Exploring the Unique Ecosystems of Temperate Forests in Australia: A Comprehensive Guide
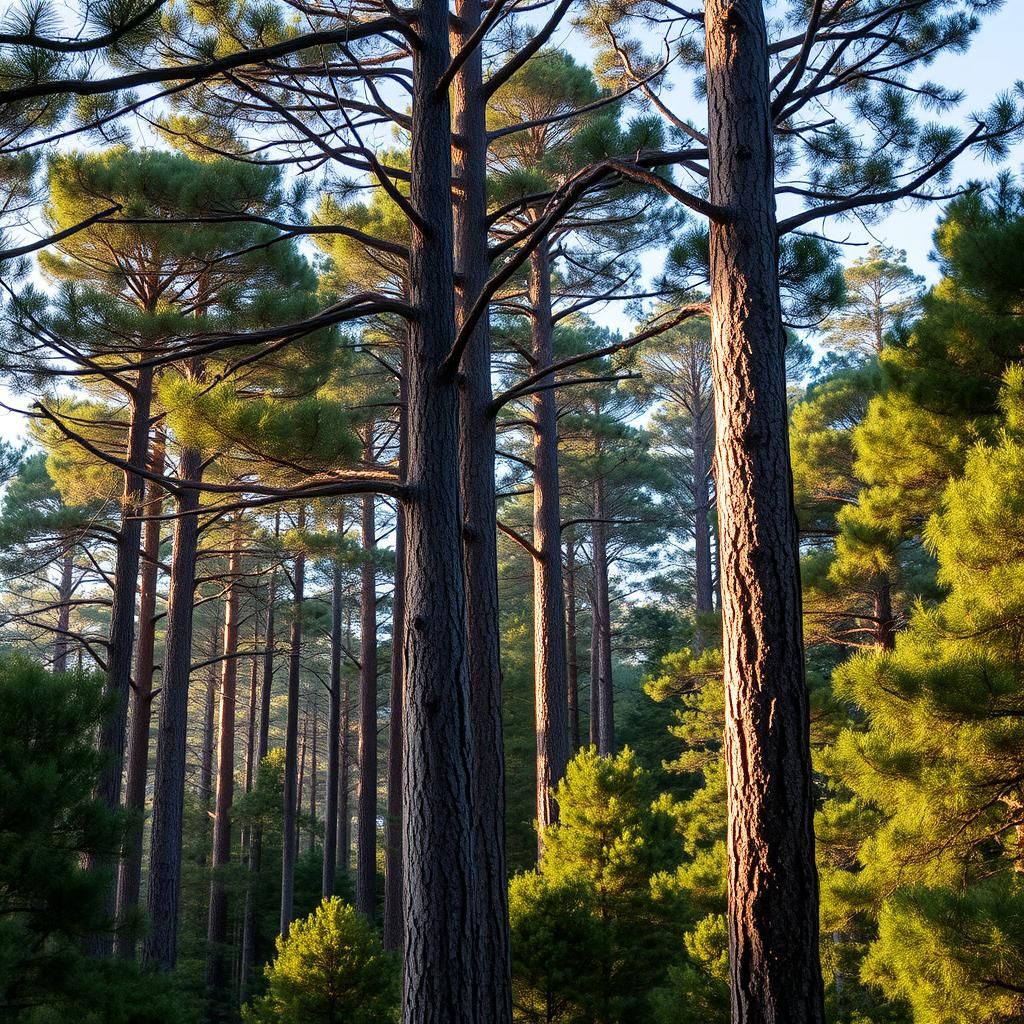

Australia's temperate forests, often overshadowed by their tropical counterparts, boast a rich tapestry of biodiversity and unique ecosystems. These lush regions are home to a variety of flora and fauna, many of which are endemic to the continent. From towering eucalyptus trees to vibrant ferns, the stunning landscapes offer crucial habitat for wildlife and intricate ecological interactions. This comprehensive guide delves into the ecological significance, unique characteristics, and conservation efforts surrounding Australia's temperate forests, highlighting the urgent need to protect these critical environments. Join us as we explore the wonders of these diverse ecosystems and their role in maintaining ecological balance.
Understanding Temperate Forests in Australia
Temperate forests in Australia are unique ecosystems characterized by a moderate climate, which supports a diverse range of flora and fauna. These forests are primarily located in the southeastern region of the country, where the climate is influenced by both oceanic and continental conditions. The dominant tree species in Australian temperate forests include eucalyptus, acacias, and various hardwoods, creating a rich habitat for numerous wildlife species, including marsupials, birds, and reptiles. The undergrowth is often lush and comprises ferns, shrubs, and a variety of ground cover plants. Due to their ecological significance and the threats posed by urban development, climate change, and invasive species, temperate forests are the focus of conservation efforts aimed at preserving their biodiversity and ecological integrity.
Ecological Importance
The ecological importance of Australia’s temperate forests cannot be overstated. These forests play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of local ecosystems and contribute significantly to the world's biodiversity. They serve as vital habitats for many native species, some of which are endemic to Australia. The forests also act as natural air filters, capturing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, thus playing a part in mitigating climate change. Moreover, their complex ecosystems provide essential services, such as soil stabilization and water regulation, supporting both environmental health and agricultural practices in adjacent areas.
Flora and Fauna
The flora and fauna of temperate forests in Australia are incredibly diverse and unique. Dominated by eucalyptus species, these forests also feature a variety of other plant species, including ferns, wildflowers, and a range of shrubs. In terms of fauna, the forests are home to distinctive species such as the koala, sugar glider, and various types of birds, including the lyrebird. This combination of plant and animal life exemplifies the ecological richness of these forests, which are adapted to the temperate climate and support various life forms.
Threats to Temperate Forests
Despite their significance, temperate forests in Australia face various threats that jeopardize their health and sustainability. Deforestation, driven by urban expansion, agriculture, and logging, has led to habitat loss and fragmentation. Additionally, climate change poses a significant risk, as alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of these ecosystems. The introduction of invasive species further exacerbates the problem, competing with native species for resources and disrupting established ecological relationships.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting Australia’s temperate forests involve a combination of legislative measures and community initiatives. Various non-profit organizations and governmental bodies work collaboratively to raise awareness and implement conservation strategies. Protected areas, such as national parks and nature reserves, have been established to safeguard these environments and restore degraded landscapes. Additionally, programs focused on reforestation and sustainable land-use practices are integral to ensuring these forests remain vibrant and diverse for future generations.
Tourism and Education
Tourism and education play vital roles in the appreciation and preservation of temperate forests in Australia. Eco-tourism initiatives encourage visitors to explore these unique ecosystems responsibly, fostering a deeper understanding of their ecological significance. Educational programs in schools and community centers aim to promote awareness about the importance of conservation and sustainable practices among the younger generation. By combining the allure of nature with educational outreach, stakeholders hope to inspire a culture of conservation and respect for Australia’s temperate forests.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Southeastern Australia |
| Dominant Tree Species | Eucalyptus, Acacia |
| Threats | Deforestation, Climate Change, Invasive Species |
| Conservation Methods | Protected Areas, Reforestation |
| Key Wildlife | Koalas, Sugar Gliders, Lyrebirds |
Where is the most temperate place in Australia?
The most temperate place in Australia is widely considered to be Hobart, the capital city of the island state of Tasmania. Its climate is characterized by mild temperatures, moderate rainfall, and distinct seasons, making it less extreme than many other parts of Australia. Hobart experiences an oceanic climate, with cool summers and mild winters, which contributes to its reputation as the most temperate region in the country.
Climate Characteristics of Hobart
Hobart's climate is defined by its moderate temperatures, influenced by its coastal location. This results in a relatively stable climate compared to other Australian cities.
- Mild Summers: The average summer temperature ranges from 16°C to 24°C (61°F to 75°F), ideal for outdoor activities.
- Cool Winters: Winter temperatures rarely drop below 3°C (37°F), providing a mild winter experience.
- Regular Rainfall: Hobart receives about 620 mm (24 inches) of rain annually, allowing lush vegetation to thrive.
Comparison with Other Australian Cities
When comparing Hobart to other major cities like Sydney and Melbourne, the difference in climate becomes evident. Hobart's weather is more temperate due to its geographical setting.
- Sydney: Experiences hotter summers and higher humidity, leading to more extreme weather.
- Melbourne: Known for its unpredictable weather, often swings between various climatic conditions.
- Perth: Features warmer temperatures and less rainfall, resulting in a much drier climate.
Flora and Fauna in Hobart
The temperate climate of Hobart supports a diverse range of flora and fauna, making it a unique ecological region within Australia.
- Eucalyptus Trees: Predominantly found in the area, adapted to the mild climate.
- Unique Wildlife: Home to species like the Tasmanian Devil, which thrives in the cooler climate.
- Lush Gardens: Botanical gardens in Hobart display a variety of plant species benefitting from temperate conditions.
Impact on Lifestyle and Recreation
The temperate climate in Hobart significantly influences the lifestyle and recreational activities available to residents and visitors.
See also:
- Outdoor Activities: Hiking, cycling, and exploration of national parks are popular due to the favorable weather.
- Festivals and Events: The mild climate allows for year-round festivities and outdoor markets.
- Wine Tours: The region's vineyards benefit from the temperate conditions, attracting wine enthusiasts.
Tourism and Attractions in Hobart
Hobart’s temperate climate enhances its appeal as a tourist destination with a range of attractions suitable for various interests.
- MONA (Museum of Old and New Art): A unique cultural experience, attracting visitors with both indoor and outdoor exhibits.
- Salamanca Market: A vibrant market held every Saturday, showcasing local produce and crafts in a pleasant atmosphere.
- Historic Sites: The city features numerous heritage sites that can be easily explored in mild weather.
What type of forests are in Australia?
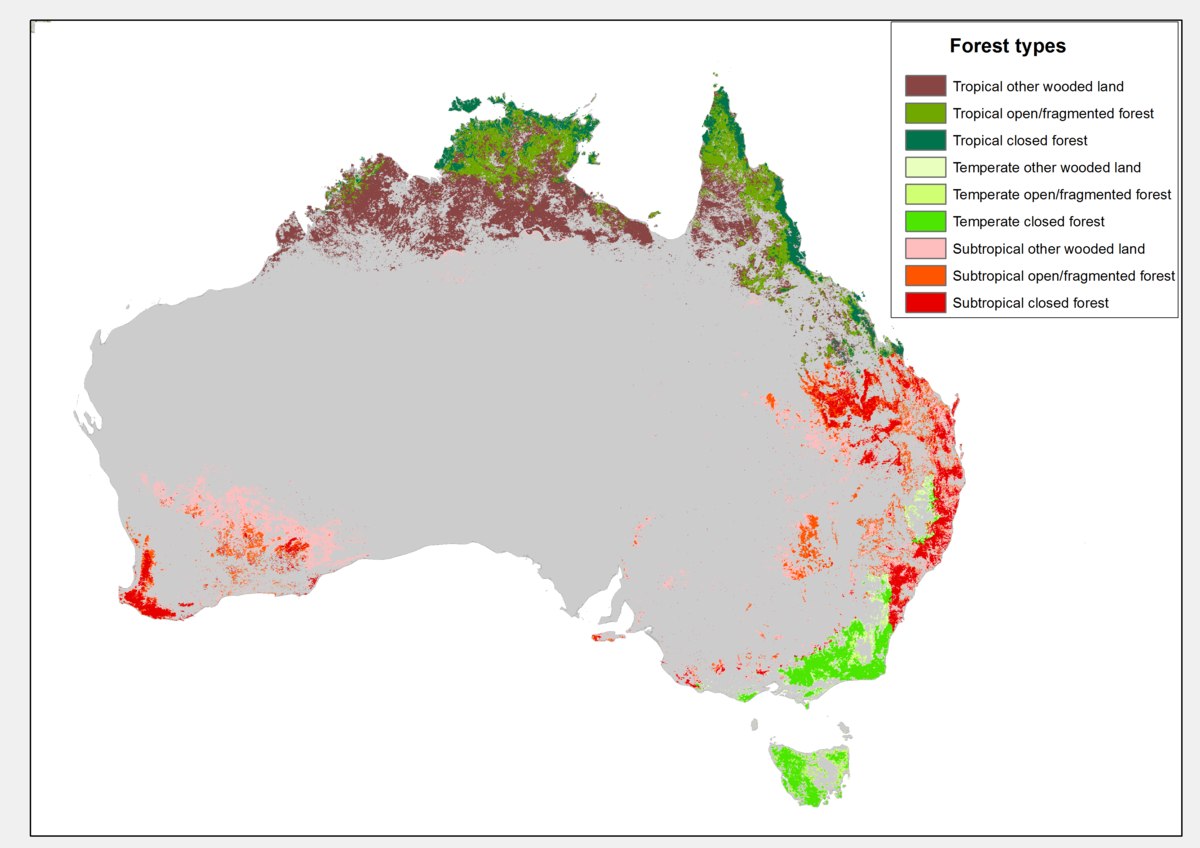
Australia boasts a diverse range of forests, each with its unique characteristics and ecological significance. The main types of forests present in Australia include temperate rainforests, tropical rainforests, eucalyptus forests, mangrove forests, and paperbark forests. Each of these forest types supports a variety of flora and fauna, contributing to Australia's rich biodiversity.
