How to Effectively Use a Tree Protection Zone Calculator for Sustainable Landscaping

In the world of sustainable landscaping, preserving existing trees is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and enhancing aesthetic appeal. A Tree Protection Zone (TPZ) Calculator serves as a vital tool for landscapers and property owners alike, ensuring that trees are adequately safeguarded during development and renovation. Understanding how to effectively utilize this calculator can significantly contribute to environmentally responsible gardening practices. This article will guide you through the steps to maximize the benefits of a TPZ Calculator, discussing its importance, functionality, and the best practices to incorporate into your landscaping projects for a greener future.
Understanding the Tree Protection Zone Calculator
The Tree Protection Zone Calculator is an essential tool designed to help property owners, landscapers, and developers determine the appropriate protective area around trees during construction or landscaping projects. This calculator takes into account factors such as the species, size, and health of the tree to establish a zone that safeguards the tree's root system and overall well-being. By utilizing this tool, users can ensure that they are compliant with regulations and best practices for tree preservation, fostering environmental sustainability and enhancing the aesthetics of their surroundings.
What is a Tree Protection Zone?
A Tree Protection Zone (TPZ) refers to the area surrounding a tree that must be left undisturbed to protect its roots, trunk, and surrounding soil from damage that can occur during construction or landscaping activities. This zone is critical for maintaining the tree’s health and stability, as it allows for proper water and nutrient absorption. When calculated correctly, the TPZ can prevent soil compaction and other harmful activities within this area, thereby improving the longevity of the tree.
How to Calculate the Tree Protection Zone?
Calculating the Tree Protection Zone involves measuring the trunk diameter of the tree at breast height (typically 4.5 feet above ground) and using a formula to determine the radius of the TPZ. A common standard is to multiply the diameter by a factor of 1.5 to 2. For instance, a tree with a trunk diameter of 12 inches may require a TPZ radius of 18 to 24 feet. This calculation can nuance based on the species and health conditions of the tree, ensuring that all factors are adequately considered.
Importance of a Tree Protection Zone Calculator
Using a Tree Protection Zone Calculator is crucial for effective land management and urban planning. It not only aids in preserving existing trees but also helps in evaluating the impact of development activities. By adhering to the guidelines provided by the calculator, stakeholders can minimize environmental degradation and promote biodiversity. Moreover, this adherence often leads to compliance with local regulations and zoning laws, ultimately benefiting both the project and the surrounding community.
Common Regulations Regarding Tree Protection Zones
Many municipalities enforce specific regulations concerning the establishment of Tree Protection Zones. These regulations often delineate the minimum required distance from the tree's trunk, as well as restrictions on activities within the TPZ, such as grading, paving, or storing construction materials. Understanding these regulations is vital for anyone involved in development to avoid penalties and to ensure that trees are preserved for future generations.
Tools and Resources for Using the Tree Protection Zone Calculator
Various tools and resources are available to assist users in effectively using the Tree Protection Zone Calculator. Online calculators can be accessed through forestry and landscaping websites, enabling users to input data about the tree species, size, and health status. In addition, many communities provide resources through their urban forestry programs, offering guidelines and best practices for tree care and protection. Utilizing these tools helps in establishing a solid understanding of how to manage trees in urban settings effectively.
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Tree Species | Affects root depth and spread |
| Diameter at Breast Height | Determines size of protection area |
| Health Status | Impacts resilience to disturbance |
| Soil Type | Influences root growth and stability |
| Environmental Conditions | Affects water and nutrient availability |
How to calculate the tree protection zone?

To calculate the tree protection zone (TPZ), you can follow a systematic approach that ensures the preservation of trees during construction and other land alterations. The TPZ is a crucial area surrounding a tree that must be protected from disturbances such as soil compaction, excavation, and other activities that could harm the tree's health and stability.
Understanding the Importance of Tree Protection Zones
Establishing a TPZ is essential for various reasons:
See also:
- Root System Protection: Tree roots extend far beyond the visible area and can be sensitive to disturbance. A properly calculated TPZ helps protect the root system.
- Soil Health: The quality of the soil in the TPZ is vital for nutrient absorption; protecting this area maintains soil integrity.
- Long-term Tree Viability: Protecting trees during construction increases their chances of survival and health in the long run.
Calculating the Tree Protection Zone Radius
The radius of the TPZ is typically based on the tree's trunk diameter. A common guideline is to use the diameter at breast height (DBH):
- Measure DBH: Measure the tree's trunk diameter at 4.5 feet above the ground.
- Apply a Multiplier: Multiply the DBH by a specific factor, such as 1.5 to 2 feet for each inch of DBH.
- Establish Radius: The result will give you the radius of the TPZ, measured in feet from the base of the tree.
Factors Influencing TPZ Size
Several factors can influence the size of the TPZ, warranting adjustments based on specific circumstances:
- Tree Species: Some species have more extensive root systems and may require larger TPZs for protection.
- Soil Type: Compacted or poor-quality soil necessitates larger TPZs to help trees access necessary nutrients and water.
- Site Conditions: Proximity to buildings and other disturbances may require adjustments to the TPZ to ensure efficient protection.
Implementing Tree Protection Zones
To effectively implement TPZs during construction, follow these steps:
- Mark the Zone: Use fencing or barriers to clearly outline the TPZ around each tree.
- Educate Workers: Inform construction personnel about the significance of the TPZ and measures to avoid damage.
- Monitor Activities: Regularly check construction activities to ensure compliance with TPZ restrictions.
Regulatory Considerations for Tree Protection
When calculating and establishing TPZs, it's important to consider local regulations and guidelines:
- Consult Local Ordinances: Check with local government for specific requirements regarding tree protection.
- Hire Professionals: Engage certified arborists or landscape professionals to ensure proper TPZ calculations.
- Obtain Permits: Certain municipalities require permits for tree removal or alteration, making compliance essential.
How much area around a tree should be protected during a construction event?

To protect a tree during a construction event, it is generally recommended to preserve an area known as the tree protection zone. This zone typically extends to the drip line of the tree – the outer edge of the tree's canopy. In practical terms, this means protecting an area that is approximately 1.5 times the diameter of the trunk at breast height (DBH) in feet. However, this can vary depending on the species of tree, its age, and environmental factors.
Understanding the Importance of Tree Protection Zones
The tree protection zone is critical for the health and stability of the tree. It helps to ensure that the tree receives adequate nutrients, water, and air without disruption. Protecting this area also reduces the risk of root damage, which can be detrimental to the tree’s overall health. Key components to consider include:
- Preservation of soil integrity.
- Minimizing mechanical damage from heavy machinery.
- Ensuring continued access to sunlight and moisture.
Factors Influencing Tree Protection Area Size
Several factors can influence how large the protection area should be, including the species of the tree, its size, and its overall health. Different species have varying root structures and depths, which may necessitate adjustments in the protection area. The following aspects should be evaluated:
- Type of tree and its root system.
- Soil type and composition.
- Age and health of the tree.
Methods of Establishing Tree Protection Zones
Establishing a tree protection zone can be accomplished through various methods that can ensure compliance during construction. It’s essential to visualize and mark this area effectively. Recommended methods include:
- Using fencing or barricades around the protection zone.
- Clearly marking the area with signage indicating No Disturbance.
- Involving an arborist for professional advice and recommendations.
Consequences of Not Protecting the Area
Failing to protect the designated area around a tree can lead to irreversible damages. The consequences can include decline in health, stability issues, and potential tree mortality. Key risks include:
See also:
- Injury or death to the tree from soil compaction.
- Reduced ability to uptake water and nutrients.
- Increased susceptibility to diseases and pests.
Best Practices for Construction Project Managers
To ensure the protection of trees during construction, project managers should adhere to best practices that foster environmental stewardship. Suggested actions include:
- Conducting a pre-construction tree assessment.
- Implementing protective measures before any construction begins.
- Training construction crews on the importance of tree protection.
What is the minimum structural root zone?
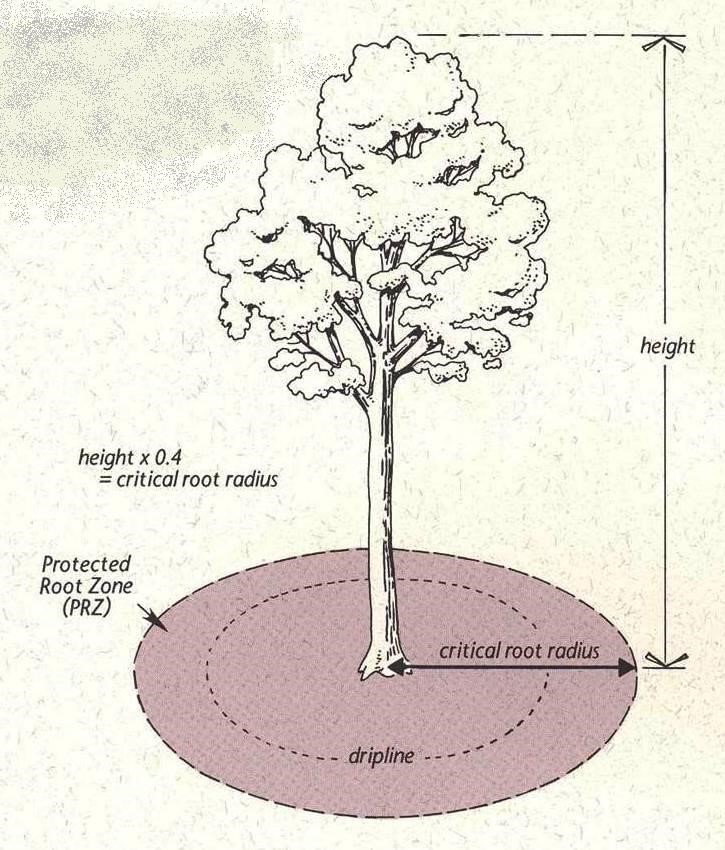
The minimum structural root zone (MSRZ) is a designated area surrounding a tree's stem that provides adequate space for root development and protection from physical disturbances. It is crucial for ensuring the overall health and stability of the tree as well as mitigating risks associated with construction and urban development. The MSRZ must be sufficient to accommodate the tree's root system and enable it to absorb water, nutrients, and oxygen effectively.
Definition of Minimum Structural Root Zone
The minimum structural root zone is defined as the smallest area needed to support the tree's structural roots adequately. This zone typically extends horizontally from the base of the trunk, encompassing the area where the majority of the roots are located. Key aspects include:
- Root Health: Ensures that roots have enough space to grow unimpeded.
- Tree Stability: Enhances the tree's resistance to wind and other forces.
- Soil Conditions: Provides a suitable medium for root growth.
Importance of the Minimum Structural Root Zone
Establishing an adequate MSRZ is vital for many reasons, including nurturing the tree's growth and maintaining ecosystem balance. Key points of importance are:
- Support Systems: Prevents structural failure of urban trees.
- Nutrient Absorption: Maximizes access to soil resources.
- Environmental Impact: Contributes positively to biodiversity in urban areas.
Calculating the Minimum Structural Root Zone
Calculating the MSRZ involves specific formulas based on tree size and species. General guidelines include:
- Diameter Measurement: Measure the tree's diameter at breast height (DBH).
- Zone Radius: Typically, the radius should be at least equal to the DBH in inches, multiplied by a factor (often 3 or more).
- Adjustments for Species: Different species may have different requirements based on root structures.
Factors Affecting the Minimum Structural Root Zone
Several factors affect the necessary size of the MSRZ, including soil type, tree species, and environmental conditions. Important considerations are:
- Soil Composition: Well-draining soils require different root zones than compacted soils.
- Tree Size and Age: Mature trees typically need larger MSRZ than younger trees.
- Environmental Stressors: Urban infrastructure and competing vegetation impact root growth
Best Practices for Managing Minimum Structural Root Zones
Implementing best practices in maintaining the MSRZ can lead to healthier trees and sustainable urban landscapes. Recommended practices are:
- Avoiding Mechanical Damage: Minimizing construction activities near the MSRZ area.
- Regular Monitoring: Observing trees for signs of stress or decline.
- Using Barriers: Installing physical barriers to protect root zones during construction.
Questions from Our Readers
What is a tree protection zone calculator?
A tree protection zone calculator is a tool used to determine the appropriate area around a tree that should be preserved during construction or landscaping activities. This calculator takes into account various factors such as the tree's size, species, and health to ensure that the tree's roots and ecosystem remain undisturbed.
Why is it important to use a tree protection zone calculator?
Using a tree protection zone calculator is crucial for maintaining the health and longevity of trees during development. The calculator helps identify the necessary space that must be kept free of construction activities, which protects the tree's root system from damage and promotes its overall well-being.
See also:
How do I use a tree protection zone calculator?
To use a tree protection zone calculator, you typically need to input specific details about the tree, such as its diameter at breast height (DBH), species, and surrounding conditions. The calculator will then provide you with the recommended protection zone dimensions to ensure the tree's health is safeguarded during any nearby activities.
Are there any regulations regarding tree protection zones?
Yes, many local and state regulations require the establishment of tree protection zones during construction projects to minimize environmental impact. These regulations often outline specific guidelines for the dimensions of the protection zones, as well as any necessary permits or assessments that must be obtained before starting work near protected trees.

If you want to read more articles like How to Effectively Use a Tree Protection Zone Calculator for Sustainable Landscaping, we recommend you check out our Landscaping category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles