Discover the Best Ginger Plants for Sale Bunnings: A Complete Buying Guide

Ginger is not only a popular spice but also a remarkable plant known for its health benefits and culinary versatility. If you're looking to add ginger to your garden, Bunnings offers a variety of ginger plants for sale, catering to both novice and experienced gardeners alike. This complete buying guide will help you navigate your options, from selecting the best ginger varieties to understanding ideal growing conditions and care tips. Discover how to enhance your gardening experience with ginger, ensuring that your choice leads to a robust and thriving plant that can elevate your cooking and well-being.
Ginger Plants Available for Purchase at Bunnings
If you are looking to add some flavor to your garden or kitchen, ginger plants can be an excellent choice. Bunnings, a popular garden supply retailer, offers a variety of ginger plants for sale, catering to both novice and experienced gardeners. These plants thrive in warm climates and can be cultivated not only for their valuable rhizomes but also for their lush foliage. When shopping at Bunnings, you can find different varieties and sizes, making it easy to select the best option that suits your gardening needs and space. With the right care and environment, growing ginger can be a rewarding experience.
Types of Ginger Plants Offered
Bunnings features several types of ginger plants suited for various needs and preferences. Among the most popular varieties available for sale, you'll find common ginger (Zingiber officinale), which is widely used for culinary purposes, and turmeric (Curcuma longa), known for its medicinal properties. Each type has unique requirements in terms of sunlight, watering, and soil conditions, so it's essential to choose the right one based on your gardening conditions and intended use.
Care Tips for Ginger Plants
Successfully growing ginger plants requires understanding their basic care requirements. They prefer warm, humid conditions and well-drained soil rich in organic matter. It's important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Providing partial shade can also be beneficial, particularly in hotter climates. Additionally, fertilizing your ginger plants with a balanced fertilizer can encourage strong growth and rhizome production.
Benefits of Growing Ginger
Growing your own ginger offers numerous benefits beyond the culinary delights it provides. Freshly harvested ginger is often more flavorful and aromatic than store-bought varieties. Furthermore, ginger is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, making it a valuable addition to your diet. Having access to fresh ginger allows you to experiment with homemade teas, soups, and various dishes, enhancing your cooking experience.
Where to Find Ginger Plants at Bunnings
When you're ready to purchase ginger plants, Bunnings makes it convenient to find them in their garden section. These plants are usually stocked alongside other herbs and tropical plants. Staff members are typically available to answer questions and provide guidance on selecting healthy plants and best practices for their care. If you're unable to find ginger plants in-store, Bunnings also offers online shopping options for easy access to their selections.
How to Harvest Ginger
Knowing how to harvest ginger is crucial to maximizing the yield of your plants. Typically, ginger is ready to be harvested about 8 to 10 months after planting, once the leaves start to yellow and die back. It’s best to carefully lift the tubers from the ground using a garden fork, taking care to avoid damaging the rhizomes. After harvesting, you can use the ginger immediately or store it properly for later use, ensuring you enjoy the fruits of your gardening labor.
| Type of Ginger | Uses | Growing Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Common Ginger | Culinary, medicinal | Warm, humid, well-drained soil |
| Turmeric | Medicinal, culinary | Sunny to partial shade, rich soil |
What is the best month to plant ginger?

The best month to plant ginger is typically in the spring, when the soil temperature is consistently above 60°F (15°C). In many regions, this corresponds to the months of March to April. Planting ginger at this time allows it to establish roots before the heat of summer, promoting healthy growth and a bountiful harvest in the fall.
Soil Temperature Requirements
To successfully grow ginger, it is crucial to have the right soil temperature. Ginger prefers warm, well-drained soil that facilitates healthy root development.
- Optimal temperature: Soil temperatures should ideally be above 60°F (15°C).
- Soil preparation: Ensure the soil is loose, rich in organic material, and well-drained to prevent rot.
- Temperature monitoring: Use a soil thermometer to check temperatures before planting.
Choosing the Right Location
Selecting an ideal growing location is vital for the successful cultivation of ginger. It thrives in partially shade to full sun, ensuring the plants receive adequate sunlight while being protected from harsh wind.
- Sunlight: Choose a spot that receives at least 4-6 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Wind protection: Look for sheltered areas to protect the plant from strong winds.
- Drainage: Ensure the chosen location has good drainage to avoid waterlogging.
Climate Considerations
The climate of your region plays a significant role in determining the optimal planting time for ginger. Ginger prefers tropical or subtropical climates with warm temperatures throughout the growing season.
- Temperature extremes: Avoid planting ginger in areas that experience frost or extreme cold conditions.
- Consistent warmth: A climate with consistent temperatures of around 70°F (21°C) to 85°F (29°C) is ideal.
- Moisture levels: Ensure your climate has sufficient rainfall or consider irrigation methods to maintain moisture without flooding.
Pre-Planting Preparations
Before planting ginger, it is essential to engage in certain preparations to maximize growth potential. These preparations involve selecting the right seed pieces and preparing the planting area.
See also:
- Seed selection: Use fresh, healthy ginger rhizomes with at least one “eye” for sprouting.
- Chitting: Set seed pieces out in a warm, humid environment to encourage sprouting before planting.
- Soil enrichment: Amend soil with rich organic matter like compost to improve fertility.
Ginger Planting Techniques
Proper planting techniques ensure that ginger thrives. The way you plant the rhizomes can affect their growth and yield.
- Depth: Plant ginger rhizomes about 2-4 inches (5-10 cm) deep in the soil.
- Spacing: Space each piece approximately 12 inches (30 cm) apart to allow room for growth.
- Watering: Water the area thoroughly after planting, ensuring the soil is moist but not soggy.
Does the ginger plant come back every year?
The ginger plant, scientifically known as Zingiber officinale, is a perennial herb. This means that it can return year after year under the right conditions. However, its life cycle and annual growth depend significantly on climate, care, and cultivation practices.
Does Ginger Survive Winter?
In regions with mild climates, ginger can survive winter months without extensive care. However, in areas with frosty conditions, the above-ground part of the plant may die back, but the underground rhizome can remain viable. These points illustrate its winter survival:
- Temperate climates: Ginger can thrive year-round.
- Frost-prone zones: Protect the plant by mulching or bringing pots indoors.
- Hardiness: Ginger rhizomes have a natural ability to survive adverse weather.
How to Harvest Ginger Without Killing the Plant?
Careful harvesting can allow you to enjoy fresh ginger while enabling the plant to continue growing. Here are some effective strategies:
- Partial Harvesting: Only take what you need, leaving enough rhizome in the soil.
- Timing: Harvest when the plant is mature but before it fully dies back.
- Technique: Use a garden fork to gently lift the rhizome instead of pulling it by the stem.
Planting Ginger in a Garden
To ensure that ginger comes back every year, proper planting and care are essential. Consider the following elements:
- Soil quality: Ginger prefers loamy, well-draining soil enriched with organic matter.
- Sunlight: Choose a location with partial shade to protect it from extreme heat.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy to avoid rot.
Fertilization and Care Needs of Ginger
Providing appropriate nutrition and care can enhance the longevity of your ginger plant. Focus on these care aspects:
- Organic fertilizers: Use compost or well-rotted manure to nourish the soil.
- Pest control: Monitor for common pests and treat them promptly to prevent damage.
- Regular watering: Ensure the plant receives enough moisture, especially during dry spells.
Signs That Your Ginger Plant is Thriving
Recognizing the indicators of a healthy ginger plant will help ensure its success year after year. Look for these signs:
- Leaf growth: Healthy, vibrant green leaves indicate good health.
- Root formation: A robust, well-developed rhizome system means the plant is thriving.
- Flowering: While not common, blooms suggest that the plant is well-established and mature.
Where is the best place to plant ornamental ginger?
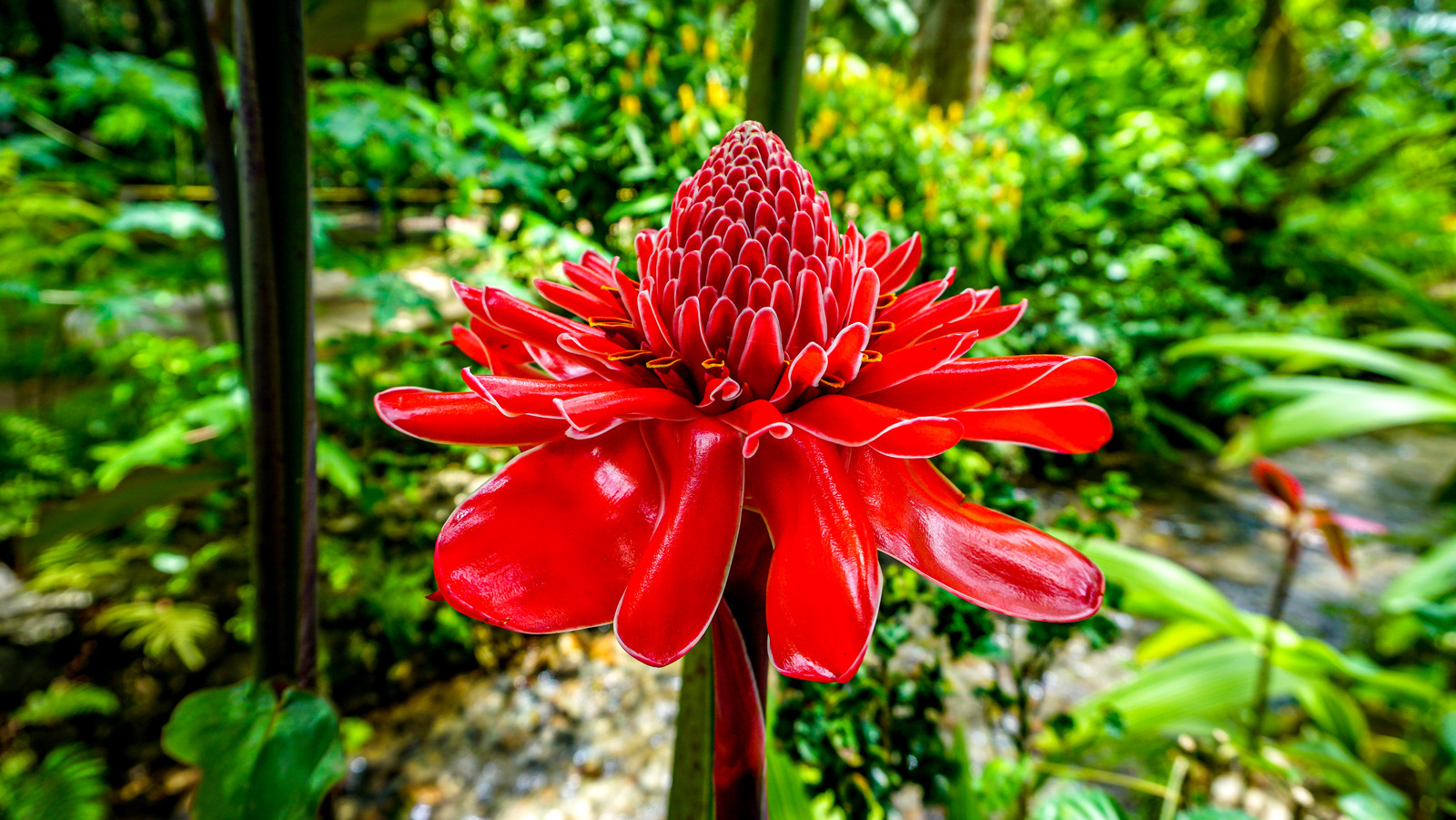
The best place to plant ornamental ginger generally depends on the type of ginger and the environmental conditions it requires. However, some general guidelines can help ensure optimal growth for this lush and vibrant plant.
1. Ideal Sunlight Conditions
Ornamental ginger thrives in bright, indirect light. While some varieties can tolerate more sunlight, too much direct sun can scorch their leaves.
- Partial Shade: Spot with filtered sunlight is perfect for most ginger varieties.
- Avoid Full Sun: Direct afternoon sun can be harmful, especially in hotter climates.
- Dappled Light: Areas under larger trees can provide a suitable balance of light and shade.
2. Soil Requirements
Well-draining soil is crucial for successful ornamental ginger cultivation. This plant does not perform well in soggy conditions, which can lead to root rot.
- Loamy Soil: Ideal for optimal drainage and nutrient retention.
- pH Level: Slightly acidic to neutral soils (pH 6-7) are preferable.
- Organic Matter: Incorporating compost can improve soil quality and nutrient supply.
3. Watering Needs
Maintaining the right moisture level is vital for ornamental ginger. The plant prefers consistently moist soil but should not be waterlogged.
See also:
- Regular Watering: During hot months, check the soil and water as needed.
- Drainage: Ensure pots or garden beds have adequate drainage to prevent standing water.
- Humidity: Higher humidity levels favor the growth of ginger, especially in indoor settings.
4. Temperature Preferences
Ornamental ginger does best in tropical to subtropical climates. It is sensitive to cold temperatures and frost.
- Temperature Range: Optimal growth occurs in temperatures between 60°F and 80°F (15°C to 27°C).
- Frost Protection: In colder regions, consider container planting to move them indoors during winter.
- Microclimates: Planting in areas protected from harsh winds can help maintain warmth.
5. Companion Planting
Selecting the right companions can enhance the growth and aesthetic appeal of ornamental ginger. It pairs well with various plants.
- Ferns: Their foliage contrasts beautifully with ginger and thrives in similar light conditions.
- Tropical Flowers: Plants like hibiscus and heliconias complement gingers well.
- Spreading Ground Covers: These can help retain soil moisture and reduce weed competition.
What not to grow next to ginger?

When considering what to plant next to ginger (Zingiber officinale), it's crucial to understand the companion planting dynamics in gardening. Certain plants can hinder ginger's growth due to factors such as nutrient competition, pest attraction, or differing growth conditions. Here are some plants you should avoid planting close to ginger to ensure the best growth and yield.
Incompatible Plants
Certain plants can create incompatibility with ginger, leading to suboptimal growth. Ginger thrives in conditions that may not align with the needs of other plants, making it vital to choose companions wisely.
- Garlic - Its strong scent can hinder ginger's growth.
- Onions - Similar to garlic, they can compete for nutrients.
- Legumes - They can attract pests that may adversely affect ginger.
Pest Attraction Issues
Some plants are known to attract pests that could harm ginger. If these pests are drawn to nearby flora, they can easily spread to your ginger plants.
- Tomatoes - They can attract aphids, which may also bother ginger.
- Peppers - Similarly, they attract pests like spider mites that target ginger.
- Eggplant - Known for pest issues, making them unsuitable companions.
Differing Soil Nutrient Requirements
Ginger has specific nutrient needs that may conflict with other plants. Certain vegetables may deplete the soil of essential nutrients that ginger requires for optimal growth.
- Cabbage - It can exhaust the soil's nutrients that ginger thrives on.
- Brussels Sprouts - They require high nitrogen, which can harm ginger's nutrient absorption.
- Swiss Chard - As a heavy feeder, it may compete for nutrients with ginger.
Climate and Watering Needs
Ginger prefers humid, warm conditions and unique watering needs. Planting alongside species that have different climatic or watering preferences can harm ginger's growth.
- Mint - It tends to spread aggressively, leading to inconsistent moisture levels.
- Thyme - Prefers drier conditions contrary to ginger's need for humidity.
- Oregano - Similar to thyme, it can affect the moisture balance required by ginger.
Growth Rate Competition
Ginger has a relatively slow growth rate compared to many vegetables. When planted near fast-growing species, ginger may struggle to thrive due to competition for space and resources.
- Corn - Its fast growth can overshadow ginger, leading to inadequate light and space.
- Sunflowers - They grow tall quickly and can steal sunlight from ginger.
- Pumpkin - Known for its sprawling nature, it can suffocate the ginger plants.
Questions from Our Readers
Are ginger plants available for sale at Bunnings?
Yes, Bunnings typically offers ginger plants for sale, especially during the planting season. You can find both the root rhizomes and live plants, making it convenient for those looking to grow their own ginger at home.
What are the ideal growing conditions for ginger plants?
Ginger plants thrive in warm and humid conditions with indirect sunlight. They require well-draining soil and should be watered regularly, but it's important to avoid waterlogging to prevent root rot.
How do I care for ginger plants after purchasing them from Bunnings?
After purchasing ginger plants from Bunnings, you should plant them in a suitable pot or garden bed, ensuring they receive adequate water and nutrients. Regularly check for pests and provide mulch to retain moisture and maintain soil temperature.
Can I grow ginger in pots, and do Bunnings sell suitable pots?
Yes, you can grow ginger in pots as long as they have good drainage. Bunnings offers a variety of pots that are suitable for ginger cultivation, allowing you the flexibility to grow them on patios or balconies.
See also:
If you want to read more articles like Discover the Best Ginger Plants for Sale Bunnings: A Complete Buying Guide, we recommend you check out our Seeds category.
Leave a Reply

Related Articles