How Do I Know If My Plants Need More Fertilizer? Essential Signs and Tips for Healthy Growth

As a plant owner, ensuring your greenery thrives is a top priority. One key aspect of plant care is understanding when to fertilize. However, determining if your plants need more nutrients can sometimes be challenging. Over-fertilization can harm your plants just as much as under-fertilization. This article will explore essential signs that indicate your plants are craving more fertilizer and provide practical tips for maintaining healthy growth. By recognizing these indicators and applying the right techniques, you can help your plants flourish and enjoy a vibrant, thriving indoor or outdoor garden.
How to Determine If Your Plants Need More Fertilizer
Knowing whether your plants need more fertilizer involves observing several factors related to their growth and overall health. Initially, recognize the signs such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or poor flowering, which may indicate nutrient deficiencies. Additionally, the type of plant and its growth stage play a crucial role; for instance, fast-growing plants typically require more nutrients during their active growth period. Checking the soil quality and conducting a soil test can reveal nutrient levels that inform your fertilization needs. Regular observation and understanding your plants' specific requirements will help maintain their vitality and growth.
Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Plants may exhibit various symptoms that signal a nutrient deficiency. Common signs include yellowing leaves (chlorosis), browning leaf tips, and slow growth. Each of these symptoms can be tied to specific nutrient shortages; for example, nitrogen deficiency often leads to yellowing of older leaves, while a lack of potassium may cause leaf edges to turn brown. Regularly monitoring your plants for these signs can help you determine if they need more fertilizer.
Soil Testing for Nutrient Levels
Conducting a soil test can provide valuable insight into the nutrient composition of your growing medium. This involves taking a sample of your soil, sending it to a lab, or using a home testing kit. The test will indicate levels of primary nutrients—including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—as well as micronutrients. Understanding these levels allows you to tailor your fertilization strategy to correct any imbalances.
Plant Growth Stages and Fertilization Needs
The growth stage of your plants impacts their nutrient requirements significantly. During the vegetative stage, plants generally need higher levels of nitrogen to support leaf and stem development. Conversely, during the flowering or fruiting stage, phosphorus and potassium become more crucial for healthy blooms and fruit production. Adjusting your fertilization routine according to the plants' growth stages maximizes their health and yields.
Type of Plant and Its Nutritional Needs
Different types of plants have unique nutritional needs. For instance, leafy greens tend to require higher nitrogen levels, while flowering plants benefit from nutrient ratios higher in phosphorus. Understanding the specific needs of your plant species can direct you to provide appropriate fertilizer types and quantities, ensuring optimal growth and health.
Timing and Frequency of Fertilization
The timing and frequency of fertilizer applications are essential for plant health. It's advisable to fertilize during the active growing season—typically in spring and summer—when plants are most receptive to nutrients. Following a schedule based on the type of fertilizer being used, whether it’s liquid or granular, can also enhance efficacy. Too much fertilizer can harm plants; thus, observing their response after each application can help guide future practices.
| Symptom | Possible Nutrient Deficiency |
|---|---|
| Yellowing leaves | Nitrogen deficiency |
| Browning leaf tips | Potassium deficiency |
| Slow growth | Multiple nutrient deficiencies |
| Purple leaves | Phosphorus deficiency |
| Leaf drop | Magnesium deficiency |
How to tell if a plant needs more fertilizer?

To determine if a plant needs more fertilizer, it’s essential to observe various factors that indicate nutrient deficiency. Healthy plants exhibit vibrant growth, rich colors, and overall vitality. When a plant lacks sufficient nutrients, especially essential ones like nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium, it will show specific signs. Here are the critical indicators to assess whether your plant requires additional fertilization:
Yellowing Leaves
One of the most common signs that a plant may need more fertilizer is yellowing leaves. This symptom often suggests that the plant is not receiving enough nitrogen, which is vital for leaf development.
See also:
- Inspect the lower leaves first; they may turn yellow while the upper leaves remain green.
- If the entire plant exhibits yellow leaves, it indicates a more generalized nutrient deficiency.
- Consider the plant species, as some might naturally exhibit yellowing during certain growth stages.
Poor Growth
If your plant exhibits stunted growth or is not growing as vigorously as it should, this could signal insufficient nutrients.
- Regularly measure the height and width of your plant to monitor its growth pattern.
- Observe for signs like smaller leaves or fewer flowers compared to usual.
- Compare your plant’s growth with similar plants grown under similar conditions for insight.
Wilting Despite Adequate Watering
A plant that wilts even when watered properly may be struggling with nutrient availability. Essential nutrients can affect the plant's ability to absorb and retain water.
- Check the soil moisture level; sometimes over-fertilization can lead to root burnout.
- Look for signs that the plant is struggling to transport water effectively.
- Ensure drainage is adequate to avoid root rot, which can mimic nutrient deficiency symptoms.
Leaf Drop
A sudden leaf drop can also indicate that a plant is stressed due to nutrient deficiencies or imbalances.
- Look for leaves dropping primarily from the bottom of the plant, which may show nitrogen deficiency.
- Monitor the environmental conditions; stress from over-fertilization or drought can exacerbate drop.
- Pay attention to how frequently the plant is losing leaves compared to its normal behavior.
Pest Infestation
A poorly nourished plant may become a target for pests, as it is weaker and less able to defend itself.
- Inspect the plant regularly for pests, especially if you notice other signs of nutrient deficiency.
- Weakened plants might have a reduced ability to recover from pest damage.
- Evaluate whether nutrient-rich fertilizers may enhance the plant's natural defenses.
How do I know when to add more fertilizer?

To determine when to add more fertilizer to your plants, it's important to assess several factors that can indicate nutrient deficiency. Here are some key indicators to consider:
Plant Growth Stages
The growth stage of your plants significantly influences their nutrient requirements. During different phases, they may need varying amounts of fertilizer.
- Seedling Stage: Young plants require lower nutrient levels to establish roots.
- Vegetative Stage: As plants grow, they need more nitrogen for leaf development.
- Flowering and Fruiting Stage: Increased phosphorus and potassium are essential during this period for flowering and fruit set.
Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Observing the physical appearance of your plants can reveal if they need more fertilizer. Certain symptoms are indicative of specific nutrient shortages.
- Yellowing Leaves: Often a sign of nitrogen deficiency.
- Purple Leaves: Can indicate phosphorus deficiency, especially in young plants.
- Stunted Growth: Can signal multiple nutrient deficiencies or imbalances.
Soil Tests
Conducting soil tests provides a scientific approach to understanding the nutrient content of your soil, allowing for more accurate fertilizer application.
- pH Level: Determines nutrient availability; some nutrients are less available at high or low pH levels.
- Nutrient Analysis: Tests can reveal specific nutrient levels (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) in the soil.
- Soil Type: Different soil types hold nutrients differently, affecting how much fertilizer to apply.
Time of Year
The season can greatly influence plant nutrient needs. Timing your fertilizer applications to align with plant growth cycles is crucial.
See also:
- Spring: Generally the best time to fertilize as plants resume active growth.
- Summer: May require additional feeding, particularly for fast-growing plants.
- Fall: Focus on preparing perennials for winter; avoid high-nitrogen fertilizers that promote new growth.
Fertilizer Type and Release Rate
Different fertilizers have varying compositions and release rates, which can affect how frequently you need to reapply.
- Slow-Release Fertilizers: These provide nutrients over an extended period; reapplication is less frequent.
- Liquid Fertilizers: Typically absorbed quickly; may require more regular applications.
- Organic vs. Synthetic: Organic fertilizers may improve soil health but generally release nutrients more slowly than synthetic options.
How to tell if a plant needs more nutrients?
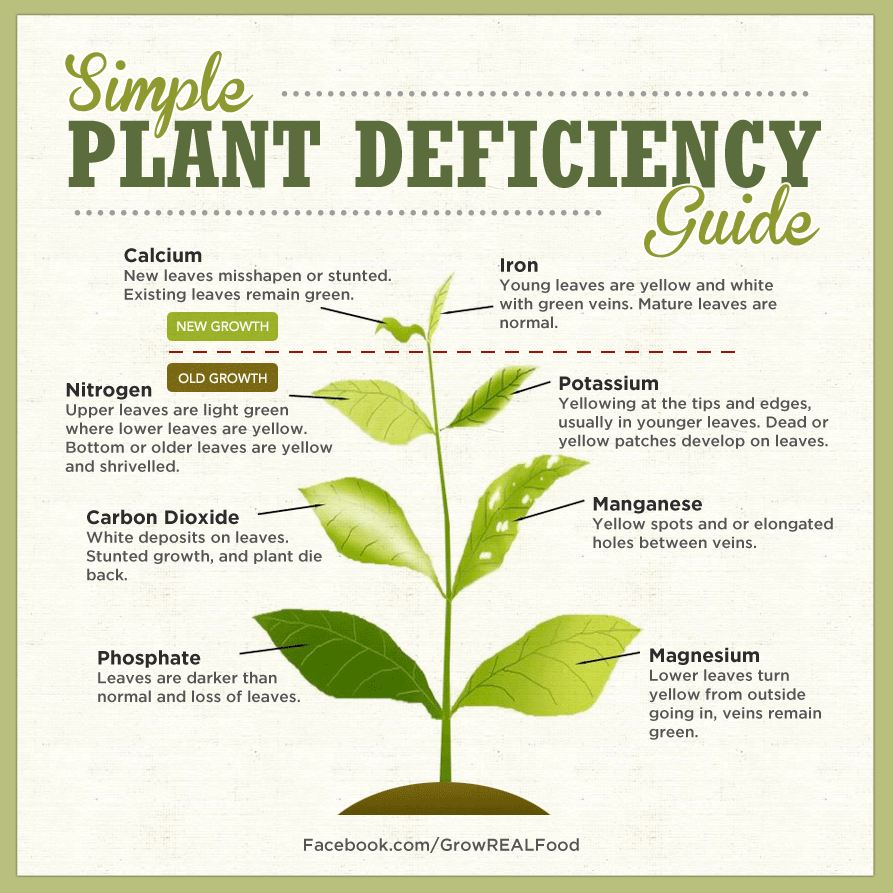
To determine if a plant needs more nutrients, several signs can be observed. These signs often manifest as changes in the plant's appearance and growth habits. Monitoring these indicators can help ensure your plants receive the necessary nutrients for optimal health.
Visual Symptoms of Nutrient Deficiency
One of the most noticeable ways to tell if a plant needs more nutrients is by observing its physical symptoms. Plants may exhibit specific signs depending on the nutrient that is lacking. Common symptoms include:
- Yellowing leaves: A lack of nitrogen often causes older leaves to yellow.
- Brown leaf edges: Potassium deficiency may result in browning or scorching of leaf tips.
- Pale new growth: New leaves may appear very light green or yellow if the plant lacks essential nutrients like magnesium.
Stunted Growth and Poor Development
Another indicator that a plant needs more nutrients is the overall growth pattern. If a plant appears stunted or is not reaching its expected size, it may not be receiving adequate nutrition. Specific indicators of stunted growth include:
- Shorter height: Plants may not grow as tall as usual.
- Smaller leaves: New leaves may be smaller than the standard size for the species.
- Reduced number of blooms: Flowering plants may produce fewer flowers if they are nutrient-deficient.
Changes in Leaf Shape and Texture
Nutrient deficiencies can also cause alterations in the shape and texture of leaves. These changes are not always easy to interpret, but they are critical for diagnosis. Look for:
- Wrinkled or curled leaves: A lack of essential nutrients can stress the leaves, causing them to curl or wrinkle.
- Discoloration spots: Certain nutrient deficiencies can lead to spotting or patches on leaves, which can be a sign of deficiencies like calcium or molybdenum.
- Necrosis: Areas of dead tissue on leaves may indicate severe nutrient shortages, often seen with potassium or magnesium deficiencies.
Pest and Disease Susceptibility
Nutrient-deficient plants are often more susceptible to pests and diseases. A healthy plant has the resilience to fight off attacks, but a weakened plant may show:
- Increased pest infestations: Fewer nutrients can make plants more attractive to pests.
- Higher disease incidence: Deficiencies may weaken a plant's immune system, leading to disease.
- Slow recovery: If a plant is sick or damaged, it may take longer to recover if nutrients are lacking.
Soil Testing and Nutrient Profiles
The most definitive method to determine if your plant needs more nutrients is through soil testing. This allows you to understand the nutrient levels in the soil better. Key aspects include:
- Soil tests: Conduct a routine soil test to assess nutrient levels like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Nutrient balance: Assess whether the soil has an adequate balance of nutrients or if it requires amendments.
- pH levels: Ensure the soil pH is within the ideal range for your plant, as it can affect nutrient availability.
Questions from Our Readers
How can I tell if my plants are lacking nutrients?
If your plants show signs of yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or poor flowering, it may indicate a lack of essential nutrients. Regularly inspecting your plants for these symptoms will help you determine if they need more fertilizer.
How often should I fertilize my plants?
The frequency of fertilization varies depending on the type of plant and the growing season. Generally, it’s recommended to fertilize every 4 to 6 weeks during the active growing period, but it's crucial to monitor your plants for any signs of over-fertilization.
See also:
What are the signs of over-fertilization?
Signs of over-fertilization can include browning leaf tips, leaf drop, and a build-up of salts in the soil. If you notice these symptoms, it's essential to reduce the amount of fertilizer and possibly flush the soil with water to remove excess nutrients.
Can different plants have different fertilizer needs?
Yes, different plants have varying nutrient requirements based on their species, growth stage, and environment. Familiarizing yourself with the specific fertilizer needs of each type of plant you grow will help ensure they receive the appropriate nutrients.

If you want to read more articles like How Do I Know If My Plants Need More Fertilizer? Essential Signs and Tips for Healthy Growth, we recommend you check out our Fertilise category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles