Can You Grow Potatoes All Year Round in Australia? A Complete Guide

Growing potatoes is a rewarding venture for many gardeners, but the question of whether you can cultivate them year-round in Australia often arises. With its diverse climates ranging from tropical in the north to temperate in the south, Australia offers unique opportunities and challenges for potato cultivation. This complete guide will explore the best practices for growing potatoes throughout the seasons, including tips on soil preparation, variety selection, and managing pests and diseases. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a novice, this article will equip you with the knowledge to enjoy fresh potatoes all year long.
Can You Grow Potatoes All Year Round in Australia?
In Australia, it is possible to grow potatoes year-round, but the approach varies significantly across different climates within the country. In regions such as Tasmania and parts of Victoria with cooler temperatures, potatoes can be planted from August to November, and a second crop can be sown in early spring. Conversely, in Northern Australia, where the climate is warmer, potatoes can be planted in the dry season between April and November. However, careful management of irrigation and soil conditions is essential to avoid issues such as pest infestations and disease, which can be exacerbated by the climate.
Climate Zones in Australia
Australia has diverse climate zones ranging from tropical in the north to temperate in the south. This diversity affects potato cultivation as the growing season depends largely on local weather patterns. For instance, the temperate southern regions allow for multiple growing cycles, while the northern regions typically experience a single growing season due to the wet and dry seasons. Understanding these climate zones is critical for successful potato production throughout the year.
Best Time to Plant Potatoes
The best time to plant potatoes in Australia varies with the region. In southern areas, the optimal planting months are from August to November, ensuring that plants mature before summer heat sets in. In contrast, the northern regions should focus on planting from April to August, coinciding with the cooler dry season. By aligning planting times with the local climate, growers can enhance yield and minimize the risk of crop failure due to extreme weather conditions.
Soil Preparation for Year-Round Growth
Preparing the soil properly is essential for successful potato cultivation throughout the year. Potatoes thrive in well-drained, loamy soil enriched with organic matter. Before planting, soil should be tested for pH levels, ideally between 5.5 and 7.0, and amended with compost or well-rotted manure to improve nutrient content. Effective soil preparation also includes tilling and removing any weeds to promote a healthy growing environment for the potatoes.
Irrigation Strategies for Potatoes
Proper irrigation is crucial for growing potatoes, particularly in regions where the climate may be too dry. During the growing season, ensuring consistent moisture levels in the soil helps in preventing issues such as scab and blight. Methods such as drip irrigation can be advantageous, as they deliver water directly to the root zone, helping to conserve water and reduce evaporation. Implementing a reliable irrigation system based on the local climate can significantly affect the success of year-round potato cultivation.
Pest and Disease Management
Managing pests and diseases is vital for successful potato growth, especially when attempting to cultivate them throughout the year. Common threats include aphids, potato beetles, and diseases like blight. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies, which combine cultural practices, biological control, and the judicious use of pesticides, can help mitigate these risks. Regular monitoring of plants and prompt action when issues arise is essential for maintaining healthy potato crops.
| Factor | Ideal Conditions |
|---|---|
| Soil Type | Loamy |
| pH Level | 5.5 - 7.0 |
| Planting Months - South | August - November |
| Planting Months - North | April - August |
| Watering Method | Drip irrigation |
Do potatoes grow all year round in Australia?

Potatoes do not grow all year round in Australia. The cultivation of potatoes is influenced by several factors, including climate, soil conditions, and specific growing seasons. Generally, potatoes in Australia are planted in late winter and harvested in spring to early summer, although the exact timing can vary depending on the region.
Growing Seasons for Potatoes in Australia
Potatoes in Australia have specific growing seasons that vary by region. This seasonal planting allows farmers to produce high-quality crops. Typically, the main growing seasons are:
- Winter plantings (July-August): Mainly in southern states.
- Spring plantings (September-October): Common in northern regions.
- Harvesting (November-January): Varies based on planting times.
Regional Variations in Potato Cultivation
Different states in Australia have diverse climates which affect potato growth. Understanding these variations helps in optimizing yields. Key regions include:
- Queensland: Warm climate allows for year-round production in some areas.
- Victoria: Ideal conditions for winter and spring crops.
- Western Australia: Has a unique growing cycle due to Mediterranean climate.
Soil and Climate Requirements
Potatoes thrive in certain soil types and climate conditions. Proper management of these factors is crucial for a good harvest. Important elements include:
- Well-draining soil: Potatoes require loose, fertile soil to grow effectively.
- Climate: Moderate temperatures are ideal; extreme heat can damage crops.
- Water availability: Consistent moisture is necessary without waterlogging.
Potato Varieties and Their Growing Conditions
Different potato varieties have unique preferences and yield performances, which can affect planting decisions. Notable types include:
See also:
- Russet: Prefers cooler climates and is often grown in winter.
- Red potatoes: Thrive in various conditions; common in summer.
- New potatoes: Young and often harvested in early spring.
Challenges in Year-Round Potato Farming
While some regions can plant potatoes year-round, certain challenges exist that can impact production. These challenges include:
- Pest and disease management: Constant growing can lead to increased pest populations.
- Soil nutrient depletion: Continuous planting may require enhanced soil management.
- Market demand fluctuations: Prices can vary throughout the year, affecting profitability.
Is it possible to grow potatoes all year round?

Growing potatoes year-round is a subject of interest for many gardeners and commercial growers. The possibility of cultivating potatoes continuously depends on several factors including climate, potato variety, and cultivation methods. While traditional planting and harvesting times vary by region, advancements in agricultural practices can sometimes allow for a more continuous supply.
Understanding Potato Growing Seasons
Growing seasons for potatoes can greatly vary depending on regional climate. In warmer climates, such as those found in tropical or subtropical areas, it is possible to grow potatoes throughout the year. Alternatively, in colder climates, potatoes are typically planted in the spring and harvested in late summer or early fall.
- In temperate regions, growers often rely on a single growing season.
- Tropical regions may allow for multiple harvests within a single year.
- Seasonal changes influence factors like soil temperature and moisture availability.
Choosing the Right Potato Varieties
Selecting the appropriate potato varieties is crucial for successful year-round cultivation. Some varieties are bred for early maturation, making them suitable for quicker harvests, while others might be more resilient to varying climate conditions.
- Early season varieties can be planted in cooler temperatures.
- Late season varieties may require longer growing conditions but can yield larger potatoes.
- Research on new hybrid varieties can provide options for diverse climates and conditions.
Utilizing High Tunnels and Greenhouses
To grow potatoes all year round, utilizing high tunnels or greenhouses can be beneficial. These structures provide controlled environments that can mitigate adverse weather conditions, allowing for extended growth periods.
- Greenhouses maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels.
- High tunnels protect plants from harsh winds and heavy rain.
- These structures help extend the growing season and improve yield potentials.
Soil Preparation and Fertilization
Proper soil preparation and fertilization are essential for successful potato growth. Adequate soil conditions not only support healthy plant development but also ensure continuous production throughout the year.
- Utilizing well-drained soil enhances root development.
- Regular testing and amending soil with organic fertilizers can improve nutrient availability.
- Crop rotation can maintain soil fertility and manage pests.
Pest and Disease Management
Managing pests and diseases is crucial for successful potato cultivation year-round. Continuous cultivation can lead to increased risk, making proactive management strategies necessary.
- Implementing integrated pest management can minimize harmful infestations.
- Regular monitoring for signs of disease allows for early intervention.
- Utilizing resistant potato varieties can reduce vulnerability to common issues.
Can you grow potatoes over summer?

Yes, you can grow potatoes over summer, but there are several factors to consider to ensure a successful harvest. Potatoes are typically grown in cooler weather, and the traditional planting season usually begins in early spring. However, with the right variety and care, summer planting can yield good results. It's important to choose potato varieties that are suitable for warmer conditions and to manage water and soil temperatures effectively.
Ideal Potatoes Varieties for Summer
When planting potatoes in the summer, it's essential to select varieties that can thrive in the warmer temperatures. Some recommended varieties include:
- Yukon Gold - A versatile choice known for its excellent flavor.
- Red Pontiac - Thrives in warmer weather and produces high yields.
- Sweet Potatoes - While not traditional potatoes, they can be grown successfully in the summer heat.
Optimal Planting Conditions
For successful summer potato cultivation, consider the following conditions:
- Soil Temperature - Potatoes prefer soil temperatures between 60°F and 70°F.
- Sun Exposure - Ensure they receive full sun for at least 6 hours daily.
- Soil Type - Well-drained, loamy soil with good organic content is best.
Watering Techniques
Maintaining proper moisture levels is crucial during the summer months. Here are effective watering techniques:
See also:
- Consistent Watering - Potatoes need regular watering, especially during dry spells.
- Drip Irrigation - This method conserves water and reduces the risk of disease.
- Mulching - Applying mulch helps retain moisture in the soil.
Pest and Disease Management
To ensure your summer potatoes grow healthy, consider pest and disease management strategies:
- Regular Monitoring - Keep an eye out for pests like potato beetles.
- Crop Rotation - Rotating crops helps prevent disease buildup in the soil.
- Organic Treatments - Use organic pesticides when necessary to minimize harm to beneficial insects.
Harvesting Timing
Knowing when to harvest your potatoes is critical for optimal yield. Keep these points in mind:
- Flowering Signs - Harvest new potatoes about two weeks after flowering starts.
- Skin Firmness - For mature potatoes, ensure the skins are firm and not easily rubbed off.
- Weather Considerations - Harvest before heavy rains to prevent waterlogging.
At what temperature do potatoes stop growing?
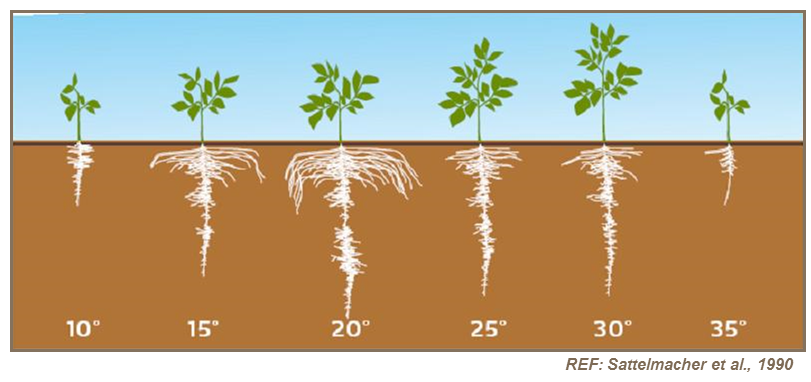
The growth of potatoes is significantly influenced by temperature. Generally, potato plants grow best in temperatures ranging between 60°F and 70°F (15°C to 21°C). Growth starts to slow down when temperatures fall below 50°F (10°C) and can practically stop when temperatures drop to around 32°F (0°C). At this point, potato plants can enter a state of dormancy as they respond to adverse conditions, and this can delay tuber formation.
Effects of Low Temperatures on Potato Growth
Low temperatures can severely affect the physiological processes of potato plants. When exposed to cold:
- Photosynthesis becomes less efficient, reducing the plant's ability to produce energy.
- Enzymatic activity decreases, which slows down growth and development.
- Root systems may become damaged, affecting nutrient absorption.
Signs of Temperature Stress in Potatoes
Potato plants exhibit several signs indicating they are under temperature stress:
- Wilting leaves due to reduced water uptake.
- Discoloration of leaves, turning yellow or purple.
- Slow growth or stunted plants, indicating a halt in development.
Optimal Growing Conditions for Potatoes
To ensure healthy growth, potatoes thrive under optimal conditions:
- Soil temperatures of 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 21°C) are ideal.
- Consistent moisture without waterlogging promotes root development.
- Adequate sunlight, at least 6 hours per day, is essential for maximizing growth.
Temperature Threshold for Tuber Development
The development of potato tubers is highly temperature-sensitive:
- Tuber formation begins when daytime temperatures are above 70°F (21°C).
- If temperatures exceed 80°F (27°C) consistently, tuber bulking may be negatively affected.
- Conversely, temperatures below 50°F (10°C) can delay tuber growth substantially.
Strategies for Managing Temperature in Potato Cultivation
Farmers and gardeners can implement several strategies to manage temperatures effectively:
- Utilize mulching to maintain soil temperature and reduce extreme fluctuations.
- Create shade using nets during high-temperature periods to protect plants.
- Use row covers to provide insulation during colder nights.
Questions from Our Readers
Can you grow potatoes all year round in Australia?
Yes, you can grow potatoes in Australia throughout the year, but it largely depends on the climate of the specific region. In warmer areas, such as northern Australia, you can cultivate potatoes in multiple seasons, while in cooler regions, they are typically grown in the spring and summer.
What is the best time to plant potatoes in Australia?
The best time to plant potatoes in Australia varies by region, but generally, it is between August and December for most areas. In southern regions, planting in spring allows potatoes to grow during the warmer months, while in northern regions, planting can occur in both autumn and spring.
What varieties of potatoes grow well in Australia?
Several varieties of potatoes thrive in Australia, including Royal Blue, Kifler, and Cream Delight. These varieties are well-suited to the Australian climate and can be cultivated for excellent yields and flavor throughout the growing seasons.
Do potatoes require special care when grown year-round?
Yes, growing potatoes year-round requires specific care such as proper watering, soil management, and pest control. Ensuring they have adequate sunlight and protecting them from extreme weather conditions will help support their healthy growth at any time of the year.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like Can You Grow Potatoes All Year Round in Australia? A Complete Guide, we recommend you check out our Seeds category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles