What are the names of the different types of soil? A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Varieties

Soil is a fundamental resource that supports life on Earth, playing a critical role in agriculture, ecology, and environmental sustainability. Understanding the various types of soil is essential for gardeners, farmers, and environmentalists alike, as each type possesses unique characteristics that affect plant growth and ecosystem health. This comprehensive guide will explore the different names and classifications of soil, including sandy, clay, silt, loamy, and others, highlighting their properties, benefits, and drawbacks. By delving into the diverse world of soil varieties, readers will gain valuable insights into how these natural resources influence agriculture and the environment.
Types of Soil and Their Characteristics
Soil is a vital natural resource that can be categorized into various types based on its texture, structure, and composition. The primary types of soil include sandy, clay, silt, sandy loam, clay loam, and loamy soils. Each type has distinct characteristics that influence its water retention, nutrient availability, and suitability for different plant species. For instance, sandy soils are well-draining but low in nutrients, while clay soils tend to retain moisture but can become compacted, making them difficult for root growth. Understanding these different soil types is essential for effective agriculture and land management.
Sandy Soil
Sandy soil is characterized by its larger particles and gritty texture, allowing for excellent drainage and aeration. This type of soil warms up quickly in the spring, making it ideal for early planting. However, sandy soil is low in nutrients and does not retain moisture well, requiring regular irrigation for successful crop growth. Its high permeability can lead to rapid nutrient leaching, posing challenges for sustainable land use.
Clay Soil
Clay soil consists of very fine particles that are tightly packed together, creating a dense and heavy texture. This type retains water remarkably well, but its poor drainage and tendency to become compacted can hinder root development. While clay soil is rich in nutrients, its management requires careful attention to prevent waterlogging and enhance its aeration, making it a bit challenging for gardening without proper amendments.
Silt Soil
Silt soil contains medium-sized particles that provide a balance between drainage and moisture retention, making it highly fertile and ideal for agriculture. Silt retains nutrients effectively, promoting healthy plant growth. Despite its excellent properties, silt soil can become easily compacted and erode when dry. It is essential to manage silt soil through effective practices to maintain its structure and fertility.
Sandy Loam Soil
Sandy loam soil is a combination of sand, silt, and clay, providing a harmonious balance of drainage and nutrient retention. This soil type is highly fertile and ideal for a wide variety of plants, as it allows for good root development while still holding moisture. Its texture supports healthy microbial life and enhances soil structure, making it a preferred choice for most gardeners and farmers seeking productive growing conditions.
Clay Loam Soil
Clay loam soil is a mixture of clay, silt, and sand that offers a balance of fertility, moisture retention, and drainage. This soil type has a rich nutrient profile, making it suitable for diverse plants and crops. The combination of textures allows for good soil aeration while still holding enough moisture to promote healthy growth. Clay loam is considered one of the best types of soil for agricultural purposes due to its versatility and balanced properties.
| Soil Type | Characteristics | Nutrient Retention | Drainage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy Soil | Gritty texture, well-draining | Low | Excellent | Quick-growing crops |
| Clay Soil | Dense, compacted, high moisture retention | High | Poor | Heavy feeders |
| Silt Soil | Fine particles, fertile | Moderate to High | Moderate | General gardening |
| Sandy Loam Soil | Balanced texture for drainage and fertility | High | Good | Most plants |
| Clay Loam Soil | Good balance of clay and sand | High | Moderate | Diverse crops |
What are the 10 types of soil?
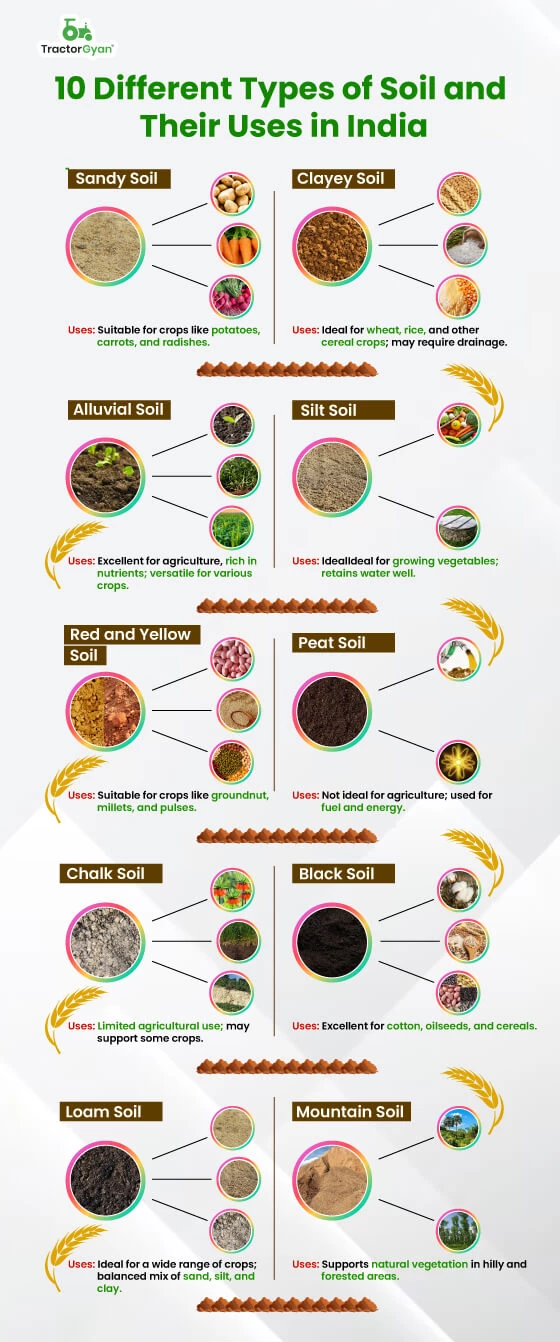
Soils can be classified into various types based on their physical and chemical properties. Here are the ten main types of soil:
1. Clay Soil: This type is composed of very fine particles and has a high capacity for water retention but poor drainage.
2. Sandy Soil: Characterized by large particles, sandy soil drains quickly and does not hold nutrients well.
3. Silty Soil: Silty soil feels smooth and is high in nutrients, making it fertile, but it can retain too much water.
4. Peaty Soil: Rich in organic material, peaty soil is dark and spongy, providing good moisture retention.
5. Saline Soil: This soil has high levels of salt, which can be detrimental to most plants.
6. Chalky Soil: Containing limestone, chalky soil is alkaline and often gives a stony texture, affecting nutrient availability.
7. Loamy Soil: A balanced mixture of clay, sand, and silt, loamy soil is ideal for gardening due to its fertility and good drainage.
8. Alluvial Soil: Found near rivers and floodplains, alluvial soil is rich in nutrients and highly fertile.
9. Laterite Soil: Typically found in tropical regions, laterite soil is rich in iron and aluminum but poor in nutrients.
10. Podzolic Soil: Usually found in cooler climates, podzolic soil is characterized by leaching, leading to a distinct layer of leached nutrients.
Properties of Clay Soil
Clay soil has unique properties that greatly affect its use and management in agriculture and gardening. The fine particles in clay make it extremely dense and compacted, causing poor drainage but excellent water retention abilities.
See also:
- Excellent water retention
- Poor drainage capabilities
- Heavy and dense texture
Characteristics of Sandy Soil
Sandy soil is known for its coarse texture, which allows water to drain swiftly, making it a challenge for retaining moisture and nutrients. Due to this, certain crop types perform better.
- Quick drainage
- Low nutrient retention
- Light and loose texture
The Fertility of Silty Soil
Silty soil is regarded as one of the most fertile types of soil due to its nutrient-rich characteristics. Its smooth texture makes it ideal for growing various plants, though careful management is essential to prevent waterlogging.
- Smooth texture
- High nutrient content
- Prone to water retention issues
Understanding Peaty Soil
Peaty soil is rich in organic material, resulting from the accumulation of decomposed plant material in wet conditions. This type of soil is beneficial for growing certain plants but can become too acidic over time.
- High organic matter content
- Excellent moisture retention
- Acidic nature over time
Properties of Loamy Soil
Loamy soil is often considered the best soil type for agricultural practices because it has a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay. This combination results in good drainage and excellent nutrient holding capabilities.
- Balanced composition
- Good drainage properties
- High fertility levels
What are the 4 main types of soil?
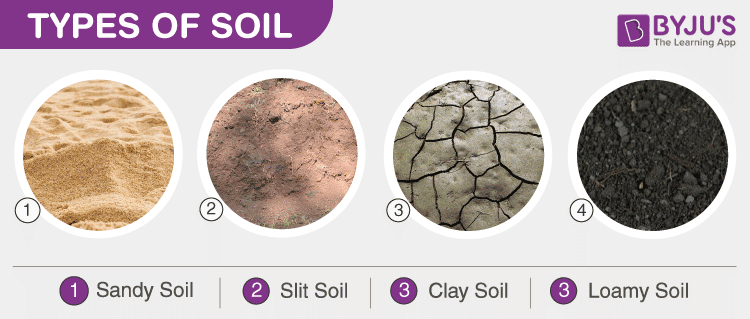
The four main types of soil are:
1. Sand
2. Silt
3. Clay
4. Loam
Sand Soil
Sand soil is characterized by its larger particle size and low water retention capacity. It drains quickly, making it difficult for plants to access moisture. Here are some key features of sand soil:
- Good drainage: Water drains away rapidly, preventing root rot.
- Heating: Sand warms up quickly in the spring, leading to early planting opportunities.
- Nutrient deficiency: Sand soil often lacks nutrients, requiring additional fertilizers for plant growth.
Silt Soil
Silt soil has medium-sized particles and retains moisture better than sand soil. This type of soil is fertile and holds nutrients well, making it suitable for many crops. Key characteristics include:
- High fertility: Rich in nutrients, silt soil is ideal for agricultural purposes.
- Good moisture retention: It holds more water than sand, providing a stable environment for plants.
- Fine texture: Silty soil feels smooth to the touch, making it easy to work with.
Clay Soil
Clay soil is composed of very fine particles that are tightly packed together. This type of soil is known for its poor drainage and can become compacted easily. Some essential aspects include:
- High water retention: Clay holds water well, which can lead to problems with overwatering.
- Reduced aeration: The compact nature of clay can limit the flow of air to plant roots.
- Temperature regulation: Clay warms slowly in the spring but retains heat well, which can benefit some plants.
Loam Soil
Loam soil is a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, making it one of the most desirable soils for gardening and agriculture. Its characteristics include:
See also:
- Ideal for plant growth: Loam provides an excellent environment due to its fertility and good structure.
- Balanced drainage: It retains moisture while allowing excess water to drain away effectively.
- Easy to cultivate: The texture of loam makes it easy to till and work with, promoting healthy root development.
What type of soil is best for planting?

The best type of soil for planting largely depends on the specific plants you wish to grow, but generally, loamy soil is considered ideal due to its balanced composition. Loamy soil retains moisture, has good drainage, and is rich in nutrients, which provides an optimal environment for seed germination and root development.
Characteristics of Loamy Soil
Loamy soil is composed of a mixture of sand, silt, and clay, making it versatile and suitable for various plants. Its characteristics include:
- Good Drainage: Loamy soil allows excess water to escape while retaining enough moisture for plant roots.
- Nutrient-Rich: The organic material in loamy soil promotes a fertile environment filled with essential nutrients.
- Easy to Work With: Loamy soil is typically softer and easier to till, facilitating planting and maintenance.
Importance of Soil pH
Soil pH plays a critical role in plant health by affecting nutrient availability. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH level (around 6.0 to 7.0). Key points regarding soil pH include:
- Affect on Nutrients: Soil pH influences how well plants can absorb nutrients; incorrect pH can lead to deficiencies.
- Adjusting pH: Amending soil with lime can increase pH, while sulfur can lower it for optimum growing conditions.
- Testing Soil: Regular soil testing can help monitor pH levels and make necessary adjustments for plant health.
Types of Soil Amendments
Adding soil amendments can enhance soil quality and promote healthy plant growth. Common amendments include:
- Compost: It adds organic matter, improving soil structure and nutrient availability.
- Manure: Well-rotted manure enriches soil with nutrients and beneficial microorganisms.
- Pearlite or Vermiculite: These substances improve aeration and drainage, especially in heavy clay soils.
Soil Testing and Preparation
Before planting, soil testing helps determine nutrient content and pH balance. Proper soil preparation involves:
- Removing Debris: Clearing old plant matter and debris creates a clean slate for new plantings.
- Testing Nutrients: Utilizing soil test kits will inform you of the existing nutrient levels and pH.
- Mixing Amendments: Incorporate amendments based on test results to enhance soil fertility and structure.
Soil Types for Specific Plants
Various plants thrive in different soil types. Understanding these preferences can guide your planting choices. Consider the following:
- Sandy Soil: Excellent for root vegetables, as it promotes good drainage and warmth.
- Clay Soil: Retains moisture and nutrients, suitable for plants like rice and willows.
- Peat Soil: Acidic and rich in organic matter, ideal for acid-loving plants like blueberries and azaleas.
Questions from Our Readers
What are the main types of soil?
The main types of soil are typically categorized into sand, silt, clay, and loam. Each of these types has distinct properties that affect their water retention, fertility, and drainage capabilities.
How do soil types differ in texture?
The texture of soil refers to the size of its particles, which can range from fine (like clay) to coarse (like sand). A soil's texture affects its aeration, moisture retention, and overall health, making it crucial for plant growth.
What is the importance of different soil types for agriculture?
Different soil types play a critical role in agriculture because they influence crop selection, irrigation needs, and soil fertility. For instance, loamy soils are known to be ideal for many crops due to their balanced structure, promoting healthy growth.
Can soil types be altered for better use?
Yes, soil types can often be altered through various management practices, such as adding organic matter or using soil amendments to improve texture and fertility. This can enhance the soil's ability to support plant life more effectively.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like What are the names of the different types of soil? A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Varieties, we recommend you check out our Soil category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles