How Many Seed Stores Are There? Discover the Numbers and Locations Today!

The world of gardening and agriculture is thriving, and seed stores play a crucial role in this vibrant ecosystem. As the demand for diverse plant varieties continues to surge, understanding the current landscape of seed retailers becomes essential. This article delves into the latest statistics, revealing the number of seed stores across various regions and highlighting their significance in supporting local farmers, gardeners, and enthusiasts. From quaint local shops to expansive online marketplaces, discover where to find these vital resources and how they contribute to sustainable gardening practices. Join us as we explore the numbers and locations of seed stores today!
How Many Seed Stores Are There?
The number of seed stores varies significantly depending on the region and local laws regarding the sale of seeds. In countries where cannabis is legal, there are often numerous specialized retailers catering to both recreational and medicinal users. For traditional crops, both large agricultural suppliers and smaller local stores contribute to the seed market. Additionally, online platforms have emerged, offering a wide range of seed options that can reach customers across different geographical locations. Overall, the total number of seed stores is influenced by various factors including legality, market demand, and regional agricultural practices.
The Global Seed Market Overview
The global seed market comprises a vast network of distributors, retailers, and online vendors. Estimates suggest that there are thousands of seed stores around the world, with significant concentrations in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. These stores sell a variety of seeds including vegetables, flowers, and grains, catering to both home gardeners and commercial farmers. The increased interest in sustainable gardening and organic practices has also led to a rise in the number of specialty shops focusing on heirloom and non-GMO seeds.
Types of Seed Stores
Seed stores can be broadly categorized into specialty shops, garden centers, and online retailers. Specialty seed shops often focus on specific types of seeds, such as organic or rare heirloom varieties, while garden centers typically offer a range of gardening supplies alongside their seed selection. Online retailers provide customers with the convenience of shopping from home, often featuring extensive catalogs that allow consumers to access hard-to-find seeds from all over the globe.
Regional Differences in Seed Availability
The availability of seed stores varies by region due to agricultural practices, climate, and local regulations. In the United States, for example, states with more progressive agricultural laws have a higher density of both physical and online seed stores. Conversely, regions with strict regulations on certain crops may see a limited number of licensed retailers. This disparity can create challenges for gardeners and farmers seeking diverse seed options in areas with restrictive laws.
Impact of Online Sales on Seed Stores
Online sales have revolutionized how seeds are sourced and purchased. The ease of access to an extensive range of seeds through online platforms has increased competition for brick-and-mortar stores, often resulting in better prices and variety for consumers. However, this trend also poses challenges for traditional seed retailers, many of which struggle to compete with large online marketplaces that can offer bulk pricing and extensive delivery options. The shift towards online purchasing is transforming the landscape of the seed industry.
Future Trends in Seed Stores
As the demand for sustainable and locally-sourced seeds grows, the future of seed stores is likely to evolve significantly. Trends indicate an increase in community-focused seed banks that preserve genetic diversity by offering local seed varieties. Additionally, educational initiatives in gardening and sustainable practices are likely to increase interest in seed purchases from local shops. The integration of technology, such as mobile apps and e-commerce platforms, will continue to shape how consumers interact with seed retailers, making the seed market more dynamic and accessible.
| Country | Estimated Number of Seed Stores | Main Types of Seeds Offered |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Over 20,000 | Vegetable, Flower, Herb |
| Canada | Around 5,000 | Vegetable, Organic, Heirloom |
| United Kingdom | Approximately 4,000 | Flower, Vegetable, Specialty |
| Australia | About 3,000 | Native, Vegetable, Flower |
| Germany | Near 6,000 | Vegetable, Organic, Heirloom |
How many seed companies are there?
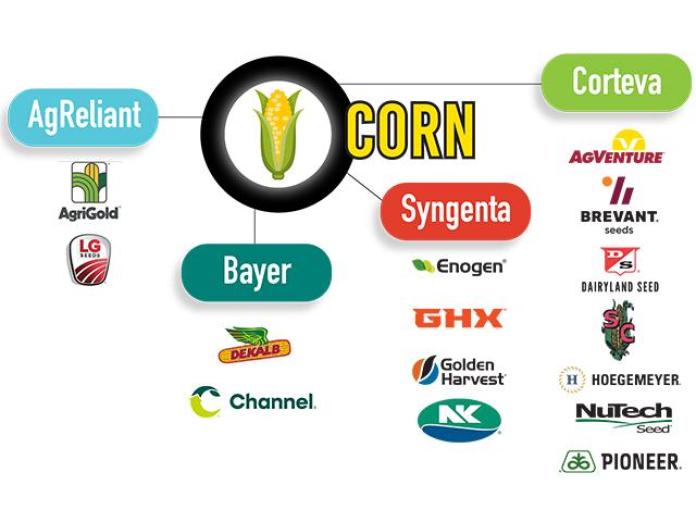
The exact number of seed companies globally is difficult to determine due to the dynamic nature of the market and the frequent mergers and acquisitions within the agricultural sector. However, estimates suggest that there are thousands of seed companies worldwide, ranging from large multinational corporations to small, regional, and niche operations. This diversity reflects the varying agricultural practices, crop preferences, and local demands across different regions.
Global Seed Industry Overview
The global seed industry has experienced significant transformation over the past few decades, with advancements in biotechnology, hybridization, and genetic engineering. The number of seed companies can be categorized into three main segments:
- Multinational Corporations: Major players like Bayer, Corteva, and Syngenta dominate the market, often accounting for a substantial share of the global seed supply.
- Regional Firms: Many companies operate within specific geographical regions, providing seeds adapted to local climates and farming practices.
- Niche Seed Companies: These focus on specialty crops, organic seeds, and heritage varieties, catering to specific customer needs.
Trends Influencing Seed Companies
Several trends are shaping the seed industry, leading to fluctuations in the number of companies:
- Consolidation: Mergers and acquisitions have reduced the number of independent companies while increasing the market power of larger firms.
- Biotechnology Advancements: Innovations in biotechnology create opportunities for new seed companies focused on developing genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Sustainable Practices: An increasing demand for sustainable agriculture is driving the emergence of companies specializing in organic and non-GMO seeds.
Regional Variations in Seed Companies
The number and types of seed companies vary widely by region:
- North America: Home to many major agribusiness players, with a strong focus on genetically modified seeds for large-scale farming.
- Europe: A mix of large companies and smaller firms, with regulations shaping market entry, especially for GMOs.
- Asia: Rapid growth in seed companies, with increasing investments in R&D and local adaptation of seed varieties.
Challenges Facing Seed Companies
Seed companies face multiple challenges that impact their operational dynamics:
See also:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating varying regulations in different countries can complicate market entry and expansion.
- Climate Change: Adaptation to changing climate conditions requires innovation and significant investment in new seed varieties.
- Intellectual Property Issues: Protecting innovations through patents can be contentious, particularly for small firms against larger competitors.
Future of Seed Companies
Looking ahead, the seed industry is likely to see various developments:
- Increased Investment: Expect continued investment in R&D as companies seek to develop resilient seed varieties.
- Collaboration with Tech Firms: Partnerships with technology companies may drive advancements in precision agriculture and data analytics.
- Focus on Biodiversity: A growing emphasis on preserving agricultural biodiversity may lead to the emergence of new seed companies focused on traditional varieties.
How many seed banks exist?

The exact number of seed banks worldwide is difficult to determine due to the continuous establishment of new facilities and the varying definitions of what constitutes a seed bank. However, as of recent estimates, there are approximately 1,750 seed banks globally. These seed banks can be categorized into different types, including those focusing on agricultural seeds, wild species, and conservation efforts.
Types of Seed Banks
There are various types of seed banks, each serving unique purposes and targets. Common categories include:
- Gene Banks: Focus on preserving genetic diversity of crops and wild species.
- Commercial Seed Banks: Sell seeds to the public and may focus on specific strains.
- Community Seed Banks: Operated by local farmers to conserve regional varieties and promote food sovereignty.
- Research Seed Banks: Often associated with academic institutions aimed at studying and preserving plant genetics.
- Emergency Seed Banks: Established in response to natural disasters or conflicts to safeguard agricultural biodiversity.
Global Distribution of Seed Banks
Seed banks are distributed across various regions worldwide, with significant concentrations in countries engaged in agriculture. The distribution includes:
- North America: Home to many commercial and community seed banks focused on diverse crops.
- Europe: Consists of numerous gene banks dedicated to conservation efforts and public-private partnerships.
- Asia: Features a mix of traditional and modern seed banks, crucial for local food security.
- Africa: Contains community-driven initiatives and some larger gene banks addressing regional biodiversity.
- Latin America: Houses several projects focused on indigenous crop varieties and sustainable agriculture.
Role of Seed Banks in Biodiversity Conservation
Seed banks play a critical role in the conservation of biodiversity, serving several key functions:
- Preservation of Plant Genetic Resources: Ensuring that plant varieties are safeguarded for future generations.
- Research and Development: Providing genetic materials for breeding programs aimed at improving crop resilience.
- Food Security: Storing seeds that can be used to grow crops in the event of agricultural losses.
- Restoration Projects: Supplying seeds for ecological restoration initiatives, restoring habitats and ecosystems.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Preserving diverse genetic material that may adapt to changing climatic conditions.
Challenges Facing Seed Banks
Despite their significance, seed banks encounter several challenges that can affect their operations:
- Funding Limitations: Many seed banks rely on limited government or donor funding, impacting their sustainability.
- Climate Change: The impacts of climate change can threaten the viability of stored seeds.
- Technological Advances: Keeping up with new methods for seed storage and genetic analysis can be resource-intensive.
- Policy and Regulation: Varying laws across countries can complicate seed exchange and preservation efforts.
- Public Awareness: Lack of awareness among the general public about the importance of seed banks can hinder support and engagement.
Future of Seed Banks
The future of seed banks looks to evolve with the challenges of modern agriculture and conservation needs. Emerging trends include:
- Improved Technology: Utilizing advanced techniques like cryopreservation and molecular genetics for better storage and research.
- Collaborative Efforts: Increased partnerships among countries and organizations to share resources and knowledge.
- Community Involvement: Greater involvement of local communities in seed saving and exchange initiatives.
- Focus on Climate Resilience: Developing and storing seeds that can withstand adverse climate conditions.
- Educational Initiatives: Promoting the importance of biodiversity and seed preservation through educational programs.
Why is replanting seeds illegal?

Replanting seeds can be illegal due to various reasons primarily linked to intellectual property rights, the regulation of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and local agricultural laws. Here are some critical points detailing why it can be deemed illegal.
Intellectual Property Rights
Replanting seeds often infringes on the intellectual property rights of seed manufacturers. Seeds, especially those developed through biotechnology, are patented by companies. The patent allows companies to control the commercial use of their seeds, preventing farmers from saving and replanting them. This system aims to encourage innovation and ensure that companies can recoup their research and development costs. Key aspects include:
- Patent Protection: Many seeds are patented, providing legal rights to the creator.
- Licensing Agreements: Farmers often enter into agreements that prohibit replanting.
- Legal Enforcement: Companies may pursue legal action against unauthorized replanting.
GMO Regulations
Genetically modified seeds are subject to strict regulatory frameworks in many countries. These regulations are in place to ensure that GMOs do not adversely affect the environment or human health. Consequently, replanting such seeds can violate these laws if they are not appropriately managed or tracked. Important considerations include:
- Environmental Concerns: Regulations aim to prevent potential ecological risks associated with GMOs.
- Health Assessments: GMOs must pass safety assessments before being allowed for commercial use.
- Traceability: Farmers must adhere to regulations regarding tracking GMO seeds.
Agricultural Law Compliance
Various countries have specific agricultural laws that dictate how seeds should be used and managed. These laws can relate to the conservation of plant varieties, ensuring that farmers use seeds that meet regulatory standards. Aspects to consider include:
See also:
- Seed Variety Protection: Some laws protect native or heritage seed varieties, limiting their use.
- Certification Processes: Farmers must often certify seeds to ensure they are compliant with agricultural regulations.
- Market Control: Regulations may be in place to control the agricultural market and prevent monopolies.
Quality Control Measures
To ensure a consistent quality of crops, many jurisdictions require farmers to follow certain quality control measures when planting seeds. These measures are crucial in maintaining productivity and food safety. Key elements include:
- Seed Quality Standards: Laws specify certain quality benchmarks for seeds to be used.
- Certification Requirements: Many seeds must pass tests and be certified before use.
- Traceability Protocols: Farmers must keep records of seed sourcing to ensure compliance with standards.
Economic Implications
Replanting seeds without permission can have significant economic implications for farmers and businesses involved in seed production. Companies invest heavily in breeding and research, and unauthorized replanting can undermine their financial sustainability. Consider these factors:
- Loss of Revenue: Companies may suffer financial losses due to unauthorized seed use.
- Investment in Research: High costs in seed development necessitate protecting their rights.
- Market Sustainability: Protecting seed patents ensures a sustainable agricultural economy.
Who are the largest seed dealers in the US?
The largest seed dealers in the United States are key players in the agricultural industry, supplying various types of seeds to farmers and growers across the country. These companies have established themselves as leaders due to their extensive product offerings, research capabilities, and distribution networks. Here are some of the most prominent seed dealers:
1. Monsanto (now part of Bayer)
Monsanto, acquired by Bayer AG in 2018, is one of the largest seed companies globally and has a significant presence in the U.S. agricultural market. The company specializes in genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and several crop varieties, including corn, soybeans, and cotton.
- Leading in research and development of biotech seeds.
- Offers a wide range of seed products and traits.
- Strong focus on sustainability and agricultural innovation.
2. DuPont Pioneer
DuPont Pioneer, now under Corteva Agriscience after the merger of Dow and DuPont, is known for its extensive seed portfolio. The company specializes in corn, soybeans, and sorghum, providing farmers with high-quality seed options.
- Invests heavily in seed technology and development.
- Offers tailored solutions to meet diverse agricultural needs.
- Prioritizes partnerships with farmers for better crop performance.
3. Syngenta
Syngenta is another major player in the seed market, focusing on both seed and crop protection products. The company provides seeds for a variety of crops, including corn, soybeans, and vegetables, promoting agricultural productivity.
- Offers a wide range of products across multiple crop categories.
- Innovations in seed treatments and biotechnology.
- Strong global presence with local expertise.
4. Beck's Hybrids
Beck's Hybrids stands out as one of the largest family-owned seed companies in the U.S. They specialize in corn and soybean seeds with a commitment to customer service and farmer relationships.
- Focuses on innovative products tailored to regional needs.
- Strong emphasis on local testing and research.
- Offers a comprehensive agronomic support program for farmers.
5. Johnny’s Selected Seeds
Johnny’s Selected Seeds is a leading supplier of vegetable, herb, and flower seeds. Known for its high-quality products and customer service, it serves a wide range of growers, from home gardeners to large commercial operations.
- Offers an extensive catalog of unique and heirloom varieties.
- Strong commitment to organic seeds and sustainable practices.
- Provides resources and expertise to help growers succeed.
Questions from Our Readers
How many seed stores are there in the United States?
The number of seed stores in the United States varies, but estimates suggest there are thousands of such stores, ranging from local garden centers to larger commercial operations.
Are there more seed stores in urban or rural areas?
Typically, there are more seed stores in rural areas, as these regions often have a stronger focus on agriculture and gardening, while urban areas may have fewer options but often feature specialty shops.
Do all seed stores offer the same variety of seeds?
Not all seed stores offer the same variety; each store usually focuses on specific brands and types of seeds, often prioritizing local varieties that are best suited for the area.
How can I find a seed store near me?
You can find a seed store near you by using online search engines, checking local directories, or asking for recommendations from gardening clubs or community groups.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like How Many Seed Stores Are There? Discover the Numbers and Locations Today!, we recommend you check out our Seeds category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles