Discovering What Are the Main Vegetation Types in Australia: A Comprehensive Guide

Australia is renowned for its diverse and unique ecosystems, shaped by its varied climate and geography. From the arid expanses of the outback to the lush rainforests of the coast, the continent boasts an array of vegetation types that support a rich tapestry of wildlife. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the primary vegetation types found in Australia, highlighting their characteristics, distribution, and ecological significance. Whether you are an avid botanist, a nature enthusiast, or simply curious about the natural world, understanding Australia's vegetation is essential to appreciating the continent's distinct environmental heritage.
Main Vegetation Types in Australia
Australia boasts a diverse range of vegetation types, influenced by its unique climate, geography, and soils. The continent's vast landscapes are characterized by distinct ecosystems, including tropical rainforests in the north, expansive deserts in the interior, and temperate forests and woodlands along the coast. Grasslands and savannas can also be found, particularly in the northern regions and inland areas, providing crucial habitats for various species. Each vegetation type supports a unique array of flora and fauna, making Australia one of the most biodiverse regions in the world and highlighting the importance of preserving these natural ecosystems.
Tropical Rainforests
Tropical rainforests in Australia are primarily located in the northeastern regions, particularly in Queensland. These forests receive heavy rainfall year-round and are characterized by a high level of biodiversity, housing a variety of plant species, including ferns, palms, and hardwood trees. The dense canopy of these rainforests creates a unique habitat that is home to many endemic species of birds, mammals, and reptiles, making them vital to conservation efforts.
Deserts
Australia's interior is dominated by vast desert regions, such as the Great Victoria Desert and the Simpson Desert. These arid landscapes receive very little rainfall and feature specialized vegetation adapted to extreme dry conditions. Common plants include spinifex grasses and various shrub species, which have evolved to survive in low water environments. Deserts play a crucial role in the ecosystem, providing habitat for uniquely adapted species like the thorny devil lizard and various small mammals.
Woodlands and Savannas
Woodlands and savannas cover a significant portion of Australia, particularly in the northern regions and parts of the south. These ecosystems are characterized by a mixture of scattered trees and grasses, allowing for plenty of sunlight to reach the ground. Species like eucalyptus dominate these areas, and they provide essential habitats for many wildlife species. The seasonal nature of rainfall in these regions supports a range of migratory birds and various insects that thrive in these environments.
Temperate Forests
Temperate forests are found in the southeastern parts of Australia, notably in Tasmania and along the Great Dividing Range. These forests are characterized by deciduous and evergreen trees, including majestic eucalyptus and various hardwood species. The rich understory often consists of ferns and shrubs, creating a lush environment that supports diverse wildlife, including the Tasmanian devil and numerous bird species. The moderate climate contributes to the unique flora and fauna found in these forests.
Grasslands
Grasslands in Australia primarily occur in the eastern and southern regions and are known for their open landscapes dominated by grasses and occasional flowering plants. These ecosystems provide critical grazing areas for livestock and wildlife, including kangaroos and various bird species. Grasslands also play an important role in soil health and are often the focus of conservation and land management practices aimed at maintaining biodiversity and preventing land degradation.
| Vegetation Type | Location | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Tropical Rainforests | Northeastern Australia | High biodiversity, heavy rainfall, dense canopy |
| Deserts | Central Australia | Low rainfall, specialized vegetation, arid climate |
| Woodlands and Savannas | Northern regions | Scattered trees, grasses, seasonal rainfall |
| Temperate Forests | Southeastern Australia (Tasmania) | Deciduous and evergreen trees, rich understory |
| Grasslands | Eastern and Southern Australia | Open landscapes, grazing areas, diverse wildlife |
What are the main types of vegetation?

Types of Forest Vegetation
Forests are one of the most diverse types of vegetation found on Earth. They are classified into various categories based on climate, geography, and types of trees. The main types include:
- Tropical Rainforests - Located near the equator, these forests are characterized by high rainfall and a vast variety of plant species.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests - Found in temperate regions, these forests experience four distinct seasons and contain trees that shed their leaves annually.
- Boreal Forests (Taiga) - These are predominantly found in northern latitudes and are composed mainly of coniferous trees, adapting to colder climates.
Grasslands and Savannas
Grasslands are expansive open spaces dominated by grasses rather than large shrubs or trees. They often occur in regions with lower precipitation and can be classified into:
- Temperate Grasslands - These regions have hot summers and cold winters, featuring deep, nutrient-rich soils ideal for agriculture.
- Tropical Savannas - Found in warmer climates, they are characterized by a mixture of grasses and scattered trees, typically experiencing a distinct wet and dry season.
Desert Vegetation
Deserts are known for their extreme conditions and limited water availability, leading to specialized plant adaptations. The main types include:
- Hot Deserts - These areas have high temperatures and minimal rainfall, with vegetation like cacti and xerophyte plants adapted to conserve water.
- Cold Deserts - Characterized by lower temperatures and seasonal snow, these deserts often have shrubs and hardy grasses that can withstand the cold.
Aquatic Vegetation
Aquatic vegetation exists in water bodies and can be broadly categorized into freshwater and saltwater types. Common forms include:
- Emergent Plants - These are plants that grow in shallow water with their roots submerged but stems and leaves above water (e.g., reeds and cattails).
- Floating Plants - These types float on the surface of water and can include species like lily pads and duckweed.
- Submerged Plants - Found completely underwater, they play crucial roles in aquatic ecosystems, providing habitat and oxygen (e.g., eelgrass).
Marine Vegetation
Marine ecosystems consist of a diverse range of vegetation adapted to saline environments. The primary types are:
- Seagrass Beds - These underwater flowering plants provide essential habitats for marine life and contribute to coastal protection.
- Kelp Forests - Large underwater forests formed by towering kelp species, offering rich biodiversity and support for various marine organisms.
- Coral Reefs - While primarily composed of corals, they include a vast variety of algae and plants, providing critical ecosystems for marine species.
What is the most predominant vegetation in Australia?
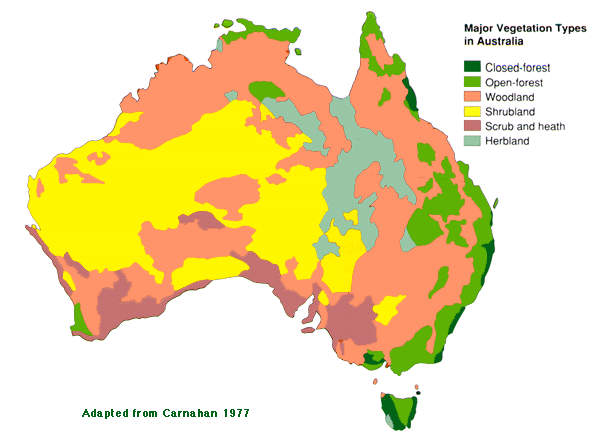
The most predominant vegetation in Australia is sclerophyll forest, which is characterized by tough, drought-resistant leaves. This type of vegetation is primarily found in regions with a Mediterranean climate, where there are hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. However, the overall vegetation of Australia varies across its vast landscapes, including various ecosystems such as shrublands, grasslands, and tropical forests.
Geographic Distribution of Sclerophyll Forests
Australia's sclerophyll forests are mainly located in the eastern and southeastern parts of the continent, including areas such as:
- New South Wales
- Victoria
- Queensland
These forests thrive in regions with well-drained soils and are adapted to survive periodic droughts.
Types of Vegetation in Australia
Australia hosts a diverse range of vegetation types besides sclerophyll forests, including:
- Rainforests: Lush, dense forests found in tropical regions.
- Grasslands: Open areas dominated by grasses, often found in inland regions.
- Desert vegetation: Including drought-resistant shrubs and obligate xerophytes.
Each type of vegetation is adapted to specific climate conditions and soil types across the continent.
Impact of Climate on Vegetation
The climate of Australia greatly influences its vegetation patterns. Key factors include:
- Rainfall: Variability leads to diverse ecosystems, from arid deserts to lush rainforests.
- Temperature: Regions with warmer climates often have thicker vegetation, while cooler areas contain varied types.
- Seasonality: Changes in seasons dictate growth patterns and types of dominant plant species.
These climatic conditions determine which plants can thrive in each environment.
Adaptations of Australian Vegetation
Australian vegetation exhibits unique adaptations to deal with the country's harsh climate, including:
- Drought resistance: Many plants have evolved thick leaves and deep root systems.
- Fire resistance: Certain species have adapted to endure and even benefit from bushfires.
- Soil adaptation: Vegetation has evolved to thrive in poor nutrient soils, utilizing symbiotic relationships with fungi.
These adaptations ensure survival and resilience in a challenging environment.
Biodiversity and Conservation of Australian Vegetation
Australia's vegetation is home to a wide variety of flora and fauna. Important aspects include:
- Unique species: Many plants are endemic to Australia, found nowhere else in the world.
- Conservation efforts: Initiatives are in place to protect endangered species and restore ecosystems.
- Threats: Habitat destruction, climate change, and invasive species pose significant risks to native vegetation.
Conservation aids in maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance in Australian landscapes.
What are the 8x main types of forest in Australia?
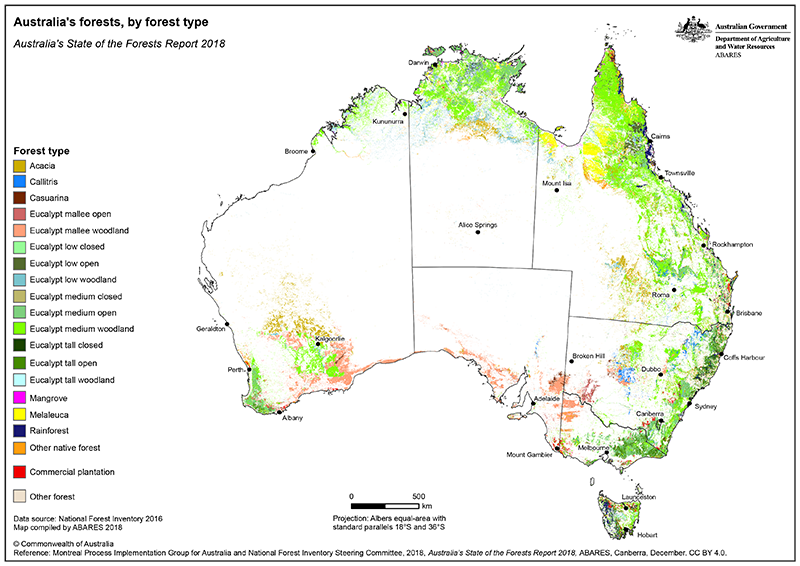
The eight main types of forest in Australia are diverse and reflect the country's unique climate, geography, and ecology. Here is a detailed overview:
1. Eucalyptus Forests
Eucalyptus forests are the most widespread type of forest in Australia and are primarily composed of Eucalyptus species. These forests thrive in a variety of climates and are especially prominent in the eastern and south-eastern regions of the country. They are important for both wildlife and the timber industry.
Characteristics of Eucalyptus Forests
- Dominance of Eucalyptus species
- Adaptation to fire, with many species developing thick bark or other protective features
- Provide habitat for diverse wildlife, including koalas and various bird species
2. Rainforests
Rainforests in Australia are located mainly in the tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in Queensland. These forests are characterized by high rainfall and humidity, making them rich in biodiversity and dense vegetation.
Features of Rainforests
- High biodiversity, housing numerous plant and animal species
- Layered structure, including emergent trees, canopy, understory, and forest floor
- Presence of epiphytes and lianas that contribute to a complex ecosystem
3. Temperate Forests
Found primarily in the cooler regions of Victoria and Tasmania, temperate forests feature a mix of deciduous and evergreen trees. These forests experience distinct seasons, with significant seasonal rainfall.
Attributes of Temperate Forests
- Combination of hardwood and softwood species
- Seasonal leaf shedding, creating rich litter layers
- Support various wildlife, including possums and various bird species
4. Mangrove Forests
Mangrove forests are coastal ecosystems found in intertidal zones, particularly along northern Australia. They are characterized by salt-tolerant trees and serve as vital buffers against coastal erosion.
Importance of Mangrove Forests
- Provide critical habitat for marine species, including fish and crustaceans
- Act as natural protectors against storm surges and flooding
- Support nutrient cycling and carbon storage in coastal areas
5. Dry Sclerophyll Forests
These forests are found in areas with less rainfall and are characterized by hard-leaved species that are drought-resistant. They mainly occur in southern Australia and consist of various Eucalyptus and Acacia species.
Dynamics of Dry Sclerophyll Forests
- Low to moderate biodiversity compared to wetter forests
- Plants adapted to fire and drought conditions
- Home to specific species like kangaroos and various reptiles
6. Woodlands
Woodlands are characterized by widely spaced trees and a more open canopy than forests. They are common in some regions such as New South Wales and parts of Queensland.
Characteristics of Woodlands
- More sunlight reaches the ground, promoting grass and low shrubs
- Support diverse fauna including birds and small mammals
- Often found in semi-arid regions where rainfall is limited
7. Savanna Woodlands
Savanna woodlands are a type of woodland characterized by a mixture of trees and grasses. They cover large areas of northern Australia and are known for their seasonal variations in moisture.
Features of Savanna Woodlands
- Grasslands dominated by scattered trees, often Eucalyptus species
- Seasonal rainfall leads to pronounced wet and dry seasons
- Support a variety of wildlife, such as kangaroos and diverse bird species
8. Alpine Forests
Alpine forests are found in elevated regions, primarily in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales and Victoria. These areas experience colder temperatures and distinct weather patterns.
Attributes of Alpine Forests
- Characterized by a unique selection of cold-tolerant vegetation
- Support wildlife adapted to harsh conditions, including the Alpine Ash tree
- Critical for catchment management and water supply in surrounding regions
What vegetation is most common in the Australian desert?

The most common vegetation in the Australian desert includes a variety of plant species that are uniquely adapted to the harsh conditions of this arid environment. Key characteristics of desert vegetation include drought tolerance, limited rainfall, and extreme temperatures. Common types of vegetation found in the Australian desert include:
1. Acacia species
2. Eucalyptus species
3. Spinifex grass
4. Saltbush
5. Wildflowers
These plants exhibit specific adaptations that allow them to thrive in the challenging climate of the desert.
Adaptations of Desert Plants
Desert plants have developed remarkable adaptations to survive in extreme conditions. These adaptations can be categorized as follows:
- Water Storage: Many desert plants, such as succulents, store water in their leaves or stems to cope with long periods of drought.
- Reduced Leaf Surface Area: Some plants have small or even absent leaves, which reduces water loss through transpiration.
- Deep Root Systems: Plants like Acacia have extensive root systems that can reach deep underground to access moisture and nutrients.
Common Types of Desert Vegetation
Several plant species are predominant in the Australian desert, each playing a vital role in the ecosystem. The most notable include:
- Acacias: Known for their hardiness, these shrubs and trees are vital for providing shade and habitat.
- Eucalypts: These trees can tolerate dry conditions and are critical for stabilizing soil and preventing erosion.
- Spinifex: A type of grass that forms dense mats, providing ground cover and helping preserve moisture.
The Role of Fire in Desert Ecosystems
Fire plays a significant role in shaping the vegetation of the Australian desert. Many species have adapted to regenerate after fire events, enhancing biodiversity. Aspects include:
- Stimulating Growth: Many plants, like certain Acacia species, require fire for germination of their seeds.
- Clearing Competing Species: Fire can reduce competition from other plants, allowing native species to thrive.
- Nutrient Recycling: Fire returns nutrients to the soil, making it accessible for the next generation of plants.
Importance of Soil in Plant Distribution
Soil type and quality play a critical role in determining where vegetation grows in the desert. Several factors include:
- Soil Composition: Sandy or sandy loam soils are common in deserts and can drain quickly, affecting water availability.
- Nutrient Levels: Low nutrient soils require plants to have specialized adaptations to extract what they need for growth.
- Salinity Factors: Plants like saltbush are adapted to higher saline soils, showcasing diverse ecological niches.
Seasonal Variations in Vegetation
The vegetation in the Australian desert experiences significant changes throughout different seasons, impacting species’ growth and survival. Key points include:
- Rainfall Variability: The occurrence of seasonal rains can lead to explosive growth of wildflowers and other annuals.
- Temperature Extremes: The extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night influence plant survival strategies.
- Adaptive Responses: Many plants enter a dormant phase during dry spells to conserve resources until conditions improve.
Questions from Our Readers
What are the main vegetation types in Australia?
Australia is characterized by a diverse range of vegetation types, primarily influenced by its climate and geography. The main types include savannas, forests, woodlands, and shrubs. Each of these types has unique plant species adapted to the varying conditions, including drought-resistant plants in the arid regions and rainforest species in the tropical areas.
How do climate and soil affect vegetation in Australia?
The climate and soil in Australia play a significant role in determining the types of vegetation found in different regions. For instance, the arid interior supports xerophytic plants that thrive in low moisture, while the fertile coastal areas host more diverse and lush vegetation, including rainforests that require higher moisture levels.
Are there any unique plant species found in Australia?
Yes, Australia is home to many unique plant species that are not found anywhere else in the world. Notable examples include the Eucalyptus, which is the most common tree in the country, and the Wollemi pine, a rare species that was thought to be extinct. These species have adapted to the specific climatic and ecological conditions present in Australia.
How does human activity impact Australia's vegetation types?
Human activity has a profound impact on Australia's vegetation types, primarily through urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation. These activities can lead to habitat loss, changes in ecosystem dynamics, and the introduction of invasive species, which threaten the native flora and disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystems.

If you want to read more articles like Discovering What Are the Main Vegetation Types in Australia: A Comprehensive Guide, we recommend you check out our Landscaping category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles