Discover the Beauty and Benefits of Northern Territory Native Trees: A Comprehensive Guide
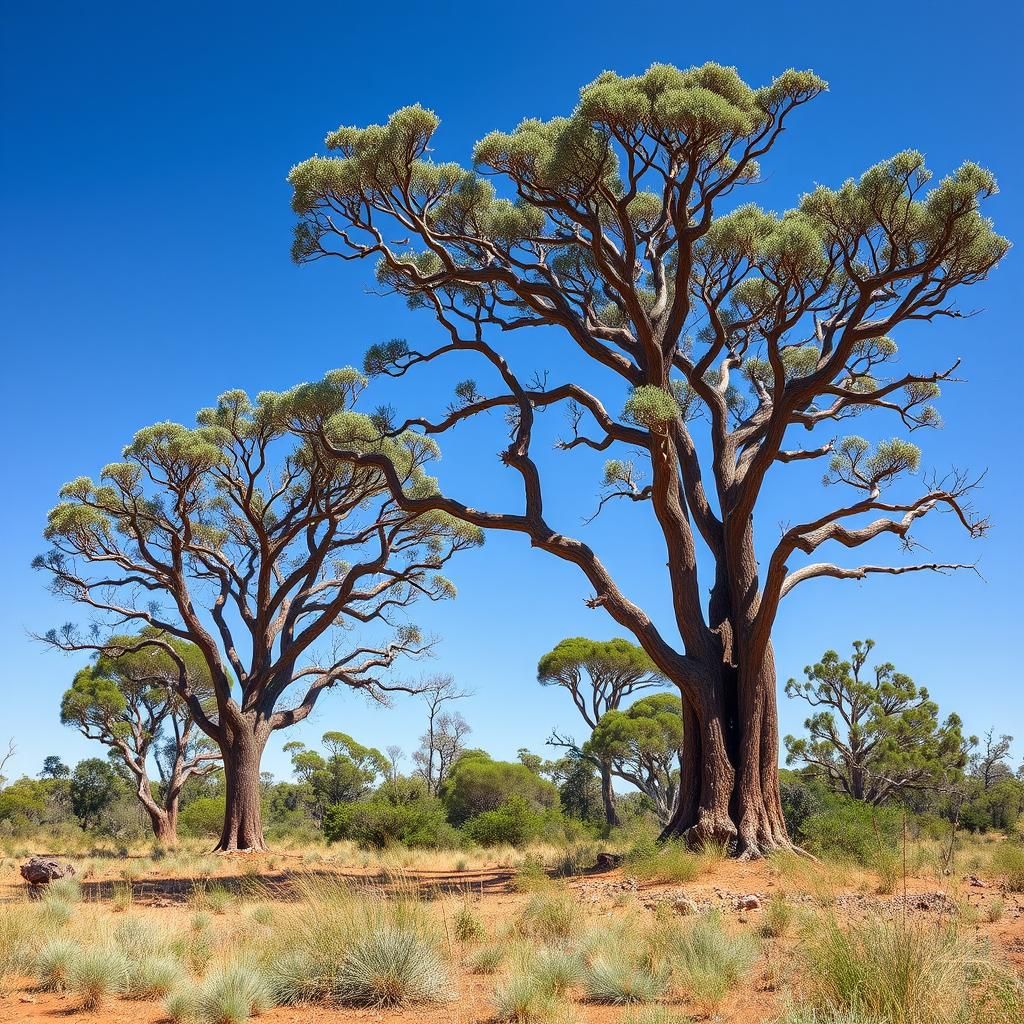

The Northern Territory of Australia is home to a remarkable array of native trees that are not only beautiful but also essential to the region's ecosystem. This comprehensive guide explores the unique characteristics, benefits, and significance of these indigenous species. From towering stringybarks to the resilient Darwin woollybutt, each tree plays a vital role in supporting local wildlife and providing invaluable resources for the environment. Whether you are a nature enthusiast, a gardener, or simply curious about the flora of this stunning region, this guide will uncover the hidden treasures of Northern Territory's native trees and inspire appreciation for their significance in our world.
- Northern Territory Native Trees: An Ecological Treasure
- What is the most common native tree in Australia?
- What is the national plant of the Northern Territory?
- What plants grow in the Northern Territory of Australia?
- What is the eucalyptus tree in the Northern Territory?
- Questions from Our Readers
- What are some common native trees found in the Northern Territory?
- How do native trees contribute to the local environment in the Northern Territory?
- Are there any endangered native tree species in the Northern Territory?
- What is the importance of planting native trees in urban areas of the Northern Territory?
Northern Territory Native Trees: An Ecological Treasure
The Northern Territory (NT) of Australia is renowned for its unique ecosystem, characterized by a diverse range of native trees that play an essential role in maintaining ecological balance. The flora of this region is adapted to withstand the harsh conditions of both the tropical and arid climates found here. Indigenous trees like the Eucalyptus, Acacia, and Corymbia not only provide habitat for various wildlife but also contribute to soil health and water conservation. The preservation of these native species is crucial for the sustainability of the environment, as they offer numerous benefits including carbon sequestration and support for native animals, making them invaluable to the Northern Territory’s biodiversity.
Diversity of Native Tree Species
The Northern Territory boasts a remarkable diversity of native tree species, numbering over 70 distinct types that thrive in various habitats throughout the region. This diversity arises from the varying climates and soil types within the NT, allowing for a multitude of adaptations. Common species include the iconic Darwin woollybutt and bloodwood, which are well-suited to the tropical climate of the Top End, while other species are found in the desert zones of the central desert region. This variety not only enriches the landscape but also ensures resilience against environmental changes, making the NT a biological hotspot.
Ecological Importance
The ecological importance of native trees in the Northern Territory cannot be overstated. These trees serve as critical components of the region's ecosystem, supporting biodiversity and providing habitats for countless species of birds, mammals, and insects. They play a vital role in the food chain, offering fruits, seeds, and leaves that are essential for animal sustenance. Moreover, native trees contribute to soil stabilization, preventing erosion and promoting healthier ecosystems that support diverse plant life. Their canopy cover also regulates microclimates, assisting in moisture retention in the landscape.
Cultural Significance
For the Indigenous peoples of the Northern Territory, native trees hold significant cultural and spiritual importance. Many tree species are intertwined with their traditions, being used for traditional medicines, crafting materials, and ceremonial practices. For instance, the bark of the Paperbark tree is often utilized for creating canoes and shelters, while other species have been traditionally valued for their nutritional or medicinal properties. The cultural connection that Indigenous communities have with these trees reinforces the importance of conserving them for future generations, as they are a living part of their history and identity.
Threats to Native Trees
Despite their importance, native trees in the Northern Territory face numerous threats that jeopardize their survival. Urbanization, land clearing for agriculture, and the impacts of climate change pose significant risks to these ecosystems. Invasive species also threaten native flora, as they can outcompete indigenous trees for resources. Additionally, changing rainfall patterns and increasing temperatures may hinder the growth of native trees, further exacerbating their decline. Awareness and proactive conservation efforts are essential to mitigate these threats and preserve the valuable native ecosystems of the Northern Territory.
Conservation Efforts
In recognition of the importance of native trees in the Northern Territory, several conservation initiatives are underway aimed at protecting and restoring these vital ecosystems. Organizations such as the National Parks and Wildlife Commission work alongside Indigenous landowners to implement sustainable land management practices that foster the health of native tree populations. Community involvement is also crucial, with programs focusing on reforestation, seed collection, and public education to encourage local stewardship of the environment. These efforts aim not only to conserve existing native trees but also to restore habitats that support biodiversity, ensuring a balanced ecological future for the Northern Territory.
| Native Tree Species | Common Uses | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Eucalyptus | Timber production, medicinal uses | Woodlands, floodplains |
| Acacia | Food source, crafting materials | Open forests, shrublands |
| Corymbia | Construction, firewood | Eucalypt woodlands, savannas |
| Terminalia | Traditional medicine, food | Riparian zones |
| Ficus | Shade, habitat for birds | Woodlands, tropical forests |
What is the most common native tree in Australia?

The most common native tree in Australia is the Eucalyptus, a genus comprising over 700 species. These trees are renowned for their adaptability to a wide range of environments, making them a dominant feature in many Australian landscapes. Eucalyptus trees, also known as gum trees, are typically characterized by their tall stature, distinctive bark, and aromatic leaves that contain oils utilized in various medicinal and industrial applications.
Characteristics of Eucalyptus Trees
Eucalyptus trees have several distinctive characteristics that make them unique among native flora. Some key traits include:
- Leaf Structure: Eucalyptus leaves are long and narrow, often displaying a glossy texture, which helps to reduce moisture loss.
- Bark Variation: The bark can vary from smooth to rugged, and many species shed their bark in strips, contributing to their striking appearance.
- Growth Habit: These trees can grow up to 60 meters tall, depending on the species, making them among the tallest trees in the world.
Habitat and Distribution
Eucalyptus trees thrive in diverse habitats across Australia, from coastal regions to the interior outback. The distribution is influenced by factors such as:
- Climate Variability: Many Eucalyptus species are well adapted to the Australian climate, which can vary significantly in temperature and rainfall.
- Soil Types: These trees can grow in different soil types, although they prefer well-drained sandy or loamy soils.
- Fire Resilience: Many Eucalyptus species are highly fire-resistant, with adaptations that allow them to survive and regenerate after bushfires.
Ecological Importance
Eucalyptus trees play a crucial role in Australian ecosystems. Their ecological contributions include:
- Habitat Provision: They provide essential habitats for a wide range of wildlife, including koalas, which primarily feed on eucalyptus leaves.
- Carbon Sequestration: These trees are significant for carbon storage, helping combat climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Soil Health: Eucalyptus leaves contribute to the nutrient cycle, enhancing soil quality as they decompose.
Cultural Significance
The Eucalyptus tree holds significant cultural relevance in Australia, impacting both Indigenous and contemporary Australian society. Its significance can be observed through:
See also:
- Indigenous Uses: Indigenous Australians have traditionally used Eucalyptus leaves for medicinal purposes, as well as for ceremonies and rituals.
- Art and Symbolism: The tree is often featured in Australian art and literature, symbolizing the unique landscape and identity of the country.
- Economic Value: Eucalyptus wood is harvested for its high-quality timber and is also used in the production of essential oils.
Popular Eucalyptus Species
There are several notable species of Eucalyptus that are particularly well-known, including:
- Eucalyptus globulus: Commonly known as the Tasmanian Blue Gum, this species is one of the most commercially valuable.
- Eucalyptus grandis: Known as the Rose Gum, it is prized for its timber and is commonly used in construction.
- Eucalyptus camaldulensis: The River Red Gum is a vital habitat for many species and is often found near waterways.
What is the national plant of the Northern Territory?
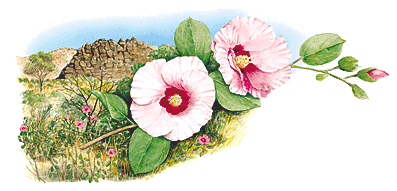
The national plant of the Northern Territory, Australia, is the Sturt's Desert Pea (Swainsona formosa). This plant is renowned for its striking appearance, characterized by its bright, red flowers that often have a dark blotch in the center. It holds symbolic significance for the Indigenous peoples of the region and is often associated with the rugged landscapes of central Australia. Being well-adapted to arid climates, Sturt's Desert Pea thrives in poor soils, making it an iconic representation of the Northern Territory's unique environment.
Physical Characteristics
The Sturt's Desert Pea can grow to a height of up to 1 meter and features a unique structure:
- Flowers: The flowers bloom primarily in shades of red and yellow, attracting various pollinators.
- Foliage: It has finely divided, almost feathery leaves that are grey-green in color.
- Seeds: The plant produces large, black seeds, which are an important food source for some wildlife species.
Habitat and Distribution
This species is typically found in the arid regions of Australia, particularly in:
- Sandy Soils: Sturt's Desert Pea thrives in sandy and well-drained soils.
- Open Woodlands: It often grows in open woodlands and along roadsides, where it can receive ample sunlight.
- Geographical Range: While primarily a staple of the Northern Territory, it can also be found in parts of Western Australia and South Australia.
Cultural Significance
The Sturt's Desert Pea holds considerable cultural importance, especially among Indigenous Australians:
- Traditional Uses: It has been used for various purposes, including medicinal applications and as an inspirational motif in art.
- Symbolism: The plant symbolizes resilience and beauty in harsh conditions, reflecting the spirit of the land.
- Art and Ceremonies: Its depiction often appears in Indigenous art and ceremonial practices, showcasing its deep-rooted ties to culture.
Ecological Role
In its native habitat, the Sturt's Desert Pea plays an essential role in the ecosystem:
- Soil Improvement: As a legume, it contributes to nitrogen fixation, improving soil quality.
- Habitat for Wildlife: The plant provides shelter and a food source for various animals, including insects and birds.
- Attraction of Pollinators: Its vibrant flowers attract bees and other pollinators that are vital for ecosystem health.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of the Sturt's Desert Pea is generally stable, but it faces threats like:
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization and agriculture can lead to the destruction of natural habitats.
- Climate Change: Increased temperatures and drought can affect its growth and reproduction.
- Invasive Species: Competition with non-native plants can threaten its survival in certain areas.
What plants grow in the Northern Territory of Australia?

The Northern Territory of Australia is home to a diverse range of plants that thrive in its unique ecosystems. The climate varies from tropical in the north to arid in the south, allowing for a wide variety of flora. Here, we can explore some of the key plant species found in this region, breaking down the various types of vegetation that contribute to its rich biodiversity.
Native Trees
Native trees play a crucial role in the ecosystem of the Northern Territory. They provide shelter and food for various wildlife species while contributing to the overall health of the environment.
- Eucalyptus: These trees are prevalent throughout the Northern Territory, with various species adapted to both tropical and arid conditions.
- Acacia: Known for their hardiness, Acacia species are commonly found in a range of habitats, providing important resources for local fauna.
- Pandanus: Often found near water sources, these trees have a distinctive appearance with spiky leaves and are significant in traditional indigenous culture.
Tropical Grasses
The vast savanna ecosystems are primarily dominated by tropical grasses, which provide essential nutrients and habitat for numerous animal species.
- Mitchell Grass: Renowned for its ability to survive in arid conditions, it forms the basis of many grasslands across the region.
- Bufallo Grass: This hardy grass thrives in both wet and dry seasons, making it a staple in many grazing areas.
- Green Panic Grass: An important pasture grass improving soil quality and providing forage for livestock and wildlife alike.
Medicinal Plants
The flora of the Northern Territory is rich in native plants known for their medicinal properties, often used by indigenous communities for healing.
See also:
- Kakadu Plum: Known for its high vitamin C content and antioxidant properties, it's often utilized in herbal medicine.
- Tea Tree: The oil extracted from its leaves is well-known for its antibacterial properties and is widely used in various health and cosmetic products.
- Billy Goat Plum: This plant is often used in traditional medicine to treat various ailments and is valued for its nutrient richness.
Flowering Plants
The Northern Territory is also home to a variety of striking flowering plants that contribute aesthetically and ecologically to the landscape.
- Desert Rose: A beautiful flowering shrub that can thrive in arid conditions, providing color and habitat within the ecosystem.
- Grevillea: These flowering plants attract birds and insects, playing a vital role in local biodiversity.
- Wildflower species: The region’s unique climate fosters numerous wildflower species, which bloom spectacularly during the wet season.
Rare and Endangered Plants
Certain plant species in the Northern Territory face threats due to habitat loss and climate change, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts.
- Arnhem Land's Dwarf Palm: This endangered species is threatened by habitat degradation and requires protection to survive.
- Two-leaved Wattle: Rare in occurrence and confined to specific locations, this plant is at risk due to ecological changes.
- Ghost Gum: Although not endangered, it faces pressures from urban sprawl and must be monitored to maintain its population.
What is the eucalyptus tree in the Northern Territory?

The eucalyptus tree, particularly in the Northern Territory of Australia, is a significant component of the region's ecosystem and cultural heritage. These trees belong to the genus Eucalyptus, which includes over 700 species. Known for their adaptability and resilience, eucalyptus trees are well-suited to the diverse conditions found in the Northern Territory, ranging from arid landscapes to tropical forests.
Eucalyptus trees are characterized by their aromatic leaves, which contain oils that can be used for medicinal purposes, as well as their distinctive bark, which can be smooth or rough depending on the species. They play a crucial role in local wildlife habitats, providing food and shelter for various animals, including koalas and many bird species.
Ecological Importance of Eucalyptus Trees
Eucalyptus trees are central to the ecosystem in the Northern Territory. They provide vital resources and support biodiversity.
- Habitat: Eucalyptus forests serve as a habitat for numerous animal species.
- Food Source: The leaves are a primary food source for koalas and other herbivores.
- Soil Protection: The trees help prevent soil erosion through their extensive root systems.
Economic Value of Eucalyptus
The economic implications of eucalyptus trees in the Northern Territory are substantial, impacting various industries.
- Lumber Production: Eucalyptus wood is valued for its durability and is widely used in construction.
- Essential Oils: The unique oils extracted from eucalyptus leaves are used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Tourism: Eucalyptus forests attract tourists, enhancing local economies through eco-tourism.
Cultural Significance
Eucalyptus trees hold a deep cultural significance for Indigenous Australians, embodying their connection to the land.
- Traditional Uses: Indigenous peoples use eucalyptus products for medicine and tools.
- Spiritual Symbolism: The trees are often featured in cultural stories and ceremonies.
- Land Management: Traditional land management practices incorporate eucalyptus to promote ecological balance.
Challenges Facing Eucalyptus in the Northern Territory
Despite their resilience, eucalyptus trees face several challenges that threaten their existence.
- Climate Change: Changing climate patterns affect growth and survival rates.
- Pests and Diseases: Eucalyptus trees are susceptible to various pests, which can lead to declines in health.
- Land Clearing: Urban development and agriculture reduce the area of eucalyptus habitats.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation initiatives are crucial for preserving eucalyptus ecosystems in the Northern Territory.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks helps safeguard critical eucalyptus habitats.
- Restoration Projects: Efforts to restore degraded lands include planting eucalyptus seedlings.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation fosters stewardship of eucalyptus forest health.
Questions from Our Readers
What are some common native trees found in the Northern Territory?
Some common native trees in the Northern Territory include Eucalyptus, Melaleuca, and Acacia species. These trees are well adapted to the region's diverse climates and soil types, providing important habitats for local wildlife and playing a crucial role in the ecosystem.
How do native trees contribute to the local environment in the Northern Territory?
Native trees contribute to the local environment by enhancing biodiversity, improving soil quality, and preventing erosion. They provide essential habitats for various animal species, regulate local climates, and assist in carbon sequestration, making them vital for a balanced ecosystem.
Are there any endangered native tree species in the Northern Territory?
Yes, several native tree species in the Northern Territory are considered endangered, primarily due to habitat loss, invasive species, and climate change. Conservation efforts are in place to protect these species and their habitats to ensure their survival for future generations.
See also:
What is the importance of planting native trees in urban areas of the Northern Territory?
Planting native trees in urban areas is important as they help to improve air quality, reduce urban heat, and provide green spaces for residents' well-being. Additionally, native trees attract local wildlife and contribute to maintaining the area's natural heritage, thereby supporting environmental sustainability.

If you want to read more articles like Discover the Beauty and Benefits of Northern Territory Native Trees: A Comprehensive Guide, we recommend you check out our Landscaping category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles