Top 5 Good Fertilizer for Blueberries: Boost Your Yield and Flavor

When it comes to cultivating blueberries, the right fertilizer can make all the difference in ensuring a bountiful harvest with exceptional flavor. Blueberries thrive in acidic soils and require a balanced nutrient supply to grow strong and productive. Selecting the best fertilizers tailored for these berries not only enhances yield but also enriches their taste profile. This article will explore the top five fertilizers that are particularly effective for blueberries, discussing their benefits and optimal application methods. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or a novice grower, these recommendations will help you achieve abundant, delicious blueberries in your garden.
Best Fertilizers for Blueberries
Blueberries thrive in acidic soils, making the selection of the right fertilizer crucial for their growth and fruit production. One of the best options is an organic fertilizer that is high in nitrogen, such as blood meal or fish emulsion. These fertilizers not only support the plant's green growth but also help maintain the soil’s acidic environment, which is essential for blueberries. Additionally, incorporating compost can enhance soil structure and provide a slow-release of nutrients. For best results, it is often recommended to apply fertilizer during the early spring as the plants begin to show signs of growth, ensuring they receive the necessary nutrients during their active growing period.
Importance of Soil pH for Blueberries
The pH level of the soil is crucial for blueberry health, as these plants require a pH between 4.5 and 5.5 to absorb nutrients effectively. When the soil is too alkaline, blueberries may struggle to take up essential minerals, leading to poor growth and reduced fruit yield. Therefore, before planting, it's advisable to test the soil pH and amend it using sulfur or ammonium sulfate if needed, to create an optimal growing environment for these acid-loving plants.
Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers
When choosing between organic and synthetic fertilizers, it's essential to consider the long-term impact on soil health. Organic fertilizers, such as compost or worm castings, improve soil structure and microbial activity, creating a sustainable ecosystem for blueberries. In contrast, synthetic fertilizers can provide quick nutrient boosts but may lead to nutrient leaching and decreased soil quality over time. A balanced approach, utilizing both types of fertilizers judiciously, can yield the best results for blueberry cultivation.
Best Time to Fertilize Blueberries
Timing is critical when it comes to fertilizing blueberries. The best time to apply fertilizer is during early spring, just as the buds begin to swell, signaling the start of the growing season. This timing allows the plant to utilize the nutrients efficiently as they prepare to produce leaves and fruit. It's also recommended to apply a second round of fertilizer after the harvest, ensuring that the plants are replenished as they prepare for the next growth cycle.
Recommended Fertilizer Types for Blueberries
Some of the most recommended fertilizers for blueberries include acidic fertilizers like conifer mulch, blueberry-specific granular fertilizers, and liquid fish fertilizers. These options not only provide essential nutrients but also help maintain the ideal acidic soil required for optimal blueberry growth. When selecting a fertilizer, look for one with a higher ratio of nitrogen and lower phosphorus levels, as blueberries do not require excessive amounts of phosphorus.
Nutrient Requirements for Blueberries
Blueberries require a balanced supply of nutrients for healthy growth and fruiting. Key nutrients include nitrogen, which promotes vigorous growth, and potassium, which is essential for fruit development. While phosphorus is necessary, blueberries are sensitive to high levels, so it should be provided in limited amounts. Additionally, micronutrients such as iron, manganese, and zinc play vital roles in various physiological processes, making it important to ensure that these minerals are present in sufficient quantities in the soil.
| Nutrient | Importance | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Promotes leaf and stem growth | Blood meal, Fish emulsion |
| Potassium | Essential for fruit quality and development | Kelp meal, Potassium sulfate |
| Phosphorus | Supports root development | Bone meal (limited amounts) |
| Iron | Prevents chlorosis, essential for photosynthesis | Irrigation with iron chelate |
| Manganese | Vital for enzyme function | Soil amendments |
What is the best fertilizer for blueberries?
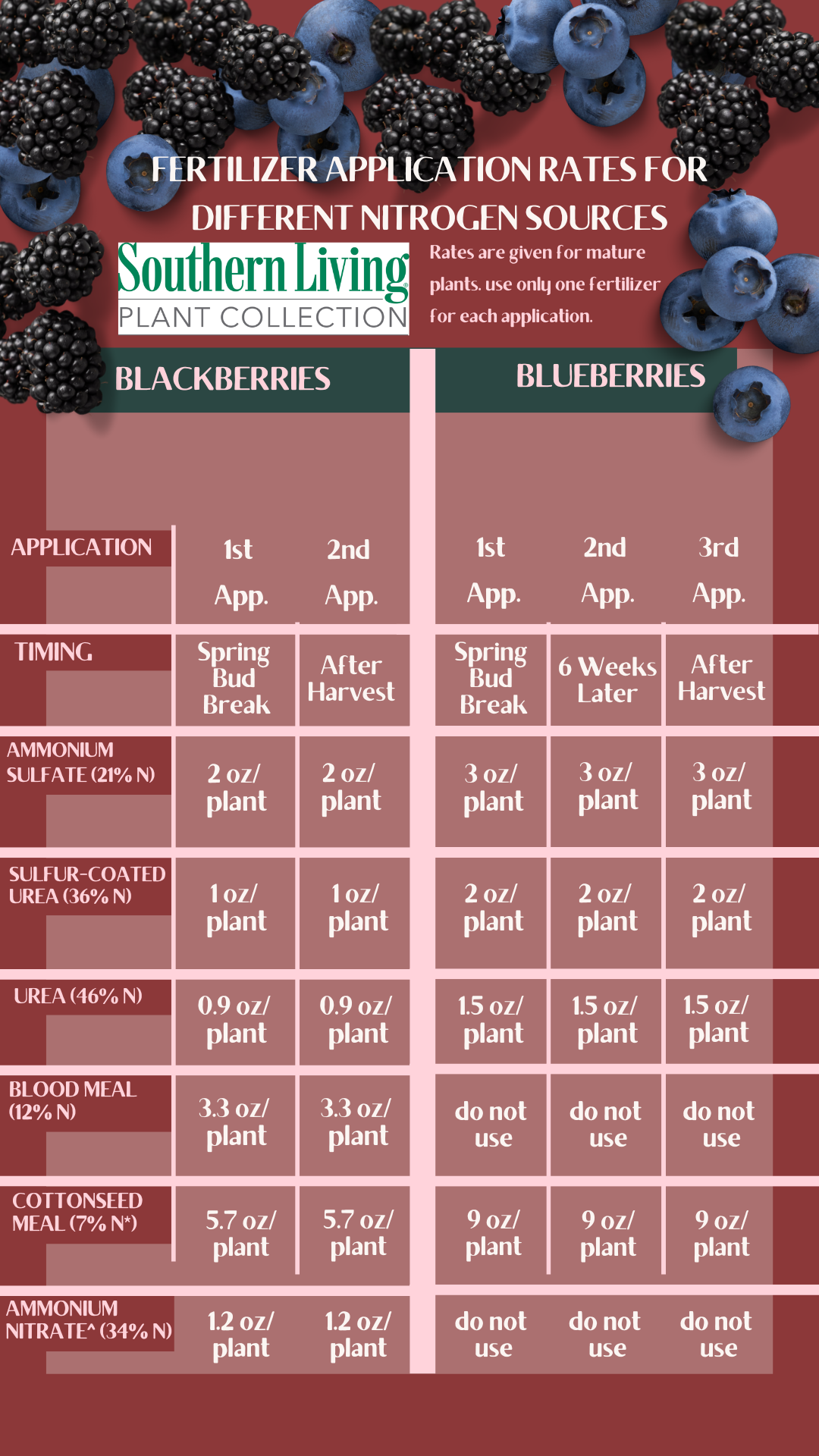
The best fertilizer for blueberries is one that provides the necessary nutrients while maintaining an acidic pH, as blueberries thrive in acidic soils. A balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for acid-loving plants is often recommended. Generally, fertilizers with a higher amount of nitrogen relative to phosphorus and potassium are beneficial. A common choice among gardeners is an organic fertilizer with a formula such as acid-based dry fertilizers (e.g., 10-20-20), or you can also use products labeled for ericaceous plants.
Additionally, it's important to consider using natural amendments like compost, aged manure, or fish emulsion to support healthy growth and improve soil structure.
Understanding Soil pH
The soil pH plays a crucial role in the health of blueberry plants. Blueberries prefer a pH between 4.5 and 5.5, which is significantly acidic compared to many other crops. Regular testing of soil pH is essential to ensure that your blueberries can absorb nutrients effectively. Here are some steps to maintain the appropriate pH:
- Test your soil using a pH kit.
- Apply sulfur or aluminum sulfate to lower the pH if necessary.
- Regularly monitor soil pH and adjust fertilization methods accordingly.
Nutrient Requirements for Blueberries
Blueberries have specific nutrient requirements essential for their growth and fruit production. Key nutrients include:
- Nitrogen: Promotes healthy leaf and shoot growth.
- Phosphorus: Supports root development and flowering.
- Potassium: Enhances fruit quality and overall plant health.
Using a fertilizer high in nitrogen can be particularly beneficial early in the growing season, while a balanced approach during later stages can help support fruit development.
Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers
When choosing fertilizers for blueberries, you can opt for either organic or synthetic fertilizers, each with its benefits:
- Organic fertilizers: Improved soil health and microbial activity; typically release nutrients slowly.
- Synthetic fertilizers: Provide nutrients in a quickly available form, but may require precise application.
- Consider personal preferences for organic gardening practices when deciding.
Both types can be effective, but organic methods often promote sustainable gardening practices.
See also:
Application Timing and Frequency
The timing and frequency of fertilizer application can significantly influence blueberry plant health. Here are some guidelines:
- Apply fertilizer in early spring as new growth begins.
- Consider a second application after fruit set to support continued growth.
- Avoid fertilizing late in the season, as this can encourage new growth that may not harden off before winter.
Proper timing ensures that plants have the nutrients available when they need them the most.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When fertilizing blueberries, some common mistakes can hinder their growth and fruit production. It's important to avoid:
- Over-fertilizing: This can lead to excessive growth and reduced fruit yield.
- Ignoring soil pH: Fertilizing without considering pH can lead to nutrient deficiencies.
- Using high phosphorus fertilizers: These can be harmful as blueberries are sensitive to excessive phosphorus.
Being mindful of these potential pitfalls can help you cultivate healthy blueberry plants.
How much 10-10-10 fertilizer for blueberries?

To determine how much 10-10-10 fertilizer to apply for blueberries, it is essential to understand several factors that influence the fertilizer requirements, such as the age of the plants, the soil type, and the nutrient content present in the soil.
Generally, a common recommendation is to apply around 1 pound (or approximately 0.45 kg) of 10-10-10 fertilizer for every 50 square feet of blueberry plants annually. This should be split into two applications: one in early spring and another in late spring or early summer. However, it is advisable to conduct a soil test beforehand to determine the specific needs of your soil and adjust the amount accordingly.
Understanding Blueberry Nutrient Needs
Blueberries require a balanced supply of Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) for optimal growth and fruit production.
- Nitrogen promotes leafy growth and is vital during the early growth stages.
- Phosphorus is essential for root development and flowering.
- Potassium helps in fruit quality and overall plant health.
When to Apply 10-10-10 Fertilizer
Timing is crucial for the effective application of 10-10-10 fertilizer.
- Early spring is the best time for the first application, just as new growth begins.
- A second application can be done in late spring or early summer, ensuring nutrients are available during the growing season.
- Avoid fertilizing in late summer or fall, as this can stimulate new growth susceptible to winter damage.
Calculating the Right Amount
To apply the correct amount of 10-10-10 fertilizer, consider the following calculation method.
- Determine the total area (in square feet) where the blueberry plants are located.
- Divide the total area by 50 to figure out how many pounds of fertilizer you need based on the 1 pound per 50 square feet guideline.
- Split the total recommended amount into two separate applications for even nutrient distribution.
Conducting a Soil Test
A soil test can provide critical insights into your soil's existing nutrient levels.
- Collect soil samples from multiple locations around your blueberry plants.
- Send samples to a local extension service or lab for analysis.
- Use the test results to adjust your fertilizer application to meet the specific needs of your soil and plants.
Possible Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Monitoring the blueberries for signs of nutrient deficiencies can help you adjust your fertilizer application.
- Yellowing leaves may indicate a lack of Nitrogen.
- Poor fruit development can signal insufficient Phosphorus levels.
- Weak plant integrity might suggest a deficiency in Potassium.
What does Epsom salt do for blueberries?

Epsom salt, chemically known as magnesium sulfate, can be beneficial for blueberries in various ways. Blueberries thrive in acidic soil, and Epsom salt can contribute to their nutrient needs by providing magnesium and sulfate, both of which play important roles in plant growth and health. Below are some details on how Epsom salt affects blueberries.
Benefits of Magnesium for Blueberries
Magnesium is a vital nutrient for blueberries as it contributes to several key functions in the plant. It is an essential component of chlorophyll, which allows for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Additionally, magnesium aids in the production of sugars and starches, crucial for the overall growth and fruit development of blueberries.
See also:
- Chlorophyll Production: Magnesium is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis, improving the plant's ability to photosynthesize.
- Sugar Formation: It helps in the conversion of carbohydrates, promoting healthier fruit.
- Overall Growth: Adequate magnesium enhances nutrient absorption and promotes robust root development.
The Role of Sulfate in Plant Health
Sulfate, the second component of Epsom salt, is equally important. It plays a key role in the synthesis of amino acids and proteins, which are essential for plant structure and function. For blueberries, the presence of sulfate can enhance the plant's ability to endure stress by improving its resistance to diseases.
- Amino Acid Synthesis: Sulfate is critical for forming proteins, vital for plant growth and repair.
- Plant Resistance: Enhanced sulfate levels can boost the plant's immunity against certain pests and diseases.
- Soil Health Improvement: Sulfate contributes to better soil structure and nutrient availability.
Application Methods for Epsom Salt
Applying Epsom salt effectively is key to maximizing its benefits for blueberries. Gardeners often use it by dissolving it in water or applying it directly to the soil. Proper application ensures that the nutrients are available for the plants when they need them most.
- Soil Application: Sprinkle Epsom salt around the base of the blueberry plants and water it in.
- Liquid Solution: Dissolve Epsom salt in water and use it as a foliar spray for quicker absorption.
- Frequency of Application: A couple of times a year is usually sufficient, particularly during the growing season.
Impact on Fruit Quality and Yield
Using Epsom salt can have a positive impact on the quality and yield of blueberries. By addressing nutrient deficiencies, Epsom salt helps in producing larger, sweeter, and healthier berries. Magnesium and sulfate contribute not only to fruit development but also to overall plant vitality.
- Improved Flavor: Adequate magnesium enhances the sweetness and flavor of the berries.
- Larger Fruit Size: Nutritional balance from Epsom salt can lead to larger blueberry sizes.
- Higher Yields: Healthy plants are more productive, resulting in more berries per harvest.
Considerations for Using Epsom Salt
While Epsom salt offers benefits, it is important to use it judiciously. Overapplication can lead to imbalances in soil nutrients, affecting plant health. It's advisable to conduct soil tests to determine existing nutrient levels before application.
- Soil Testing: Conduct tests to identify existing magnesium and sulfate levels.
- Appropriate Dosage: Follow recommended guidelines to avoid overapplication.
- Monitor Plant Health: Observe for any signs of nutrient deficiency or excess following application.
What do coffee grounds do for blueberry plants?

Coffee grounds can be beneficial for blueberry plants in several ways. These grounds are rich in nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth. Moreover, they can help improve soil structure, increase acidity, and attract beneficial organisms.
Benefits of Coffee Grounds for Soil
Coffee grounds serve as a natural fertilizer that enhances soil nutrient content. They can improve the physical properties of the soil and foster a healthier growing environment for blueberry plants. Some benefits include:
- Increased Nitrogen: Provides essential nutrients that promote healthy growth.
- Soil Structure Improvement: Helps create a more aerated and well-draining soil.
- Microbial Activity: Encourages the presence of beneficial microorganisms that aid in nutrient absorption.
Impact on Soil Acidity
Blueberries thrive in acidic soil, typically with a pH of 4.5 to 5.5. Coffee grounds can help achieve this desired acidity. Their contribution to soil acidity can be summarized as follows:
- pH Reduction: Helps lower the soil pH, making it more suitable for blueberries.
- Enhanced Nutrient Availability: Certain nutrients become more available for absorption in acidic conditions.
- Natural Mulching: Aids in moisture retention while gradually affecting soil pH.
Attracting Beneficial Organisms
Incorporating coffee grounds into the garden can attract various beneficial organisms that assist blueberry growth. These organisms include:
- Earthworms: Improve soil structure and fertility.
- Beneficial Insects: Aid in pollination and pest control.
- Mycorrhizae Fungi: Form symbiotic relationships with roots, enhancing nutrient uptake.
How to Apply Coffee Grounds
Applying coffee grounds correctly is crucial for maximizing their benefits. Follow these guidelines for effective application:
- Mix with Soil: Combine grounds with existing soil to ensure even distribution.
- Use as Mulch: Apply a thin layer on the surface to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
- Avoid Overuse: Limit the amount used to prevent potential imbalances in soil nutrients.
Potential Drawbacks of Coffee Grounds
While coffee grounds offer numerous benefits, some drawbacks should be considered:
- Caffeine Sensitivity: Some plants may be sensitive to caffeine, which could impede growth.
- pH Fluctuations: Excessive use may lead to unpredictable changes in soil pH.
- Pest Attraction: In some cases, it may attract unwanted pests or mold.
Questions from Our Readers
What is the best fertilizer for blueberries?
The best fertilizer for blueberries is one that is high in acidic nutrients. Typically, a fertilizer with an N-P-K ratio of 5-10-10 is recommended, as it provides sufficient nitrogen, promotes root development, and helps maintain the required soil acidity. Look for fertilizers specifically designed for acid-loving plants.
How often should I fertilize my blueberry plants?
You should fertilize your blueberry plants twice a year, usually in early spring and again in late spring after blooming. This allows the plants to absorb nutrients during their critical growth phases, ensuring they have enough energy for fruit production and overall health throughout the growing season.
Can I use organic fertilizers on blueberries?
Yes, organic fertilizers are an excellent choice for blueberries, as they provide a slow release of nutrients and improve soil health over time. Products like pine bark, peat moss, or fish emulsion are suitable options that contribute to the acidic environment these plants thrive in while promoting a robust root system.
Is it necessary to test the soil before fertilizing blueberries?
Yes, testing the soil before fertilizing blueberries is highly recommended. A soil test will help you determine the pH level and nutrient content, allowing you to choose the most appropriate fertilizer that maintains optimal acidity (around pH 4.5 to 5.5) for healthy blueberry growth.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like Top 5 Good Fertilizer for Blueberries: Boost Your Yield and Flavor, we recommend you check out our Fertilise category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles