Is It Better for a Greenhouse to Get Morning or Afternoon Sun? A Comprehensive Guide to Maximizing Plant Growth

When it comes to maximizing plant growth in a greenhouse, one crucial factor often overlooked is sunlight exposure. Gardeners frequently debate whether morning or afternoon sun is more beneficial for their plants. Each time of day offers distinct advantages and challenges that can significantly influence growth rates, flowering, and overall health. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the benefits of both morning and afternoon sunlight, helping you determine which option best suits your greenhouse environment and the specific needs of your plants. Understanding the impact of sunlight timing can lead to healthier, more productive gardening outcomes.
Is Morning or Afternoon Sun Better for Greenhouses?
In determining whether a greenhouse benefits more from morning or afternoon sun, many factors come into play, including the types of plants being grown, local climate conditions, and desired growth rates. Generally, morning sunlight is preferred as it provides gentle warmth and helps dry any dew or moisture that may accumulate overnight, reducing the risk of fungal diseases. Additionally, the consistent early light can promote stronger and healthier plant growth, allowing for the ideal conditions for photosynthesis before the heat of the day sets in. In contrast, afternoon sun brings harsher, more intense heat, which can lead to plant stress if not managed properly with shading or ventilation. Ultimately, choosing the right exposure depends on the specific environment and plant needs.
Benefits of Morning Sun
Morning sun provides a gentle warming effect that helps kickstart photosynthesis in plants. As temperatures rise gradually, plants are less likely to suffer from heat stress, and moisture from the night’s dew evaporates more rapidly, lowering the risk of diseases such as mildew. Additionally, many plants thrive under this steady exposure, promoting their overall health and growth rates.
Challenges of Afternoon Sun
While afternoon sun may appear advantageous due to increased light exposure, it can present challenges, especially in warmer climates. The intensity of afternoon heat often leads to high temperatures within the greenhouse, which can quickly desiccate plants, resulting in wilting or sunburn. For plants sensitive to heat, managing this exposure through shading or ventilation becomes crucial to prevent damage.
Plant Type Considerations
Different plants have varying light and temperature requirements that influence their performance under morning versus afternoon sun. For instance, cool-season crops like lettuce and spinach may prefer morning sunlight, as they thrive in cooler conditions. Conversely, warm-season crops such as tomatoes may adapt better to the rigorous afternoon light, provided they have adequate water and airflow to mitigate heat stress.
Climate Impact
In cooler climates, morning sun can be particularly advantageous, as it helps raise temperatures early in the day, allowing for effective growth, even in less-than-ideal conditions. In warmer regions, however, careful management is necessary to balance the benefits of afternoon sun with potential overheating. Understanding the local climate's seasonal variations helps in making informed decisions about greenhouse orientation and design.
Optimal Greenhouse Design
To maximize the benefits of sunlight exposure, the design of the greenhouse is crucial. Features such as ventilation systems, thermal mass, and reflective surfaces can help mitigate the extremes of afternoon heat while enhancing the advantages of morning light. Additionally, proper location and orientation ensure that the greenhouse captures the optimal amount of both morning and afternoon sun to support the varied needs of different plants.
| Feature | Morning Sun | Afternoon Sun |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Impact | Gradual warming | Intense heat |
| Disease Risk | Lower (due to moisture evaporation) | Higher (risk of overheating) |
| Ideal Plant Types | Cool-season plants | Warm-season plants |
| Climate Suitability | Cooler climates | Warmer climates |
| Greenhouse Design Needs | Less ventilation required | Better ventilation and shading needed |
What is the best sunlight for a greenhouse?
The best sunlight for a greenhouse is essential for promoting plant growth and maximizing yields. Greenhouses are designed to create a controlled environment for plants by providing adequate light, temperature, and humidity. The optimal sunlight conditions can vary depending on the type of plants you're growing, but generally, the following factors are crucial for the best sunlight exposure:
1. Quality of Light: The quality of sunlight refers to the spectrum of light that reaches the plants. Plants primarily use light in the blue (400-500 nm) and red (600-700 nm) wavelengths for photosynthesis. Therefore, a greenhouse that allows these light spectrums to penetrate effectively will enhance growth.
See also:
2. Quantity of Light: Quantity refers to the intensity or amount of sunlight that reaches the plants. Most vegetables and flowers require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. This amount varies; some plants may thrive under lower light conditions, while others may require a more intense light exposure.
3. Duration of Light: The duration of light exposure during the day plays a critical role in plant development. Longer daylight hours can trigger flowering in some plants and promote vegetative growth in others. Greenhouses should be strategically placed to maximize light exposure throughout the day, acknowledging seasonal variations.
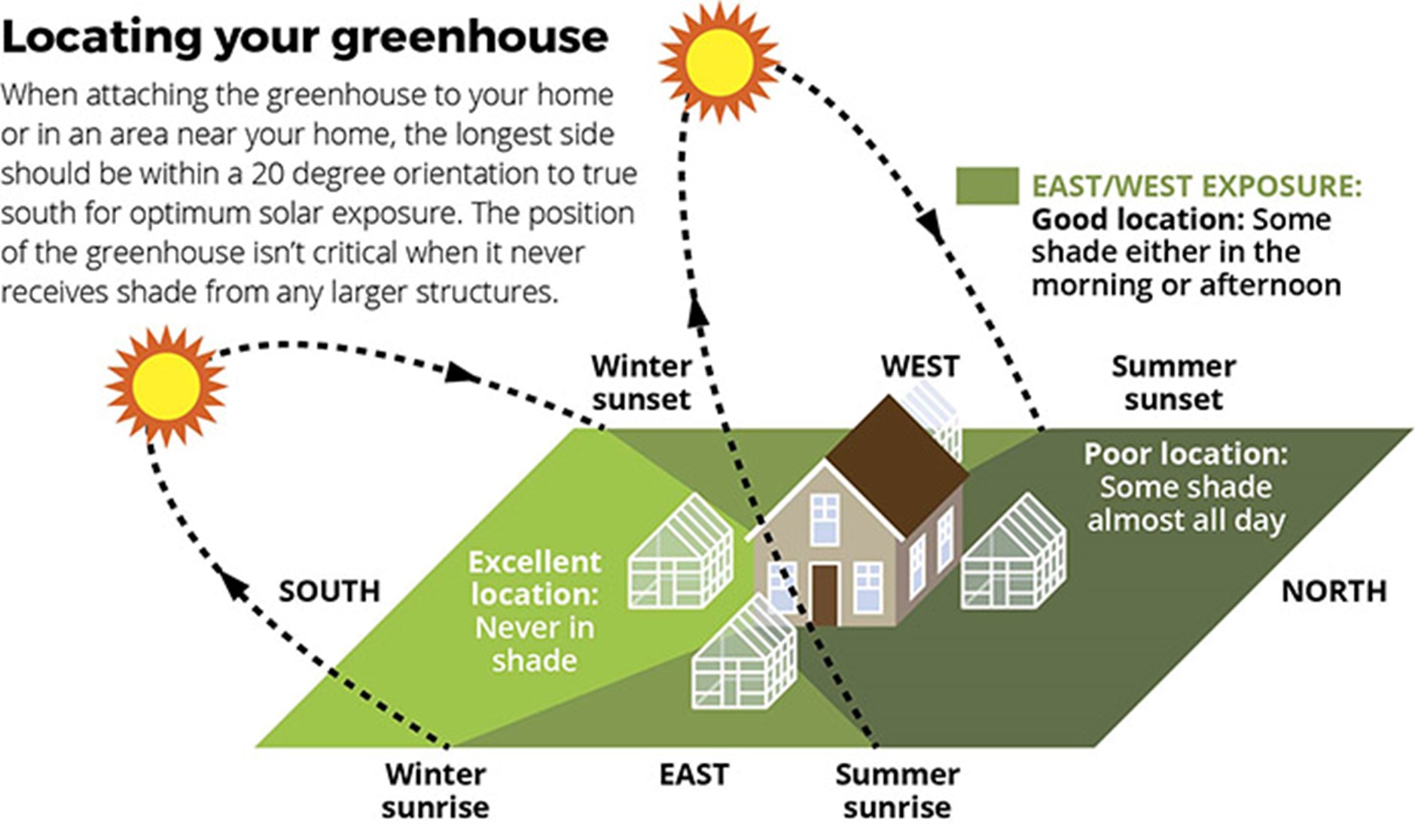
4. Sunlight Orientation: The direction from which sunlight enters the greenhouse can affect plant growth. Ideally, a greenhouse should be oriented north to south to maximize sunlight throughout the day. This orientation helps avoid excessive shading from structures or trees.
5. Seasonal Variations: The angle of the sunlight changes with seasons, affecting how much light the greenhouse receives. During winter, the sun is lower in the sky, leading to reduced light exposure. Greenhouse owners should consider using supplemental lighting or adjusting the layout of plants during these times to compensate for reduced natural light.
Quality of Light in a Greenhouse
The quality of light that penetrates a greenhouse impacts plant health and growth. Effective photosynthesis depends on specific light wavelengths crucial for chlorophyll activity. To ensure adequate quality of light in a greenhouse:
- Use transparent or translucent materials for the walls and roof to allow suitable light spectrums.
- Avoid using materials that filter out essential wavelengths for plant growth.
- Consider using reflectors to optimize light distribution within the greenhouse.
Quantity of Light Needed for Different Crops
Different crops have varying light needs, and understanding this is vital for optimizing growth. While some ornamentals may thrive in lower light conditions, most vegetables need higher light levels. To determine the quantity of light needed:
- Research specific light requirements for each type of plant you intend to grow.
- Monitor and measure light intensity inside the greenhouse using a light meter.
- Adjust plant positioning to ensure they receive adequate sunlight exposure.
Duration of Light Exposure
Duration or photoperiod affects plant growth rates and flowering times. Longer light durations can be beneficial to specific crops. To manage duration effectively:
- Utilize timers to simulate longer daylight hours during shorter winter days.
- Introduce supplemental LED grow lights for plants requiring extended light exposure.
- Track seasonal changes to adjust lighting accordingly and maintain plant health.
Sunlight Orientation for Maximum Exposure
The orientation of a greenhouse is a crucial factor in maximizing sunlight exposure. Proper orientation can significantly enhance light intake. Consider the following:
- Orient the greenhouse with its long side facing north to enhance sun exposure all day.
- Avoid locating the greenhouse near tall structures or trees that may cast shadows during peak sun hours.
- Consider incorporating adjustable shading systems to manage excessive sunlight during peak summer months.
Adapting to Seasonal Light Changes
Seasonal changes impact how much light your greenhouse receives, which can influence plant growth efficacy. To adapt to these changes:
- Monitor the natural light levels to adjust plants or supplemental lighting as needed.
- Utilize movable benches to shift plants according to seasonal sunlight patterns.
- Plan crop rotations to take advantage of seasonal light variations effectively.
What is the best exposure for a greenhouse?


The best exposure for a greenhouse is primarily determined by the location and climate of the area where it is situated. Generally, the ideal exposure for a greenhouse is to the south or southeast, as this positioning allows for optimal sunlight during the day, facilitating the growth of plants.
The following aspects should be considered when determining the best exposure for a greenhouse:
Optimal Sunlight Exposure
Exposure to adequate sunlight is crucial for all types of plants. A greenhouse located on the south side receives the most sunlight, which helps in maintaining a consistent and warm temperature inside.
- South-facing greenhouses get sunlight for the longest portion of the day.
- This exposure helps in maximizing photosynthesis.
- In colder climates, this is especially beneficial as it helps in retaining heat.
Wind Protection
Wind can significantly affect the internal environment of a greenhouse. Positioning a greenhouse with consideration for prevailing winds can protect it from damage and temperature fluctuations.
- Locate the greenhouse away from dominant wind directions.
- Using natural barriers such as trees or buildings for wind protection can help.
- A sheltered site retains heat and reduces drafts, ensuring a more stable environment.
Orientation for Temperature Regulation
The orientation of a greenhouse not only affects light but also how heat is distributed and retained inside.
- A poorly oriented greenhouse can lead to uneven temperature distribution.
- Use thermal mass (like water tanks or concrete) to help regulate temperature throughout the day.
- Ensure the roof angles enhance solar gain while managing excess heat in summer.
Accessibility to Water and Resources
The greenhouse should be positioned considering the accessibility of water and other essential resources needed for plant care.
- Proximity to a water source can simplify irrigation processes.
- Proper drainage will prevent waterlogging and promote healthy plant growth.
- Facilitating easy access to gardening tools and resources can improve overall efficiency.
Local Climate Considerations
Every location has specific climatic conditions that can affect greenhouse performance. Understanding these factors is essential for optimal placement.
- In hot climates, consider ventilation features to regulate internal temperatures.
- In cooler climates, maximizing sunlight in winter months is vital.
- Assess seasonal climate variations to determine the best seasonal adjustments for light and temperature control.
Questions from Our Readers
Is morning sun or afternoon sun better for a greenhouse?
The answer largely depends on the climate of the area; however, morning sun tends to be more beneficial as it warms up the greenhouse gently and helps plants avoid the stress of extreme heat during the day. This gradual heating can also lead to improved plant health and growth.
What are the benefits of morning sunlight in a greenhouse?
Morning sunlight exposes plants to light early, which can boost photosynthesis and metabolism early in the day. This can also help in preventing the development of diseases, as temperatures are milder and humidity levels are often lower in the morning.
Can afternoon sun be detrimental to greenhouse plants?
Yes, afternoon sun can lead to excessive heat and can cause heat stress on plants, especially in hotter climates. If the greenhouse is not adequately ventilated, plants can suffer from dehydration and damage due to high temperatures.
See also:
How can I optimize light exposure in my greenhouse?
To ensure optimal light exposure, consider using reflective materials on the exterior to maximize morning sunlight and implementing proper ventilation systems to manage heat during the afternoon. This balance is crucial for maintaining the ideal growing environment for your plants.

If you want to read more articles like Is It Better for a Greenhouse to Get Morning or Afternoon Sun? A Comprehensive Guide to Maximizing Plant Growth, we recommend you check out our Greenhouse category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles