What are the disadvantages of plastic greenhouses? A Comprehensive Guide

Plastic greenhouses have gained popularity among gardeners and commercial growers alike for their affordability and ease of installation. However, despite their advantages, there are several disadvantages that potential users should consider. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the downsides of plastic greenhouses, including their durability, insulation properties, and environmental impact. Understanding these limitations is crucial for anyone looking to invest in a greenhouse, as it can influence both the success of their gardening endeavors and their long-term sustainability. Join us as we delve into the various challenges associated with plastic greenhouses and how they compare to alternative options.
What Are the Disadvantages of Plastic Greenhouses?
Plastic greenhouses, while popular for their cost-effectiveness and ease of assembly, come with several significant disadvantages that can impact their long-term viability for growers. One of the primary issues is their durability; over time, exposure to UV radiation can cause the plastic to degrade and become brittle, leading to cracks and leaks. Additionally, plastic greenhouses generally offer less insulation compared to their glass counterparts, making it challenging to maintain optimal temperature levels, particularly in extreme weather conditions. They may also trap excess moisture, leading to a higher incidence of diseases and pests. Furthermore, the reliance on plastic raises environmental concerns, as most plastics are not biodegradable and can contribute to pollution. Lastly, cleaning and maintaining clarity in the plastic panels can be more labor-intensive and may require specialized cleaners to prevent algae build-up.
Durability Issues
One of the main disadvantages of plastic greenhouses is their lack of durability compared to traditional glass greenhouses. Over time, the plastic can become brittle from UV exposure, resulting in cracks that can compromise the greenhouse's integrity. These cracks allow for air and water leakage, which can seriously affect the growing conditions inside.
Insulation Challenges
Plastic greenhouses tend to provide inferior insulation compared to glass structures. This means that during colder months, it can be difficult to maintain a consistent and optimal temperature for plants, often requiring additional heating systems that increase operational costs and energy consumption.
Pest and Disease Risks
The moist environment that often develops inside plastic greenhouses can create an ideal breeding ground for various pests and diseases. The lack of proper ventilation can lead to condensation, which not only fosters fungal growth but also attracts unwanted insects, making pest management a more challenging task.
Environmental Concerns
The environmental impact of plastic greenhouses cannot be overlooked. Most plastics are derived from fossil fuels and are not biodegradable, raising concerns over long-term pollution. Additionally, when plastic greenhouses reach the end of their life cycle, they often contribute to the growing issue of plastic waste in landfills.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Maintaining clarity in plastic greenhouse panels is another challenge that can be labor-intensive. Algae and dust can accumulate quickly, requiring regular cleaning with specialized solutions to ensure sufficient light penetration. This necessity adds to the upkeep costs and time, which might detract from other gardening activities.
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Durability Issues | Plastic degrades over time due to UV exposure, leading to cracks. |
| Insulation Challenges | Inadequate insulation makes temperature control difficult. |
| Pest and Disease Risks | Moisture can foster pest infestations and disease outbreaks. |
| Environmental Concerns | Plastics are not biodegradable and contribute to pollution. |
| Cleaning and Maintenance | Regular cleaning is required to maintain light penetration. |
What are the 5 disadvantages of the greenhouse effect?
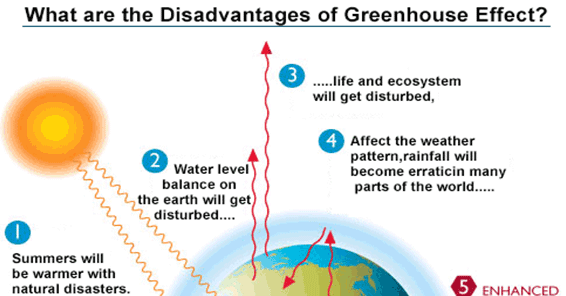
1. Increased Global Temperatures
The greenhouse effect leads to an overall increase in global temperatures. This phenomenon has several serious implications, including but not limited to:
- Heat Waves: More frequent and intense heat waves can occur, posing health risks to vulnerable populations.
- Melting Ice Caps: Increased temperatures can cause polar ice caps and glaciers to melt, contributing to rising sea levels.
- Climate Extremes: Such temperature fluctuations can exacerbate extreme weather conditions, such as hurricanes and droughts.
2. Ocean Acidification
As the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases due to the greenhouse effect, a significant portion is absorbed by oceans, leading to ocean acidification. The consequences include:
- Coral Reefs Damage: Lower pH levels negatively impact coral reefs, which are vital for marine biodiversity.
- Shellfish Challenges: Organisms like oysters and clams struggle to form shells, affecting fisheries and the food supply.
- Altered Ecosystems: Various marine ecosystems face disruption, which can result in loss of species and biodiversity.
3. Impacts on Agriculture
The greenhouse effect directly influences weather patterns that are critical for agriculture. These impacts include:
- Crop Yields: Changes in temperature and precipitation can reduce crop yields, threatening food security.
- Pest Infestations: Warmer conditions can lead to an increase in pests and diseases that affect crops, further endangering food production.
- Water Scarcity: Altered rainfall patterns may lead to droughts, limiting water availability for irrigation.
4. Loss of Biodiversity
The greenhouse effect poses a significant threat to the planet's biodiversity. With changes in climate, many species face:
See also:
- Habitat Changes: Shifts in temperature and weather can lead to habitat destruction and alteration, impacting wildlife.
- Species Extinction: Many species that cannot adapt quickly enough to changing conditions may face extinction.
- Migration Patterns: Animals may be forced to migrate to more favorable climates, disrupting existing ecosystems.
5. Health Risks
The greenhouse effect can lead to significant public health challenges. Some of the key health risks include:
- Heat Stress: Increased temperatures can lead to heat-related illnesses, particularly among vulnerable groups like the elderly.
- Respiratory Issues: Poor air quality associated with climate change can exacerbate respiratory conditions like asthma.
- Infectious Diseases: Changing climates can expand the habitats of disease-carrying organisms (like mosquitoes), increasing disease transmission.
What should you not grow in a greenhouse?

When considering what to grow in a greenhouse, there are certain plants that are generally not well-suited for this controlled environment. A greenhouse provides warmth, humidity, and protection from pests, but not all plants thrive under these conditions. Here are some plants you should avoid growing in a greenhouse:
1. Plants Requiring Cold Climates
Some plants thrive in cold climates and may suffer in the warm, humid conditions of a greenhouse. These include:
- Blueberries - Native to colder regions, they require certain chilling hours to produce fruit.
- Rhubarb - This plant prefers cool temperatures and can bolt (flower prematurely) in heat.
- Peonies - They thrive best in cooler conditions and may not perform well in a greenhouse setting.
2. Plants Prone to Mold and Fungal Diseases
The humid environment of a greenhouse can promote the growth of mold and fungal diseases. Some plants are particularly susceptible, such as:
- Strawberries - While they can grow well in a greenhouse, they are prone to botrytis blight in humid conditions.
- Ferns - These can develop mold due to excessive moisture in a greenhouse.
- Cucumbers - Although some varieties do well, they are often susceptible to powdery mildew in warm, damp conditions.
3. Very Large or Vining Plants
Some plants can become unwieldy in the confined space of a greenhouse, making them challenging to manage:
- Grapes - While they can be grown in a greenhouse, their vigorous growth can quickly take over.
- Squash - Their sprawling nature can make it difficult to maintain space and airflow.
- Corn - Tall and bulky, they may not be practical in smaller greenhouses.
4. Legumes with Extensive Root Systems
Plants like legumes can sometimes have extensive root systems that may be unsuitable for greenhouse growing:
- Peas - Though they can be grown in greenhouses, they often do better outdoors.
- Beans - They can take up a lot of space and may not perform as well in high humidity.
- Chickpeas - They prefer to grow in well-drained soil and can struggle with excess moisture.
5. Weedy or Invasive Species
Certain plants are considered weeds or invasive species and should be avoided in any growing environment, including greenhouses:
- Purslane - This plant can spread rapidly and outcompete other plants for resources.
- Mint - It is notorious for its invasive roots that can take over garden spaces.
- Creeping Jenny - This low-growing plant can be difficult to control in a confined area.
How long do plastic greenhouses last?

Plastic greenhouses can last anywhere from 5 to 15 years, depending on several factors including the quality of the materials used, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. The frame material, type of plastic covering, and the overall construction quality all play crucial roles in determining the longevity of a plastic greenhouse.
Factors Affecting the Longevity of Plastic Greenhouses
The lifespan of a plastic greenhouse is significantly influenced by several key factors:
- Material Quality: Higher quality plastics, like polycarbonate or UV-stabilized polyethylene, tend to last longer and resist degradation from sunlight.
- Environmental Conditions: Harsh climates, such as extreme temperatures, intense sunlight, or heavy snowfall, can shorten the life of a greenhouse.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including cleaning the plastic and checking for tears or damage, can extend the lifetime of the greenhouse.
Types of Plastic Used in Greenhouses
Different types of plastic materials are used for greenhouse coverings, which can affect their durability:
See also:
- Polyethylene: Typically lasts 5 to 10 years and is vulnerable to UV deterioration unless treated.
- Polycarbonate: More durable and can last upwards of 10 to 15 years, providing better insulation and resistance to impact.
- Acrylic: Offers good light transmission and can last up to 15 years, although it's more expensive than polyethylene.
Impact of Climate on Plastic Greenhouses
Climate plays a significant role in determining how long a plastic greenhouse lasts:
- Sun Exposure: Extended exposure to the sun can degrade plastic more quickly, reducing its lifespan.
- Temperature Variations: Fluctuations between hot and cold can lead to material stress, contributing to wear and tear.
- Weather Conditions: Frequent snow, rain, and wind can physically damage the structure and covering, necessitating repairs or replacement.
Proper Installation for Longevity
The way a plastic greenhouse is installed is crucial for its lifespan:
- Foundation: A solid foundation helps prevent shifting and settling, which can lead to structural issues.
- Frame Construction: Quality frames constructed from strong materials help support the plastic covering effectively.
- Sealing and Insulation: Proper sealing can prevent moisture buildup, which can lead to mold and mildew that degrade materials.
Signs That a Plastic Greenhouse Needs Replacement
Knowing when to replace a plastic greenhouse is essential for ongoing gardening success:
- Visible Damage: Cracks, tears, or discoloration in the plastic are strong indicators that replacement is necessary.
- Insulation Properties: If plants are not thriving due to poor insulation, it may be time for a new covering.
- Structural Integrity: If the frame shows signs of rust or weakness, the greenhouse may no longer be safe or effective.
Are plastic-covered greenhouses any good?

Plastic-covered greenhouses, often referred to as polycarbonate or poly film greenhouses, can be an excellent investment for both amateur and professional gardeners. They provide several advantages that can enhance plant growth and extend the growing season. However, they also come with certain disadvantages that gardeners need to consider before making a purchase. Below is a detailed examination of their benefits and drawbacks.
Advantages of Plastic-Covered Greenhouses
One of the primary benefits of plastic-covered greenhouses is their affordability compared to glass greenhouses. They also offer remarkable insulation properties, which help maintain a stable temperature inside. Here’s a list of their significant advantages:
- Cost-effective: Plastic greenhouses are generally cheaper to install and maintain than their glass counterparts.
- Light Transmission: Plastic films can allow over 90% of sunlight to enter, promoting healthy plant growth.
- Insulation: They provide excellent insulation, keeping the internal temperature higher in cold conditions while remaining cooler during hot weather.
Disadvantages of Plastic-Covered Greenhouses
Despite their many advantages, plastic-covered greenhouses also have some drawbacks that should be taken into account. These can affect their longevity and performance. Here are the key disadvantages:
- Durability: Plastic covers can degrade over time due to UV exposure and harsh weather conditions.
- Maintenance: They may require more frequent repairs and replacements compared to glass structures.
- Condensation: Plastic can create condensation, leading to potential issues with mold and mildew if not ventilated properly.
Comparison with Glass Greenhouses
When it comes to material comparison, plastic-covered greenhouses and glass greenhouses offer different benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these differences can help gardeners make informed decisions:
- Weight: Plastic is significantly lighter than glass, making plastic greenhouses easier to transport and set up.
- Installation: Plastic greenhouses typically require less complicated installation; they can be assembled quickly.
- Longevity: Glass can last much longer, while plastic may need replacement every few years.
Best Plants for Plastic-Covered Greenhouses
Plastic-covered greenhouses are versatile and can accommodate a wide variety of plants. However, some species thrive better under plastic cover than others. The following are some of the best plants suited for these greenhouses:
- Herbs: Basil, parsley, and cilantro grow well and benefit from a controlled environment.
- Vegetables: Crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers often flourish in the warmth provided by plastic greenhouses.
- Flowers: Many annuals and perennials, such as geraniums and petunias, can be successfully cultivated.
Choosing the Right Plastic for Your Greenhouse
Selecting the appropriate type of plastic cover is crucial for the efficiency and effectiveness of a greenhouse. Different materials offer different levels of insulation, durability, and light transmission. Here’s what you should consider:
- Polyethylene Film: This is a common choice, offering excellent light transmission but will need replacement every 3-5 years.
- Polycarbonate Panels: These are more durable and resistant to UV degradation, although they may come at a higher cost.
- Greenhouse Shade Cloth: Useful for regulating temperature during hot months; it can be used in conjunction with plastic covers to provide better climate control.
Questions from Our Readers
What are the main disadvantages of plastic greenhouses?
Plastic greenhouses can have several disadvantages, such as limited durability compared to traditional glass greenhouses, which can lead to increased maintenance costs and the need for replacement. Additionally, they can suffer from reduced light transmission over time, as UV rays can degrade the plastic, impacting plant growth.
Do plastic greenhouses provide adequate insulation?
While plastic greenhouses offer some insulation, they typically do not insulate as well as glass structures. This can result in temperature fluctuations that may be detrimental to sensitive plants, requiring additional heating or cooling measures to maintain a stable environment.
See also:
Are plastic greenhouses environmentally friendly?
Plastic greenhouses pose environmental concerns since they are often made from materials that are not biodegradable and can contribute to plastic waste if not properly recycled. The production and disposal processes of these plastics can also have a significant carbon footprint.
How does weather affect plastic greenhouses?
Plastic greenhouses can be vulnerable to extreme weather conditions, such as heavy winds or hail, which can lead to damage or even complete failure of the structure. Additionally, prolonged exposure to harsh weather can shorten the lifespan of the plastic material used in these greenhouses.

If you want to read more articles like What are the disadvantages of plastic greenhouses? A Comprehensive Guide, we recommend you check out our Greenhouse category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles