How Long Does It Take a Plant to Recover from Pruning? Expert Tips for Faster Recovery

Pruning is an essential gardening practice that promotes healthy growth, enhances the plant's shape, and even allows for better fruit production. However, one common concern among gardeners is the recovery time for plants after pruning. Understanding the factors that influence recovery duration can help ensure your plants bounce back quickly and thrive. In this article, we will explore the average time it takes for various types of plants to recover from pruning, along with expert tips to accelerate their healing process. Armed with this knowledge, you can effectively care for your garden and promote robust, vibrant growth.
How Long Does It Take a Plant to Recover from Pruning?
When a plant is pruned, the recovery time can vary significantly depending on factors such as the type of plant, the extent of pruning, and the environmental conditions. On average, many plants will begin to show signs of recovery within two to four weeks after pruning, but complete recovery, where the plant regains its previous size and health, can take several months to even a year. For instance, fast-growing species like tomatoes or basil may bounce back sooner, while perennials or woody plants could require a longer period to fully recover and establish new growth. Supporting them with proper care, such as adequate watering, fertilization, and protection from pests, can also accelerate their recovery process.
Factors Influencing Recovery Time
The recovery time for a plant after pruning is influenced by several factors, including the plant species itself, its growth rate, and its overall health. Fast-growing plants generally recover more quickly than slower-growing varieties. Additionally, if a plant is already stressed due to environmental factors like drought or poor soil quality, its ability to recover may be hindered, prolonging the process. Ensuring optimal conditions can make a significant difference in how quickly a plant can bounce back after pruning.
Pruning Techniques and Their Impact
The way in which a plant is pruned can greatly affect its recovery time. Techniques such as light pruning may lead to quicker recovery, as they involve removing only a portion of the plant, allowing for a swift regeneration of new growth. In contrast, severe pruning—removing a large portion of the plant—can lead to a longer recovery period as the plant needs to expend more energy to recuperate and develop new shoots and foliage.
Environmental Conditions for Recovery
The environment where the plant is located plays a crucial role in its recovery after pruning. Factors such as light exposure, temperature, and moisture levels can influence how quickly a plant heals. Ensuring that the plant receives enough sunlight and is watered appropriately while avoiding extreme temperatures can create a conducive environment for fast recovery. For instance, a plant kept in bright but indirect sunlight may recover faster than a plant in a shaded area with limited water supply.
Signs of Recovery
After pruning, it’s important to monitor the plant for signs of recovery. Indicators that a plant is recuperating include the emergence of new buds, the growth of new leaves, and an overall increase in vitality. These signs typically become visible within a few weeks after pruning, but more robust growth may take several months to appear. Observing these changes can help gardeners assess the health of their plants post-pruning and adjust care practices accordingly.
Care After Pruning
Providing proper care after pruning is essential for the timely recovery of the plant. This includes ensuring adequate watering, applying the right type of fertilizer to promote growth, and protecting the plant from pests and diseases. Regularly checking for pests and monitoring soil moisture levels are important steps to ensure the plant can recover efficiently. Additionally, avoiding over-fertilization will help prevent stress, allowing the plant to focus on regrowth and recovery.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Plant Species | Different species have varying recovery times. |
| Pruning Technique | Light pruning generally yields faster recovery compared to severe pruning. |
| Environmental Conditions | Sunlight, temperature, and water availability affect recovery speed. |
| Signs of Recovery | New growth and increased vitality are indicators of recovery. |
| Care Post-Pruning | Proper watering and protection are critical for recovery. |
How long do pruning cuts take to heal?

When it comes to the healing of pruning cuts, the duration can vary significantly based on several factors. Generally, pruning cuts on trees and shrubs can take between several weeks to months to heal properly. The healing process involves the formation of callus tissue and, eventually, the differentiation of this tissue into new wood as the plant repairs itself. Here are several factors that influence the healing time:
Factors Affecting Healing Time
The healing time of pruning cuts can be influenced by various factors that affect a plant's ability to recover. These include:
- Tree Species: Different species have varying rates of healing. Some species are naturally quicker at closing wounds than others.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors such as temperature, humidity, and soil moisture play a critical role in the plant's metabolic processes and healing capability.
- Size of the Cut: Larger cuts generally take longer to heal than smaller ones due to the greater amount of tissue that must regenerate.
Best Practices for Pruning
To ensure the fastest possible healing of pruning cuts, the following best practices should be observed:
- Use Clean Tools: Always use sharp and sanitized tools to make clean cuts, which reduces the risk of injury and disease.
- Avoid Topping: Topping trees can lead to larger wounds that take longer to heal. Instead, opt for proper thinning techniques.
- Appropriate Timing: Pruning during the plant's dormant season can promote quicker healing when the tree is less stressed.
Signs of Healing
Understanding the signs of healing can help gardeners know if their plants are recovering well:
- Callus Formation: The plant will begin to form a callus around the cut, indicating that it is starting to heal.
- New Growth: Look for new growth or buds developing near the cut, which is a good sign of successful recovery.
- Color Change: A darkening of the cut surface may indicate that the plant is sealing off the wound effectively.
Common Issues During Healing
Sometimes, pruning cuts can face complications that hinder the healing process:
- Disease Infection: Open wounds can attract pathogens, causing infections that slow down healing.
- Pests: Insects may exploit the pruning cuts, inflicting further damage and delaying recovery.
- Environmental Stress: Extreme weather conditions, such as drought or excessive rain, can adversely impact the healing process.
Importance of Proper Healing
The healing of pruning cuts is crucial for the long-term health of the plant:
See also:
- Prevention of Disease: Proper healing helps to seal off cuts, reducing the risk of opportunistic infections.
- Structural Integrity: Well-healed cuts contribute to the overall structural strength of the tree or shrub.
- Enhanced Growth: Healthy plants can better absorb nutrients and water, leading to robust growth and vitality.
How long to grow back after pruning?

How long it takes for plants to grow back after pruning varies significantly depending on several factors including the type of plant, the extent of the pruning, and the growing conditions. Generally, pruning stimulates growth, but the timeframe for noticeable regrowth can range from a few weeks to several months. Here are some factors to consider:
Factors Affecting Regrowth Time
The regrowth time after pruning can be influenced by several key factors:
- Plant Species: Different plants have varying growth rates. Fast-growing plants may rebound quickly, while slow-growing species take more time.
- Pruning Severity: Light pruning typically results in quicker regrowth compared to heavy pruning, which can take longer for the plant to recover.
- Season: Timing also plays a role—pruning in the growing season often leads to faster regrowth than pruning during dormancy.
Best Practices for Pruning
Implementing appropriate pruning techniques can enhance regrowth potential:
- Clean Cuts: Make sure cuts are clean and angled properly to encourage quicker healing and growth.
- Avoid Over-Pruning: Only remove what is necessary to ensure that the plant retains enough foliage for photosynthesis.
- Timing: Prune during the right season for your specific plant type for optimal growth.
Signs of Healthy Regrowth
After pruning, it's essential to monitor for signs of recovery:
- New Growth: Look for new shoots or leaves emerging from the cut areas as a sign of vitality.
- Healthy Color: Leaves should have a vibrant color; yellowing may indicate stress or poor recovery.
- Overall Vigor: An increase in overall plant robustness is a positive sign that recovery is taking place.
Differences Between Trees and Shrubs
Understand that trees and shrubs respond differently to pruning:
- Trees: Generally, trees can take longer to respond due to their size and complexity, often seen with renewed growth in a few months.
- Shrubs: Shrubs typically exhibit quicker regrowth, sometimes within just weeks of being pruned.
- Maintenance Practices: Continuous maintenance on shrubs can foster a more consistent growth cycle.
Environmental Impact on Regrowth
Environmental conditions also play a crucial role in determining how fast a plant grows back:
- Soil Quality: Nutrient-rich soil promotes faster recovery compared to depleted soil.
- Water Availability: Adequate watering is vital; water-stressed plants will regrow slower.
- Sunlight Exposure: Ensuring the plant receives enough sunlight is essential for robust growth post-pruning.
How long does it take for a plant to come back from shock?

The recovery time for a plant coming back from shock can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the type of plant, the severity of the shock, environmental conditions, and care provided during the recovery period. Generally, it can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks for a plant to regain its health after experiencing shock.
Factors Influencing Recovery Time
Factors Influencing Recovery Time
The recovery time of a plant from shock is influenced by various factors. Understanding these can help you better manage your plant's recovery process.
- Type of Plant: Different species have different resilience levels; some may bounce back quickly, while others take longer.
- Severity of Shock: Minor stresses may lead to faster recovery, while severe shock, such as root damage, can extend recovery times.
- Environmental Conditions: Adequate light, humidity, and temperature can significantly affect how quickly a plant can recover.
- Care Provided: Proper watering, feeding, and pruning during the recovery phase can speed up the healing process.
- Pest and Disease Presence: If a plant is dealing with pests or diseases, recovery can be hindered and take longer.
Signs of Shock in Plants
Signs of Shock in Plants
Recognizing the signs of shock in a plant can help you address the issue promptly, which in turn can aid in a quicker recovery.
- Wilting Leaves: This is often the first visible sign that a plant is experiencing stress.
- Leaf Drop: Sudden loss of leaves can occur as the plant reallocates resources.
- Discoloration: Leaves may turn yellow or brown, indicating distress.
- Stunted Growth: A sudden halt in growth is a common reaction to shock.
- Root Damage: If the roots have been disturbed, you may notice unusual growth patterns.
Best Practices for Recovery
See also:
Best Practices for Recovery
Implementing effective care techniques can significantly help your plant recover after experiencing shock.
- Maintain Moisture: Keeping the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged can encourage root recovery.
- Provide Appropriate Light: Ensure that your plant receives the right amount of sunlight, based on its species requirements.
- Avoid Fertilizing: Let the plant recover before introducing fertilizer, as this can stress the plant further.
- Prune Damaged Areas: Carefully remove any dead or dying leaves or stems to promote new growth.
- Monitor for Pest Issues: Check for pests regularly, as they can exacerbate stress and prolong recovery.
Timeframe for Different Plant Types
Timeframe for Different Plant Types
Different types of plants have varying recovery timelines. Knowing these can help set realistic expectations for their recovery.
- Succulents: Typically recover within a week due to their ability to store water.
- Tropical Plants: May take 2-3 weeks to show signs of recovery due to their sensitivity to shock.
- Perennials: Generally can take about 2-4 weeks to bounce back, depending on environmental factors.
- Annuals: These may show quick recovery, around 1-2 weeks, if conditions are favorable.
- Woody Plants: Trees and shrubs can take a month or more, especially if pruned or transplanted.
Long-Term Care After Recovery
Long-Term Care After Recovery
Once a plant has started to recover from shock, it’s important to continue providing the right care to ensure its long-term health.
- Gradual Exposure: If the plant was moved to a new environment, gradually reintroduce it to full light conditions.
- Consistent Watering: Maintain a consistent watering schedule to support ongoing growth.
- Nutrients: After about a month, consider using a balanced fertilizer to promote healthy regrowth.
- Observe Growth Patterns: Keep an eye on how the plant grows; this can indicate its ongoing health.
- Preventative Measures: Implement strategies to avoid future shock, such as avoiding drastic environmental changes.
What is the 1/3 rule for pruning?
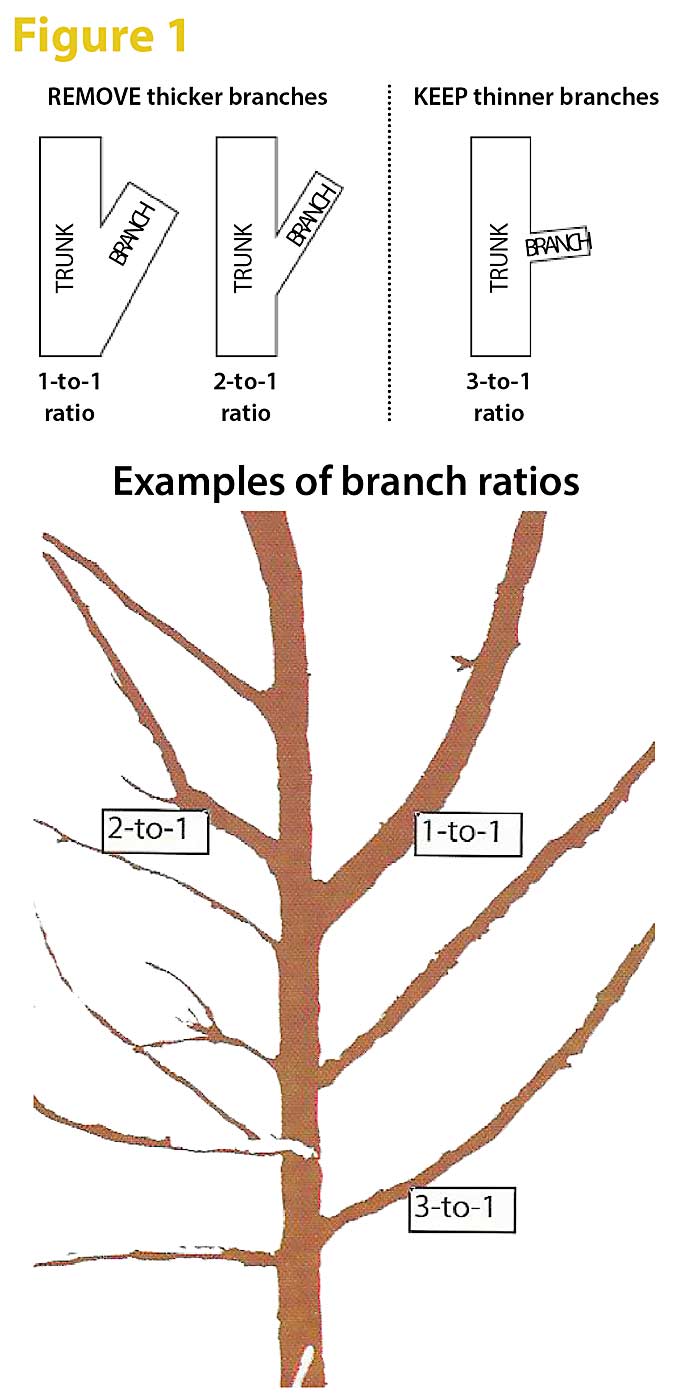
The 1/3 rule for pruning is a guideline that suggests that no more than one-third of a plant’s foliage should be removed in a single pruning session. This approach is crucial for maintaining the health and vitality of the plant, minimizing stress, and stimulating growth. Over-pruning can lead to shock, reduce the plant's ability to photosynthesize, and may even invite diseases. The rule provides a balanced approach to pruning that allows for the rejuvenation of the plant while ensuring its ongoing growth and flowering.
Importance of the 1/3 Rule
The importance of the 1/3 rule lies in its role in promoting healthy plant growth. By adhering to this guideline, gardeners can ensure that plants retain enough foliage to support photosynthesis. This reduces the risk of stress and potential damage to the plant. The benefits include:
- Maintaining vitality - Protects the plant's overall health.
- Encouraging new growth - Pruning stimulates fresh shoots and flower production.
- Minimizing shock - Reduces plant stress, allowing it to recover more easily.
Pruning Techniques to Implement the 1/3 Rule
To effectively apply the 1/3 rule, various pruning techniques should be employed. It’s essential to understand how to approach the task to achieve the best results. Techniques include:
- Thinning - Removing specific branches to enhance airflow and light penetration.
- Crown reduction - Cutting back the height and spread of the plant while preserving its overall structure.
- Deadheading - Removing spent flowers to encourage more blooms without compromising the plant's health.
When to Prune Under the 1/3 Rule
Timing is critical when it comes to pruning under the 1/3 rule. The best time to prune varies by plant species but generally falls within specific seasons. Consider the following points:
- Late winter - Ideal for many deciduous plants as they are still dormant.
- Post-bloom - For flowering plants, prune after flowering to promote future blooms.
- Early spring - Some shrubs benefit from pruning just before new growth begins.
Understanding common mistakes can help ensure the 1/3 rule is applied effectively. Avoiding these pitfalls is essential for successful pruning. Common mistakes include:
- Removing too much foliage - Exceeding the one-third limit can weaken the plant.
- Improper tools - Using dull or incorrect tools can damage the plant.
- Ignoring plant needs - Not considering the specific requirements of the plant being pruned.
Benefits of Adhering to the 1/3 Rule
Following the 1/3 rule has several benefits that contribute to long-term plant health and aesthetic appeal. These can enhance the overall gardening experience. The benefits include:
- Improved health - Plants recover faster and produce better foliage and flowers.
- Aesthetic value - Well-pruned plants look more attractive in the landscape.
- Longer lifespan - Healthy plants tend to live longer and resist diseases better.
Questions from Our Readers
How long does it take for a plant to recover from pruning?
The recovery time for a plant after pruning varies depending on the species, health, and type of pruning performed. Generally, most plants can show signs of recovery within a few weeks to several months, as they redirect energy towards new growth.
Does the time of year affect the recovery time after pruning?
Yes, the season in which pruning occurs can significantly impact recovery. Pruning during the dormant period (usually late winter or early spring) often allows plants to recover more quickly compared to pruning during their active growth phase, when they may be stressed.
See also:
What factors influence how quickly a plant recovers from pruning?
Several factors can influence recovery speed, including plant type, environmental conditions, and care provided after pruning. Adequate water, sunlight, and proper fertilization can enhance recovery times, while neglect may extend them.
Should I fertilize my plant after pruning to aid recovery?
Fertilizing after pruning can be beneficial, but it should be done cautiously. Providing a balanced fertilizer can support new growth, but over-fertilization may cause stress or even damage. Timing and dosage are key to effective recovery.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=5E9GEQ6aqgk
If you want to read more articles like How Long Does It Take a Plant to Recover from Pruning? Expert Tips for Faster Recovery, we recommend you check out our Pruning category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles