The Ultimate Guide to Discovering 'What Plant Growing Zone Am I In' for Successful Gardening

Understanding your plant growing zone is crucial for successful gardening. It determines the types of plants that will thrive in your area, helping you make informed choices whether you're a novice or an experienced gardener. In this ultimate guide, we will explore how to identify your growing zone, the significance of climate factors, and tips for selecting the best plants for your region. From frost dates to temperature ranges, you'll gain insights that will empower you to cultivate a flourishing garden. Let’s embark on this journey to enhance your gardening success and ensure your plants flourish in their optimal environment.
Understanding Your Plant Growing Zone
Determining your plant growing zone is essential for successful gardening and landscaping. In the United States, the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a widely used reference that categorizes regions based on their minimum winter temperatures. Understanding your zone allows you to select plants that are well-suited to your local climate, reducing the chances of planting flora that may struggle or fail to thrive due to temperature extremes. You can determine your growing zone by entering your zip code on the USDA website or consulting local gardening resources. This knowledge is particularly important for choosing perennials, shrubs, and trees that can survive in your area's specific conditions.
What is a Plant Growing Zone?
A plant growing zone is a geographical area defined by specific climatic conditions, particularly the minimum winter temperatures that can be expected. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides the U.S. into 13 zones, ranging from zone 1 (the coldest) to zone 13 (the warmest). Each zone represents a range of average low temperatures, which helps gardeners understand what types of plants will survive winter in their area. Knowing your zone is critical for selecting plants that not only flourish during the growing season but also endure the winter months, ensuring a healthier garden.
How to Determine Your Plant Growing Zone
To find out your plant growing zone, you can use a couple of straightforward methods. The most common way is to consult the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, available online. By entering your zip code, you can easily identify your zone. Another option is to refer to local gardening centers or cooperative extension offices, which often have resources tailored to your specific area. Additionally, factors like microclimates—areas that may experience slightly different conditions—can influence your growing zone, so it's advisable to assess your local environment as well.
Importance of Knowing Your Growing Zone
Knowing your growing zone is crucial when it comes to successful gardening and landscaping. It informs your plant selection, allowing you to choose species that will thrive in your climate. This ensures better growth and resilience against diseases and pests, which are more likely to afflict plants struggling against environmental stresses. Additionally, understanding your zone can help you avoid the frustration of planting species that may not survive the winter or perform poorly due to temperature variations, saving both time and resources.
Climate Factors Affecting Growing Zones
Several climate factors play a role in determining the characteristics of a growing zone. Aside from temperature, factors such as humidity, elevation, and soil type can significantly influence which plants are suitable for a particular area. For instance, areas with high humidity may support more tropical plants, whereas higher elevation regions might experience cooler temperatures and shorter growing seasons. Additionally, the microclimates created by structures, bodies of water, and varying topography can alter the growing conditions, further complicating the selection of appropriate plants.
See also:
Adapting Your Gardening Practices to Your Zone
Once you have determined your plant growing zone, it is vital to adapt your gardening practices accordingly. This includes selecting the right planting dates, as the timing of frost can vary by zone, impacting when to sow seeds or transplant seedlings. Additionally, knowing your zone helps in determining your watering, fertilizing, and pruning schedules. Adapting your practices not only maximizes the potential of your plants but also minimizes waste and the need for chemical interventions by fostering natural growth patterns suited to your local climate.
| Zone | Temperature Range (°F) | Typical Plants |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -60 to -50 | Primarily hardy perennials |
| 2 | -50 to -40 | Cold-tolerant shrubs |
| 3 | -40 to -30 | Some fruit trees and evergreens |
| 4 | -30 to -20 | Pansies, bulbs, and various ground covers |
| 5 | -20 to -10 | Many varieties of roses and herbs |
What plant zone is Indiana in?
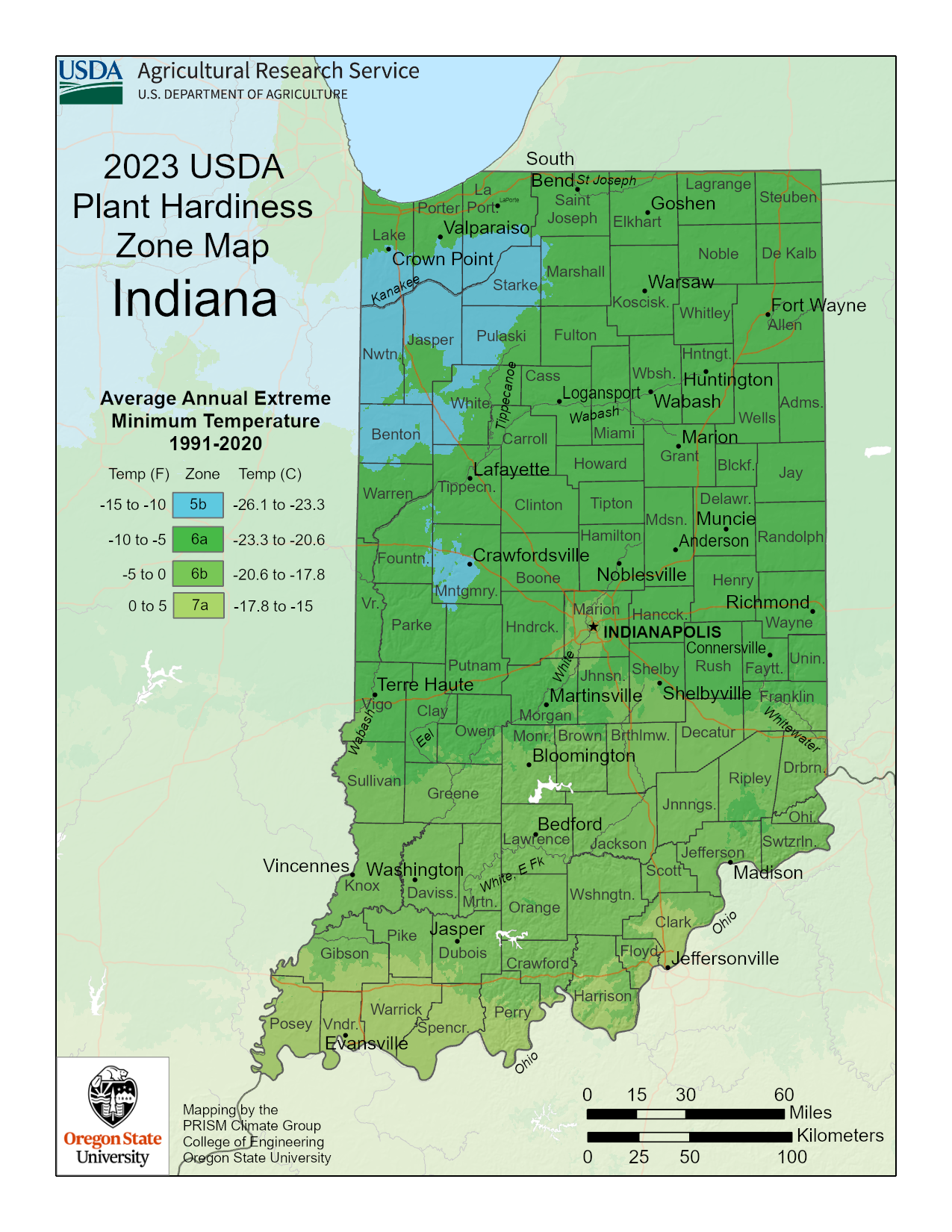
Indiana is primarily classified within USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 5b to 6a. This classification is critical for gardeners and agricultural planners as it provides insight into which plants are likely to thrive in the region based on average annual minimum winter temperatures. Zone 5b has minimum temperatures ranging from -15 to -10 degrees Fahrenheit (-26 to -23 degrees Celsius), while zone 6a has a range of -10 to -5 degrees Fahrenheit (-23 to -21 degrees Celsius). Understanding these zones can greatly assist in making effective decisions about planting and landscaping.
Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones
Understanding plant hardiness zones is essential for selecting the right plants for your garden. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map categorizes regions based on temperature and climate variations. Here are some key points:
- Temperature Ranges: Each zone represents a particular range of minimum temperatures.
- Regional Variance: Zones can vary significantly even within a state, affecting specific gardening choices.
- Plant Selection: Knowing the zone aids gardeners in selecting plants that will survive and thrive.
Common Plants for Indiana's Climate
When selecting plants for Indiana, it is beneficial to choose those that are compatible with zones 5b and 6a. Some common choices include:
- Perennials: Coneflowers, Daylilies, and Hostas are hardy and popular choices.
- Trees: Red Maple, Eastern Redbud, and Oak trees thrive well in Indiana's climate.
- Shrubs: Hydrangeas and Boxwoods are commonly used for landscaping in Indiana.
Seasonal Planting Considerations
Indiana's seasonal climate greatly affects planting schedules. Understanding this can help maximize growth potential. Key factors include:
See also:
- Frost Dates: Know the last frost date in spring and first frost date in fall to optimize planting times.
- Soil Conditions: Assess soil temperature and moisture levels for better planting success.
- Seasonal Plants: Select plants that will flourish in each specific season, such as cool-weather crops in spring and fall.
Impact of Microclimates in Indiana
Within Indiana, microclimates can significantly influence the success of various plant species. Understanding these can enhance gardening strategies. Consider the following:
- Urban vs. Rural: Urban areas may retain more heat compared to rural areas, allowing different species to thrive.
- Elevation Changes: Higher elevations may have cooler temperatures affecting plant selections.
- Wind Protection: Areas shielded from harsh winds can create favorable conditions for more delicate species.
Resources for Indiana Gardeners
Several resources are available to assist Indiana gardeners in choosing the right plants and understanding their hardiness zones. Useful resources include:
- Extension Services: Local universities often provide agricultural extension services with valuable information.
- Online Plant Databases: Websites dedicated to plant hardiness can help identify suitable varieties.
- Gardening Workshops: Participating in local gardening workshops can provide practical advice and networking opportunities.
Questions from Our Readers
What is a plant growing zone?
A plant growing zone, also known as a hardiness zone, is a geographic area defined by climate conditions, specifically the average minimum winter temperature. These zones help identify which plants are likely to thrive in your specific location, allowing for better gardening and landscaping decisions.
How can I determine my plant growing zone?
You can determine your plant growing zone by consulting a hardiness zone map, which is usually provided by gardening organizations or local agricultural extensions. By inputting your zip code or locating your area on the map, you can find out the average minimum temperatures and corresponding plant zones for your region.
Why is knowing my plant growing zone important?
Knowing your plant growing zone is important because it guides you in selecting plants that are suited to your local climate, thus ensuring they will survive and thrive. Choosing plants that are inappropriate for your zone can lead to poor growth, damage, or even plant loss due to extreme temperatures or unsuitable conditions.
Can my growing zone change over time?
Yes, your growing zone can change over time due to factors such as climate change, urban development, or shifts in local weather patterns. It’s advisable to periodically check updated zone maps or local guidance to ensure your plant choices remain suitable for the evolving climate in your area.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like The Ultimate Guide to Discovering 'What Plant Growing Zone Am I In' for Successful Gardening, we recommend you check out our Gardeners category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles