Their time in the wilderness served to prune their dependence on worldly comforts and teach reliance on God.
- Job's Trials: Job experienced loss and suffering, leading him to a deeper knowledge of God's sovereignty and faithfulness.
- David’s Life: David faced numerous challenges, including exile and persecution, which ultimately shaped him into a leader after God's own heart.
Spiritual Fruits as a Result of Pruning
The ultimate goal of pruning is to produce spiritual fruits in the lives of believers. These fruits signify the evidence of a life transformed by God.
- Love: Genuine love serves as a hallmark of a believer's relationship with God and others.
- Joy: Pruning fosters joy that transcends circumstances, rooted in a deep connection with God.
- Peace: Those who undergo pruning often emerge with a profound sense of peace that comes from trusting God's plan.
The Call to Embrace the Pruning Process
Believers are encouraged to embrace the pruning process, viewing it as a necessary step in their spiritual journey.
- Trust in God’s Plan: Recognizing that pruning is part of God’s loving discipline helps believers to trust Him during tough times.
- Willingness to Change: Embracing the process requires an openness to change and a desire to grow closer to God.
- Community Support: Engaging in fellowship with other believers can provide encouragement and strength during pruning seasons.
What are the 3 C's of pruning?

The 3 C's of pruning are Clean cuts, Curing wounds, and Caring for the tree. These principles are essential for ensuring that pruning practices promote healthy growth and minimize damage to the plant. Pruning, when done correctly, can greatly enhance the vitality and aesthetics of trees and shrubs.
Clean Cuts
Making clean cuts during pruning is crucial for the health of the plant. A clean cut minimizes damage to the plant tissue and allows for quicker healing. This involves using sharp, well-maintained tools to make precise cuts without tearing or crushing the branches. Proper technique also prevents the formation of jagged edges, which can harbor disease and pests.
- Use sharp tools: Ensure all pruning tools, such as shears and saws, are properly sharpened.
- Avoid tearing: Cut at an angle to avoid ragged edges that can slow the healing process.
- Focus on the branch collar: Cut just outside the branch collar to support natural healing.
Curing Wounds
After making cuts, it's important to consider how to cure wounds effectively. When branches are removed, the exposed area can be vulnerable to pathogens. Properly sealing or treating these cuts can help prevent infection.
- Sealants: Use pruning sealants sparingly; they can sometimes trap moisture and cause rot.
- Natural healing: Encourage natural healing by not over-treating; most trees heal well on their own.
- Monitor for diseases: Keep an eye on the pruned areas for signs of infection or decay post-pruning.
Caring for the Tree
Incorporating ongoing care after pruning is vital for the tree's recovery and growth. This includes providing appropriate nutrients, water, and monitoring for stress.
- Watering: Ensure the tree receives adequate water, especially in the weeks following pruning.
- Fertilization: Apply a suitable fertilizer to promote healthy regrowth, if necessary.
- Post-pruning care: Regularly check the tree for signs of stress or disease after pruning.
Timing of Pruning
Understanding the best timing for pruning is an integral part of the 3 C’s. Different species have specific needs regarding when they should be pruned for optimal health.
- Seasonal considerations: Prune in late winter or early spring before new growth begins.
- Specific species needs: Research when to prune different plants, as some may have unique timing.
- Avoiding stress: Prune during a period that minimizes stress on the tree.
Types of Pruning Techniques
Employing appropriate pruning techniques is crucial for achieving desired outcomes while following the 3 C's.
- Thinning: Remove selective branches to improve light penetration and air circulation.
- Heading back: Shortening branches to encourage bushier growth.
- Rejuvenation: Drastically cutting back older plants to stimulate new growth.
Questions from Our Readers
What are the stages of pruning?
Pruning generally involves several stages that ensure effective plant management. The main stages include assessment, where you evaluate the plant's structure and health; planning, in which you decide what needs to be cut; execution, where you carry out the pruning using appropriate tools; and finally, aftermath care, which involves monitoring the plant's recovery and health post-pruning.
How do I start the pruning process?
To start the pruning process, first conduct a thorough assessment of your plant. Look for dead, diseased, or damaged branches that need removing. Understand the plant's growth pattern to make informed decisions. Finally, plan your cuts to promote healthy growth and shape while minimizing stress on the plant.
When is the best time to prune?
The best time to prune varies by plant species but generally falls during dormant periods such as late winter or early spring before new growth begins. This timing allows plants to heal effectively and reduces stress, fostering strong growth in the following growing season.
What tools are essential for pruning?
Essential tools for pruning include hand pruners for small branches, loppers for thicker limbs, and saws for larger branches. Additionally, having gloves and safety glasses is vital for protection. Using the right tools will ensure clean cuts that promote plant health and recovery.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like What Are the Stages of Pruning? A Comprehensive Guide to Perfecting Your Hedges and Trees, we recommend you check out our Pruning category.
Leave a Reply

Related Articles