Temperate Rainforests
Temperate rainforests are found primarily along the southeastern coast of Australia. These forests experience high annual rainfall and are characterized by dense canopies, towering trees, and a rich understorey of ferns and mosses. Some key features include:
- High Biodiversity: These forests are home to numerous plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region.
- Climate: The climate is generally mild with abundant rainfall throughout the year, supporting lush vegetation.
- Tree Species: Common tree species include the Southern Blue Gum and the Mountain Ash, known for their impressive height.
Tropical Rainforests
Tropical rainforests in Australia are primarily located in the northern regions, particularly in Queensland. These forests thrive in warm, humid conditions and are known for their layered structure and incredible biodiversity. Notable aspects include:
- Lush Foliage: The dense foliage provides habitat for a multitude of bird, mammal, and reptile species.
- Climate Conditions: These rainforests have a tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons, leading to rich biological interactions.
- Flora Diversity: Significant tree species include the Hoop Pine and various types of hardwood trees, contributing to the rich ecosystem.
Eucalyptus Forests
Eucalyptus forests are the most dominant forest type in Australia, covering vast areas across the continent. They are characterized by the presence of eucalyptus trees, which are well adapted to the Australian climate. Key characteristics include:
- Fire Adaptation: Many eucalyptus species have adapted to withstand fire, which is a common occurrence in these forests.
- Wildlife Habitat: Eucalyptus forests provide essential habitats for iconic Australian wildlife, such as koalas and various marsupials.
- Variety of Species: The eucalyptus genus contains over 700 species, showcasing significant diversity within these forests.
Mangrove Forests
Mangrove forests are located along Australia's coastlines, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. They thrive in saline coastal water and play a critical role in coastal ecology. Important features include:
- Ecological Importance: Mangroves provide vital habitats for fish and various marine species while protecting coastlines from erosion.
- Adaptations: Mangrove trees have specialized adaptations that allow them to tolerate saltwater and fluctuating tides.
- Carbon Sequestration: These forests are significant for carbon storage, helping to mitigate climate change impacts.
Paperbark Forests
Paperbark forests are characterized by the presence of Melaleuca species with distinctive papery bark. These forests are typically found in areas with seasonal flooding and have unique ecological roles. Key points include:
- Flood Tolerance: Paperbark trees are adapted to grow in poorly draining soils and areas that are inundated.
- Habitat Creation: These forests provide important habitats for birds, insects, and other wildlife, enhancing local biodiversity.
- Ecosystem Services: They play a crucial role in water filtration and contributing to the health of surrounding water systems.
What is a temperate climate in Australia?
A temperate climate in Australia refers to regions with moderate temperatures, typically characterized by distinct seasons and an overall mild atmosphere. This climate type is primarily found in the southeastern parts of Australia, including areas like parts of New South Wales, Victoria, and South Australia. The temperate climate is defined by its seasonal changes; summers are warm to hot while winters are generally cool to cold.
Characteristics of Temperate Climate
The temperate climate in Australia is marked by specific characteristics that differentiate it from other climate types. These include:
- Seasonality: The regions experience four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
- Precipitation: Rainfall is fairly even throughout the year but can peak in certain seasons depending on the area.
- Temperature Range: Average temperatures can range from mild in winter to quite hot in summer, offering a diverse climate experience.
Geographic Distribution
The distribution of the temperate climate in Australia spans several key areas, influencing both the ecology and the lifestyle of the inhabitants:
- Southeastern Australia: This area includes cities like Sydney and Melbourne, which are prime examples of a temperate climate.
- Coastal Regions: Proximity to the ocean moderates temperatures, making coastal sites more temperate than inland areas.
- Altitude Influence: Areas at higher elevations, like the Snowy Mountains, also display a temperate climate but with cooler temperatures.
Flora and Fauna
The temperate climate of Australia supports a diverse range of flora and fauna, which are adapted to the seasonal changes:
See also:
- Vegetation: Deciduous trees such as oaks and maples thrive in the cooler seasons, providing stunning autumn displays.
- Wildlife Diversity: Animals, including kangaroos and various bird species, have adapted to the seasonal variations, with some exhibiting migratory behaviors.
- Conservation Areas: Many natural reserves exist to protect the unique ecosystems found within these temperate zones.
Cultural and Economic Impacts
The temperate climate significantly influences cultural practices and economic activities in Australia:
- Agriculture: The temperate climate is conducive to diverse farming activities, including vineyards and orchards.
- Seasonal Festivals: Many regions celebrate cultural events that align with the changing seasons, such as harvest festivals.
- Tourism Opportunities: The mild weather attracts tourists year-round, enhancing local economies.
Climate Change Effects
Climate change is increasingly impacting the temperate regions of Australia, leading to various challenges:
- Altered Weather Patterns: Unpredictable rainfall and temperature extremes can disrupt traditional agriculture.
- Increased Extreme Weather: Rising temperatures can lead to more frequent heatwaves and severe weather events.
- Biodiversity Threats: Changes in climate can threaten native species and lead to ecosystem imbalances.
What is the largest temperate rainforest in Australia?
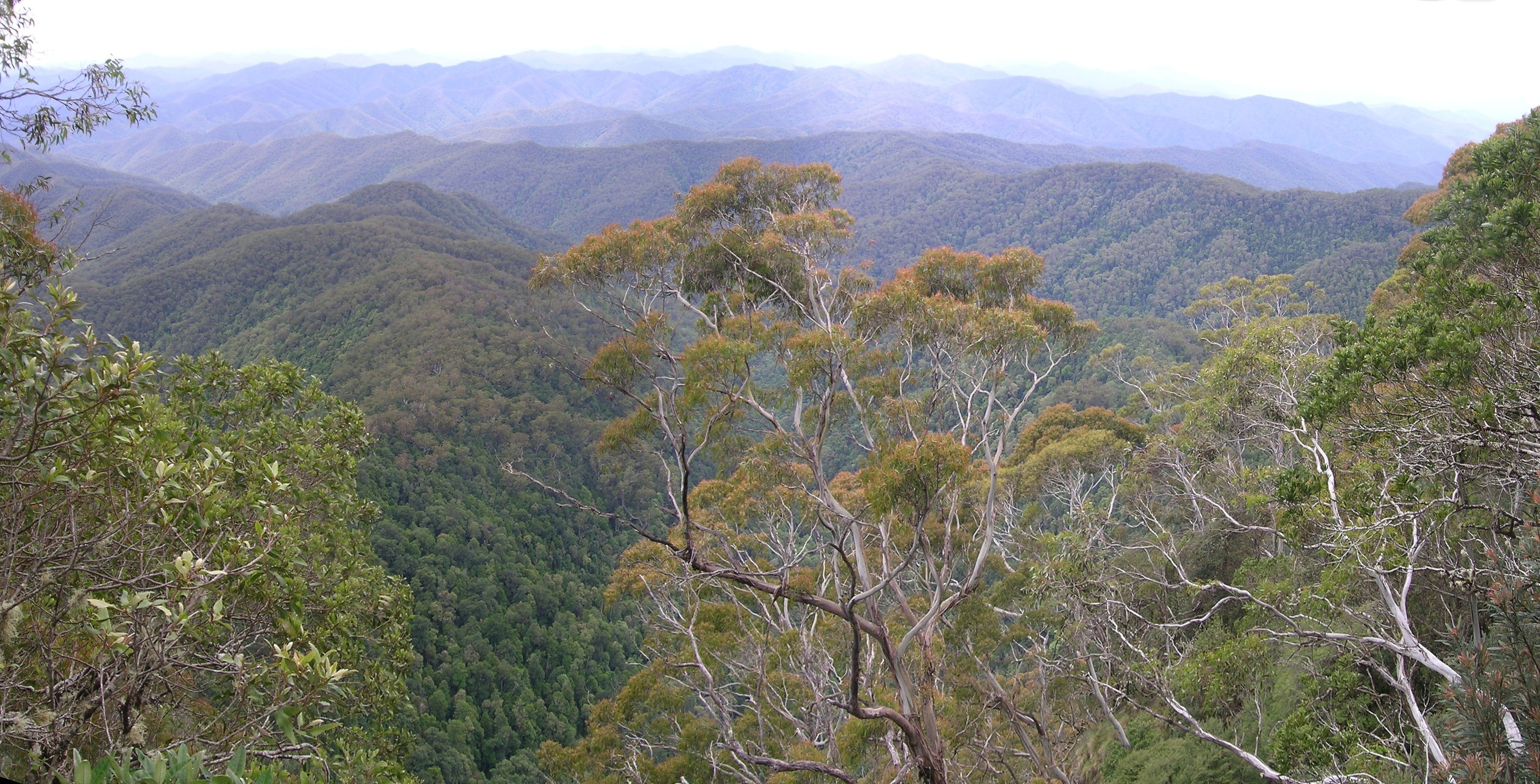

The largest temperate rainforest in Australia is the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area, located in the state of Tasmania. This region encompasses an area of over 1.5 million hectares and is recognized for its exceptional biodiversity and unique ecosystems that include towering trees, lush ferns, and a variety of animal species. The temperate rainforest here is characterized by a mild climate, high rainfall, and a rich tapestry of plant life, making it one of the most significant natural ecosystems in Australia.
The Biodiversity of Tasmania's Temperate Rainforest
The temperate rainforest of Tasmania is home to an incredible variety of flora and fauna. This biodiversity is crucial for the ecosystem's health and maintenance.
- The forests consist of ancient tree species like Myrtle Beech and Giant Mountain Ash, some of which are over 80 meters tall.
- Numerous wildlife species, including the endemic Tasmanian devil and the Eastern barred bandicoot, thrive in this environment.
- The rainforest is also a habitat for many bird species, such as the forty-spotted pardalote, which is endangered and highly dependent on this ecosystem.
Climate and Weather Conditions
The climate of Tasmania's temperate rainforest is characterized by consistent rainfall and mild temperatures, creating an ideal environment for the growth of diverse plant and animal life.
- Average rainfall can exceed 2000mm per year, making it one of the wettest regions in Australia.
- The temperature typically ranges between 8°C and 20°C, allowing for a stable and conducive environment for the rainforest's unique species.
- This consistent climate supports year-round vegetation growth and contributes to the lush appearance of the forest.
Conservation Efforts in Tasmania
Given its ecological significance, numerous conservation efforts are in place to protect the temperate rainforest of Tasmania.
- The area was designated as a World Heritage Site in 1982, emphasizing the global importance of its conservation.
- Conservation programs work to prevent threats such as logging and land development while promoting sustainable tourism practices.
- Many local organizations engage in restoration projects, aiming to rehabilitate degraded areas of the rainforest.
The Role of Indigenous Culture
Indigenous peoples have a profound connection to Tasmania's temperate rainforest, and their traditional ecological knowledge is valuable for conservation.
- Aboriginal communities have lived sustainably in this region for thousands of years, using natural resources respectfully.
- Understanding traditional practices can help inform conservation strategies that align with both ecological health and cultural heritage.
- Community-led initiatives often involve collaboration between Indigenous groups and conservation organizations to preserve both the biodiversity and cultural significance of the rainforest.
Tourism and Research in Tasmania's Rainforest
Tourism and scientific research in Tasmania's temperate rainforest contribute to its economic value and ongoing conservation efforts.
- Visitors can explore the region through numerous walking trails, providing an opportunity to experience its beauty while promoting awareness about its ecological importance.
- Research conducted in this unique environment has led to discoveries related to climate change, biodiversity, and ecosystem services.
- Engaging tourists in educational programs helps foster a sense of stewardship, encouraging responsible interactions with the environment.
Questions from Our Readers
What are temperate forests in Australia?
Temperate forests in Australia are characterized by their moderate temperatures and distinct seasons. These forests typically feature a diverse range of flora, including deciduous trees and evergreens, and are primarily found along the eastern coast of the country, extending into parts of Tasmania and Victoria.
What types of trees are commonly found in Australia's temperate forests?
Australia's temperate forests are home to various species of trees, including eucalypts, acacias, and beech trees. These trees are adapted to the region's climate and contribute significantly to the biodiversity of the forest ecosystems.
How do temperate forests in Australia differ from tropical forests?
Temperate forests in Australia differ from tropical forests primarily in their climate, with temperate regions experiencing cooler temperatures and more pronounced seasonal changes. While tropical forests are characterized by high humidity and a lack of distinct seasons, temperate forests have more defined growing seasons and often experience deciduous leaf fall in winter.
What is the ecological importance of temperate forests in Australia?
The ecological importance of temperate forests in Australia lies in their role as habitats for numerous species of wildlife, including birds, mammals, and insects. These forests also play a crucial role in carbon storage, help regulate the water cycle, and contribute to soil health, making them vital for maintaining ecological balance.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like Exploring the Unique Ecosystems of Temperate Forests in Australia: A Comprehensive Guide, we recommend you check out our Landscaping category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles